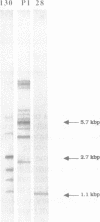
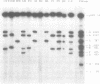
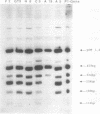
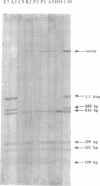
Abstract
Mycoplasma pneumoniae, a bacterium pathogenic for humans, has a relatively small genome size of 840 kbp. Even though, several repeated DNA elements have been identified in the genome of this prokaryote, particularly within the P1 gene which codes for a major adhesin protein of M. pneumoniae. These elements were characterized in detail with respect to size, number and distribution on the genome, represented by an ordered cloned library covering the complete chromosome. Three different repetitive elements were detected in and around the P1 gene designated as RepMP2/3, RepMP4 and RepMP5. The length of these elements varies between 1.1-1.5 kbp (RepMP4), 1.8 kbp (RepMP2/3) and 1.9-2.2 kpb (RepMP5). They occur at least 8 to 10 times on the chromosome. Possible functions are discussed and a uniform nomenclature for these repeats is proposed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barile M. F., Chandler D. K., Yoshida H., Grabowski M. W., Harasawa R., Razin S. Parameters of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in Syrian hamsters. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2443–2449. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2443-2449.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman S. D., Hu P. C., Bott K. F. Prevalence of novel repeat sequences in and around the P1 operon in the genome of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Gene. 1990 Mar 1;87(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90498-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Reed R. R. Transpositional recombination in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:863–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas R., Meyer T. F. The repertoire of silent pilus genes in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: evidence for gene conversion. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90489-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Cole R. M., Huang Y. S., Graham J. A., Gardner D. E., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: role of a surface protein in the attachment organelle. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.6801766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inamine J. M., Denny T. P., Loechel S., Schaper U., Huang C. H., Bott K. F., Hu P. C. Nucleotide sequence of the P1 attachment-protein gene of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Gene. 1988 Apr 29;64(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inamine J. M., Loechel S., Hu P. C. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of the P1 operon of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniloff J. Anomalous values of Mycoplasma genomes sizes determined by pulse-field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1268–1268. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier J. T., Simon M. I., Barbour A. G. Antigenic variation is associated with DNA rearrangements in a relapsing fever Borrelia. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):403–409. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morowitz H. J. The completeness of molecular biology. Isr J Med Sci. 1984 Sep;20(9):750–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle L. E., Corcoran L. N., Cocks B. G., Bergemann A. D., Whitley J. C., Finch L. R. Pulsed-field electrophoresis indicates larger-than-expected sizes for mycoplasma genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6015–6025. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Molecular biology and genetics of mycoplasmas (Mollicutes). Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):419–455. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.419-455.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. J., Ames G. F., Smith N. H., Robinson E. C., Higgins C. F. Repetitive extragenic palindromic sequences: a major component of the bacterial genome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C. J., Chavoya A., Baseman J. B. Regions of Mycoplasma pneumoniae cytadhesin P1 structural gene exist as multiple copies. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3157–3161. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3157-3161.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C. J., Tryon V. V., Baseman J. B. Cloning and sequence analysis of cytadhesin P1 gene from Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3023–3029. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3023-3029.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. A., Ferrell R. V., Wise K. S., McIntosh M. A. Reiterated DNA sequences defining genomic diversity within the species Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Sep;2(5):665–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu A. C., Foy H. M., Cartwright F. D., Kenny G. E. The principal protein antigens of isolates of Mycoplasma pneumoniae as measured by levels of immunoglobulin G in human serum are stable in strains collected over a 10-year period. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1830–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1830-1836.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R., Herrmann R. Cloning of the complete Mycoplasma pneumoniae genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 12;17(17):7029–7043. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.17.7029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R., Herrmann R. Physical mapping of the Mycoplasma pneumoniae genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8323–8336. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R., Herrmann R. Repetitive DNA sequences in Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8337–8350. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Stackebrandt E., Ludwig W. What are mycoplasmas: the relationship of tempo and mode in bacterial evolution. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(4):305–316. doi: 10.1007/BF02115648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Silverman M., Hilmen M., Simon M. Recombinational switch for gene expression. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):170–172. doi: 10.1126/science.322276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]