Abstract
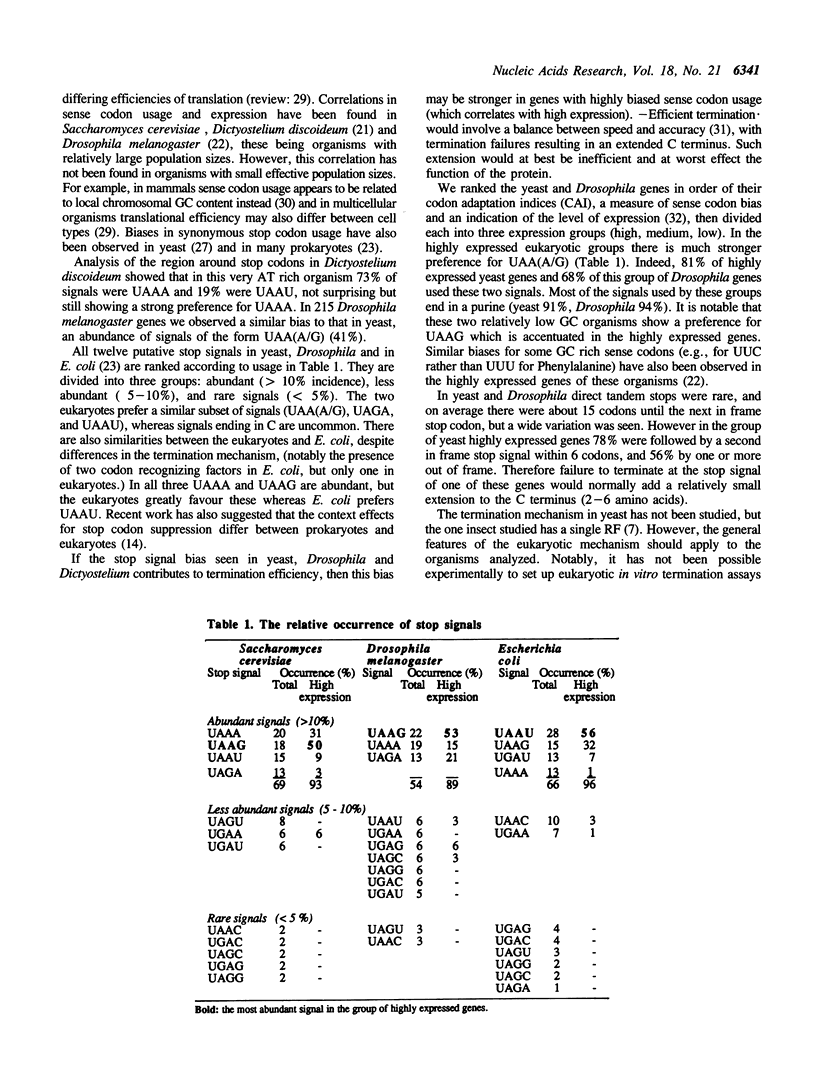
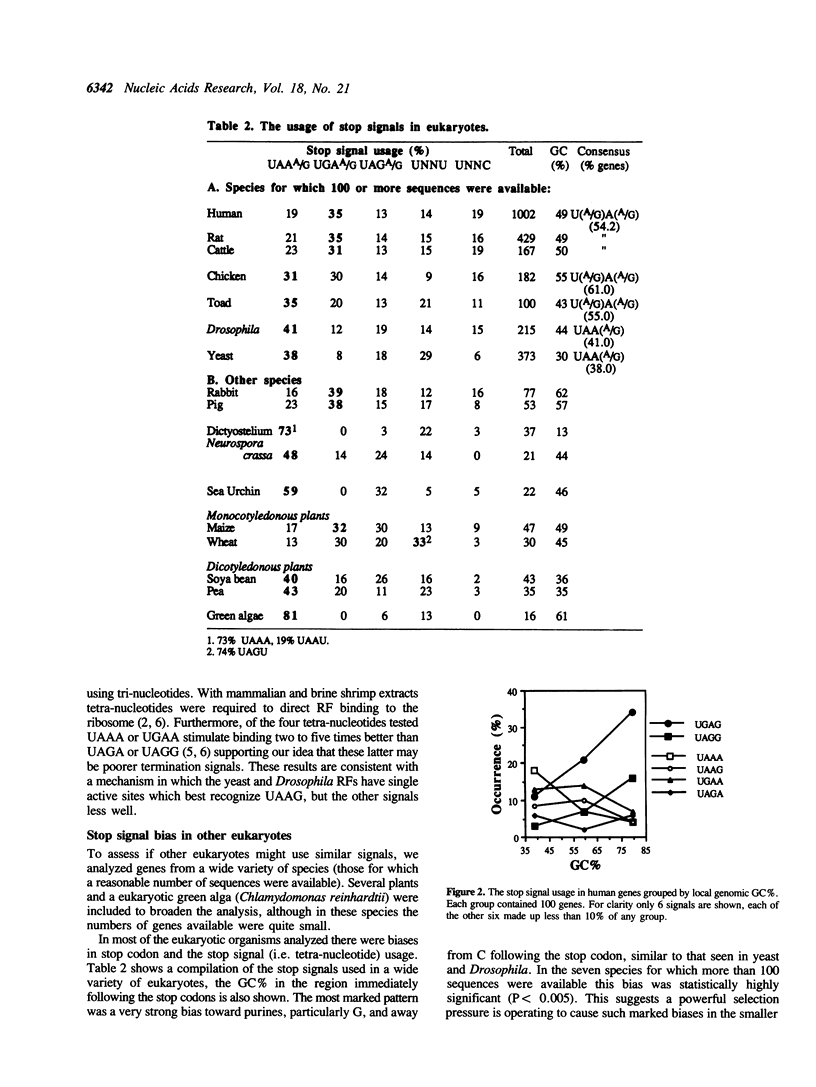
An increasing number of cases where tri-nucleotide stop codons do not signal the termination of protein synthesis are being reported. In order to identify what constitutes an efficient stop signal, we analysed the region around natural stop codons in genes from a wide variety of eukaryotic species and gene families. Certain stop codons and nucleotides following stop codons are over-represented, and this pattern is accentuated in highly expressed genes. For example, the preferred signal for Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Drosophila melanogaster highly expressed genes is UAAG, and generally the signals UAA(A/G) and UGA(A/G) are preferred in eukaryotes. The GC% of the organism or DNA region can affect whether there is A or G in the second or fourth positions. We suggest therefore, that the stop codon and the nucleotide following it comprise a tetra-nucleotide stop signal. A model is proposed in which the polypeptide chain release factor, a protein, recognises this sequence, but will tolerate some substitution, particularly A to G in the second or third positions.
Full text
PDF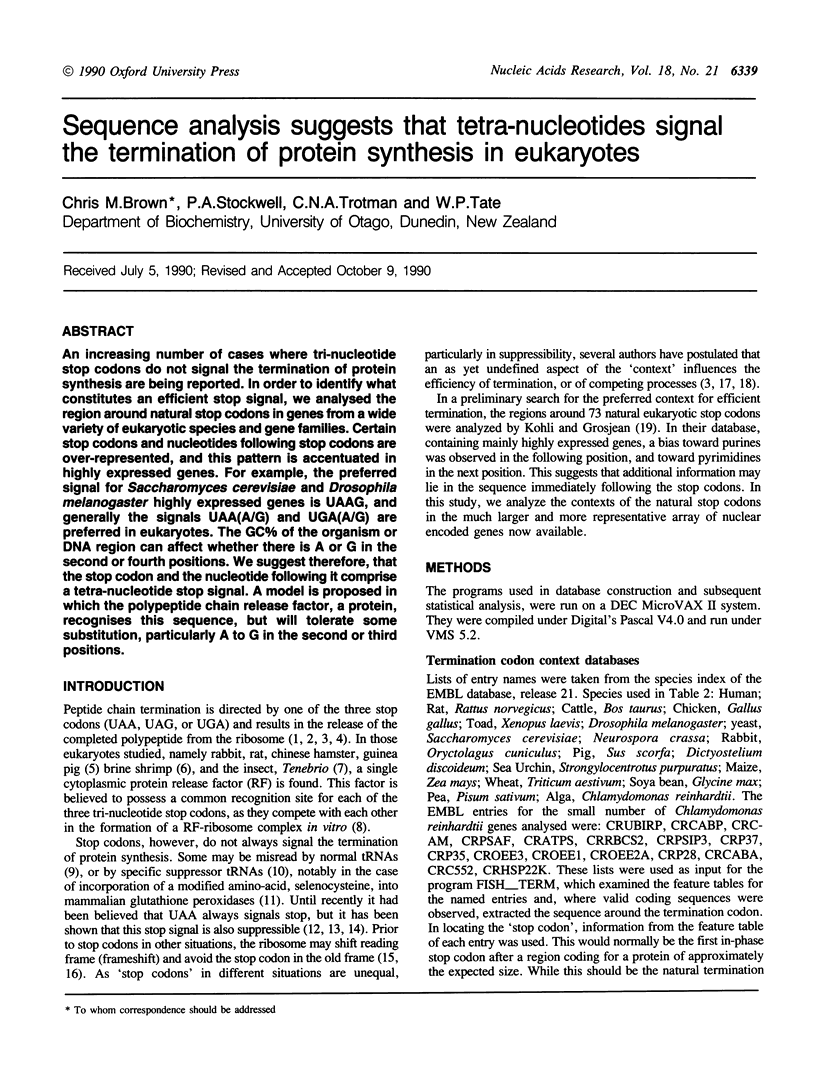




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aota S., Ikemura T. Diversity in G + C content at the third position of codons in vertebrate genes and its cause. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6345–6355. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins J. F., Weiss R. B., Gesteland R. F. Ribosome gymnastics--degree of difficulty 9.5, style 10.0. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90007-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Digard P., Inglis S. C. Characterization of an efficient coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal: requirement for an RNA pseudoknot. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Stockwell P. A., Trotman C. N., Tate W. P. The signal for the termination of protein synthesis in procaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2079–2086. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers I., Frampton J., Goldfarb P., Affara N., McBain W., Harrison P. R. The structure of the mouse glutathione peroxidase gene: the selenocysteine in the active site is encoded by the 'termination' codon, TGA. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1221–1227. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04350.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigen W. J., Lee C. C., Caskey C. T. Recent advances in peptide chain termination. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jun;4(6):861–865. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00658.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denisenko O. N., Yarchuk O. B. Regulation of LacZ mRNA translatability in a cell-free system at heat shock by the last four sense codons. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 24;247(2):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81346-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y. X., Levin J. G., Hatfield D. L., Schaefer T. S., Gorelick R. J., Rein A. Suppression of UAA and UGA termination codons in mutant murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2870–2873. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2870-2873.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluck M. M., Salser W., Epstein R. H. The influence of the reading context upon the suppression of nonsense codons. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 7;151(2):137–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00338688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Rich A. A UGA termination suppression tRNATrp active in rabbit reticulocytes. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):41–46. doi: 10.1038/283041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Beaudet A. L., Caskey C. T. Peptide chain termination with mammalian release factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):99–106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D. L., Smith D. W., Lee B. J., Worland P. J., Oroszlan S. Structure and function of suppressor tRNAs in higher eukaryotes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(2):71–96. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield D., Thorgeirsson S. S., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S., Bustin M. Immunopurification of the suppressor tRNA dependent rabbit beta-globin readthrough protein. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 23;27(4):1179–1183. doi: 10.1021/bi00404a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Jan;2(1):13–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. Translational suppression in gene expression in retroviruses and retrotransposons. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;157:93–124. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75218-6_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi C. P. Putative polyadenylation signals in nuclear genes of higher plants: a compilation and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9627–9640. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohli J., Grosjean H. Usage of the three termination codons: compilation and analysis of the known eukaryotic and prokaryotic translation termination sequences. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(3):430–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00293932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konecki D. S., Aune K. C., Tate W., Caskey C. T. Characterization of reticulocyte release factor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4514–4520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman N., Jukes T. H. Genetic code development by stop codon takeover. J Theor Biol. 1988 Nov 21;135(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(88)80074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. P., Rice C. M. Mutagenesis of the in-frame opal termination codon preceding nsP4 of Sindbis virus: studies of translational readthrough and its effect on virus replication. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1326–1337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1326-1337.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Mogg A. E., Heywood L. A., Nitschke L., Burke J. F. Aminoglycoside suppression at UAG, UAA and UGA codons in Escherichia coli and human tissue culture cells. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):411–418. doi: 10.1007/BF02464911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. F., Hinnebusch A. G. Sequences that surround the stop codons of upstream open reading frames in GCN4 mRNA determine their distinct functions in translational control. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1217–1225. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray E. E., Lotzer J., Eberle M. Codon usage in plant genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):477–498. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussinov R. Eukaryotic dinucleotide preference rules and their implications for degenerate codon usage. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Muto A., Jukes T. H., Ohama T. Evolutionary changes in the genetic code. Proc Biol Sci. 1990 Jul 23;241(1300):19–28. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Ohama T., Jukes T. H., Watanabe K. Evolution of the mitochondrial genetic code. I. Origin of AGR serine and stop codons in metazoan mitochondria. J Mol Evol. 1989 Sep;29(3):202–207. doi: 10.1007/BF02100203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddington M. A., Tate W. P. A polypeptide chain release factor from the undeveloped cyst of the brine shrimp, Artemia salina. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 15;97(2):335–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salser W. The influence of the reading context upon the suppression of nonsense codons. Mol Gen Genet. 1969 Oct 13;105(2):125–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00445682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Bulmer M. Selective differences among translation termination codons. Gene. 1988;63(1):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90553-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Cowe E., Higgins D. G., Shields D. C., Wolfe K. H., Wright F. Codon usage patterns in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens; a review of the considerable within-species diversity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8207–8211. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Devine K. M. Codon usage and gene expression level in Dictyostelium discoideum: highly expressed genes do 'prefer' optimal codons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5029–5039. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Li W. H. The codon Adaptation Index--a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1281–1295. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Tuohy T. M., Mosurski K. R. Codon usage in yeast: cluster analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5125–5143. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate W. P., Beaudet A. L., Caskey C. T. Influence of guanine nucleotides and elongation factors on interaction of release factors with the ribosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2350–2355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valle R. P., Morch M. D. Stop making sense: or Regulation at the level of termination in eukaryotic protein synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81225-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells D., McBride C. A comprehensive compilation and alignment of histones and histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17 (Suppl):r311–r346. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.suppl.r311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Ribosome pausing and stacking during translation of a eukaryotic mRNA. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3559–3569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinoni F., Heider J., Böck A. Features of the formate dehydrogenase mRNA necessary for decoding of the UGA codon as selenocysteine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4660–4664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


