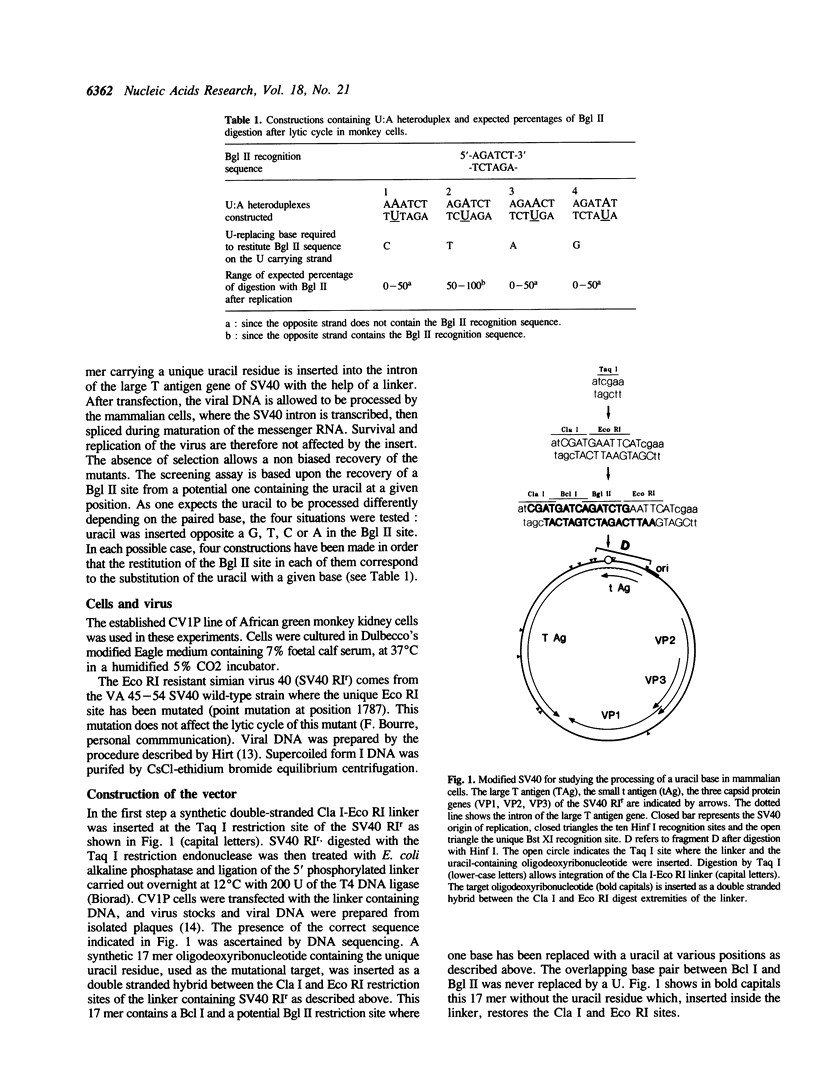
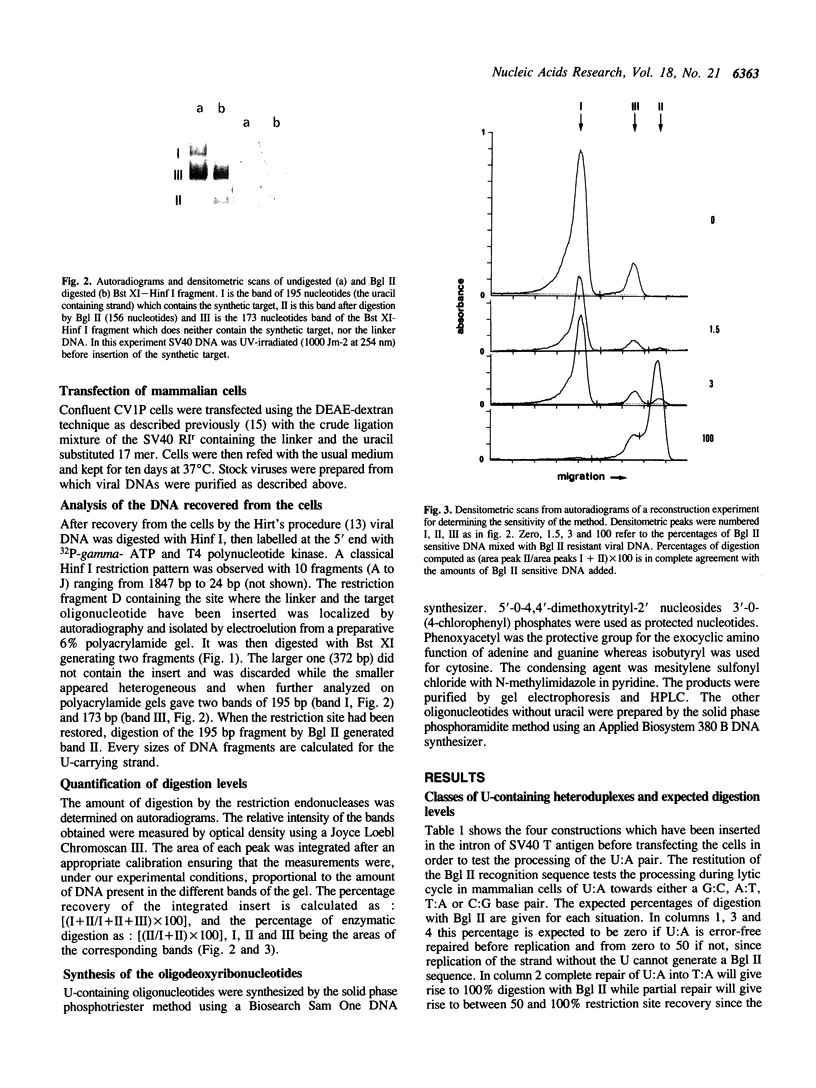
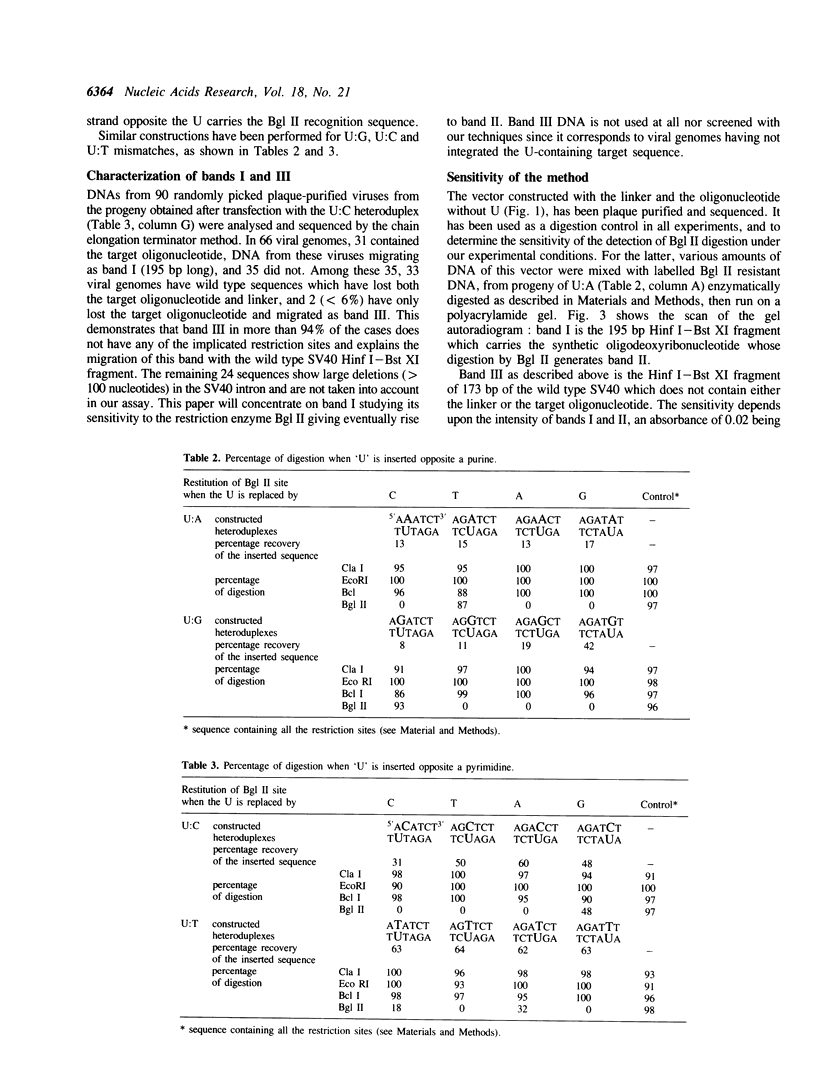
Abstract
The processing of a unique uracil in DNA has been studied in mammalian cells. A synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide carrying a potential Bgl II restriction site, where one base has been substituted with a uracil, was inserted in the early intron of SV40 genome. Various heteroduplexes were constructed in such a manner that the restitution of an active Bgl II restriction site corresponds in each case to the specific substitution of the uracil by one of the four bases normally present in the DNA. DNA cuts by this restriction enzyme in one or several constructed heteroduplexes immediately determine the type of base pair substitution produced at the site of the U residue. When the uracil is inserted opposite a purine it is fully repaired; when facing a guanine it is replaced by a cytosine and opposite an adenine it is replaced by a thymine. These results indicate the error-free repair of uracil when it appears in the cell with the usual mechanisms such as cytosine deamination or incorporation of dUTP in place of dTTP during replication. When the uracil is inserted opposite a pyrimidine no error free repair at all is detected for U:C or U:T mismatches. It appears, moreover, that in approximately 18% of the cases U:T mismatch leads to a C:G base pairing. In the majority of the U:pyrimidine mismatches, mutations occur in the vicinity of the uracil, including base substitutions and frameshifts by addition of one or several bases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown T. C., Brown-Luedi M. L. G/U lesions are efficiently corrected to G/C in SV40 DNA. Mutat Res. 1989 Dec;227(4):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(89)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caradonna S. J., Cheng Y. C. Uracil DNA-glycosylase. Purification and properties of this enzyme isolated from blast cells of acute myelocytic leukemia patients. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2293–2300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake J. W., Baltz R. H. The biochemistry of mutagenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:11–37. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.000303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan B. K., Miller J. H. Mutagenic deamination of cytosine residues in DNA. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):560–561. doi: 10.1038/287560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentil A., Margot A., Sarasin A. 2-(N-acetoxy-N-acetylamino)fluorene mutagenesis in mammalian cells: sequence-specific hot spot. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9556–9560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentil A., Margot A., Sarasin A. Apurinic sites cause mutations in simian virus 40. Mutat Res. 1984 Nov;129(2):141–147. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(84)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffel-Schwartz N., Maenhaut-Michel G., Fuchs R. P. Specific strand loss in N-2-acetylaminofluorene-modified DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):651–659. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. DNA glycosylases, endonucleases for apurinic/apyrimidinic sites, and base excision-repair. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1979;22:135–192. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60800-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T. DNA repair enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:61–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Ljungquist S., Siegert W., Nyberg B., Sperens B. DNA N-glycosidases: properties of uracil-DNA glycosidase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3286–3294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madzak C., Menck C. F., Armier J., Sarasin A. Analysis of single-stranded DNA stability and damage-induced strand loss in mammalian cells using SV40-based shuttle vectors. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 5;205(3):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuth M. The genetic consequences of nucleotide precursor pool imbalance in mammalian cells. Mutat Res. 1984 Apr;126(2):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(84)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuth M. The molecular basis of mutations induced by deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate pool imbalances in mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Apr;181(2):305–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M. DNA intermediates at the Escherichia coli replication fork: effect of dUTP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):238–242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal G., Brech K., Karp S. J., Cool B. L., Sirover M. A. Immunological lesions in human uracil DNA glycosylase: association with Bloom syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2339–2343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy S., Ehrlich K. C., Ehrlich M. Repair of thymine.guanine and uracil.guanine mismatched base-pairs in bacteriophage M13mp18 DNA heteroduplexes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 20;197(4):617–626. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90468-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tye B. K., Nyman P. O., Lehman I. R., Hochhauser S., Weiss B. Transient accumulation of Okazaki fragments as a result of uracil incorporation into nascent DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):154–157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]