Abstract
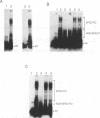
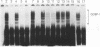
We have identified a protein (GCBP-1) in nuclear extracts from maize suspension cell cultures that binds to specific sequences within the Anaerobic Responsive Element (ARE) of the maize Adh1 promoter. Competition analyses show that the GCBP-1 binding activity distinguishes ARE sequence motifs from other enhancer elements or pUC19 sequences. The binding activities of several mutant ARE sequences define two regions of the ARE important for GCBP-1 binding in vitro, between nucleotides -135 to -131 and nucleotides -120 to -112 of the maize Adh1 promoter. Both regions are required for efficient GCBP-1 binding to occur in vitro. The minimum consensus binding site for GCBP-1 is 5'-GC(G/C)CC-3'. This sequence is similar to a part of the binding site of the human transcription factor Sp1 (1). We demonstrate that maize GCBP-1 and human Sp1 have similar recognition properties. Using ARE mutants in a transient assay in maize protoplasts we have shown that mutation of the GCBP-1 binding sites prevents significant hypoxic activation of the maize Adh1 promoter. These results suggest a direct role for GCBP-1 in the hypoxic activation of Adh1 gene expression. GCBP-1 is present in both uninduced and induced nuclei, indicating that inducible gene expression is not dependent upon synthesis of GCBP-1 and suggesting that post-translational modification of bound GCBP-1 may be important for enhanced transcription to occur.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. G., Llewellyn D. J., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. Maize Adh-1 promoter sequences control anaerobic regulation: addition of upstream promoter elements from constitutive genes is necessary for expression in tobacco. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):11–16. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferl R. J. ARF-B(2): A Protein Complex that Specifically Binds to Part of the Anaerobic Response Element of Maize Adh 1. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jul;93(3):1094–1101. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.3.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferl R. J., Nick H. S. In vivo detection of regulatory factor binding sites in the 5' flanking region of maize Adh1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):7947–7950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M. E., Taylor L. P., Walbot V. Stable transformation of maize after gene transfer by electroporation. 1986 Feb 27-Mar 5Nature. 319(6056):791–793. doi: 10.1038/319791a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlach W. L., Pryor A. J., Dennis E. S., Ferl R. J., Sachs M. M., Peacock W. J. cDNA cloning and induction of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene (Adh1) of maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2981–2985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Yong M. H., Cuozzo M., Kano-Murakami Y., Silverstein P., Chua N. H. Binding site requirements for pea nuclear protein factor GT-1 correlate with sequences required for light-dependent transcriptional activation of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4035–4044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hake S., Kelley P. M., Taylor W. C., Freeling M. Coordinate induction of alcohol dehydrogenase 1, aldolase, and other anaerobic RNAs in maize. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5050–5054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höller M., Westin G., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Sp1 transcription factor binds DNA and activates transcription even when the binding site is CpG methylated. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1127–1135. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Tjian R. Sp1 binds to promoter sequences and activates herpes simplex virus 'immediate-early' gene transcription in vitro. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):179–182. doi: 10.1038/317179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latchman D. S. Eukaryotic transcription factors. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):281–289. doi: 10.1042/bj2700281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthe D. S., Quatrano R. S. Transcription in Isolated Wheat Nuclei: I. ISOLATION OF NUCLEI AND ELIMINATION OF ENDOGENOUS RIBONUCLEASE ACTIVITY. Plant Physiol. 1980 Feb;65(2):305–308. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olive M. R., Walker J. C., Singh K., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. Functional properties of the anaerobic responsive element of the maize Adh1 gene. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Oct;15(4):593–604. doi: 10.1007/BF00017834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Sambucetti L. C., Curran T., Distel R. J., Spiegelman B. M. Common DNA binding site for Fos protein complexes and transcription factor AP-1. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):471–480. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland L. J., Strommer J. N. Anaerobic treatment of maize roots affects transcription of Adh1 and transcript stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3368–3372. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs M. M., Freeling M., Okimoto R. The anaerobic proteins of maize. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):761–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler U., Cashmore A. R. Photoregulated gene expression may involve ubiquitous DNA binding proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3415–3427. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Tokuhisa J. G., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. Saturation mutagenesis of the octopine synthase enhancer: correlation of mutant phenotypes with binding of a nuclear protein factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3733–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. Heat shock factor is regulated differently in yeast and HeLa cells. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):81–84. doi: 10.1038/329081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Yeast heat shock factor is an essential DNA-binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Helix-turn-helix, zinc-finger, and leucine-zipper motifs for eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Apr;14(4):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90145-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. C., Howard E. A., Dennis E. S., Peacock W. J. DNA sequences required for anaerobic expression of the maize alcohol dehydrogenase 1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6624–6628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Schaffner W. A zinc-responsive factor interacts with a metal-regulated enhancer element (MRE) of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3763–3770. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Schaffner W. Heavy metal ions in transcription factors from HeLa cells: Sp1, but not octamer transcription factor requires zinc for DNA binding and for activator function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5771–5781. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]