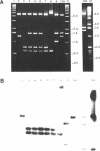
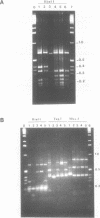
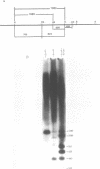
Abstract
The repetitive LINE (L1) elements of the mouse, which are present at about 10(5) copies per genome and share over 80% of sequence homology, were examined for their ability to undergo genetic exchange with exogenous L1 sequences. The exogenous L1 sequences, carried by a shuttle vector, consisted of an internal fragment from L1Md-A2, a previously described member of the L1 family of the mouse. Using an assay that does not require the reconstitution of a selectable marker we found that this vector, in either circular or linear form, acquired DNA sequences from endogenous L1 elements at a frequency of 10(-3) to 10(-4) per rescued vector. Physical analysis of the acquired L1 sequences revealed that distinct endogenous L1 elements acted as donors and that different subfamilies participated. These results demonstrate that L1 elements are readily capable of genetic exchange. Apart from gene conversion events, the acquisition of L1 sequences outside the region of homology suggested that a second mechanism was also involved in the genetic exchange. A model which accounts for this mechanism is presented and its potential implication on the rearrangement of L1 elements is discussed.
Full text
PDF

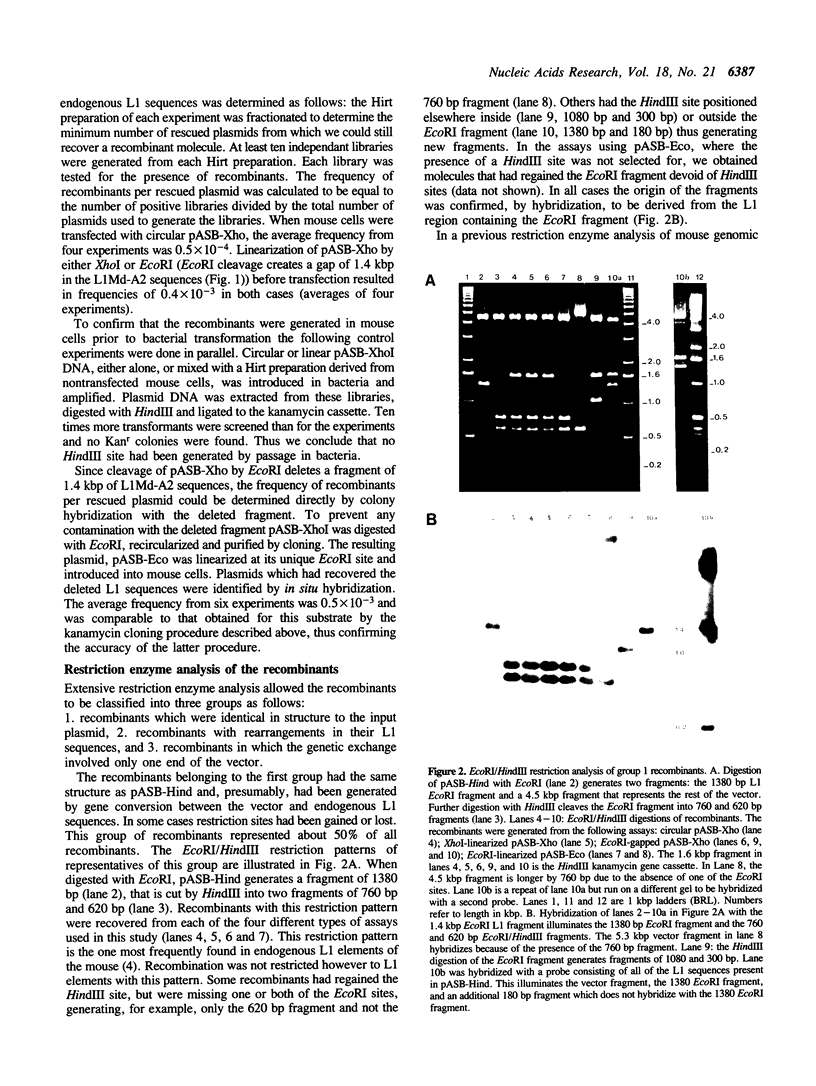
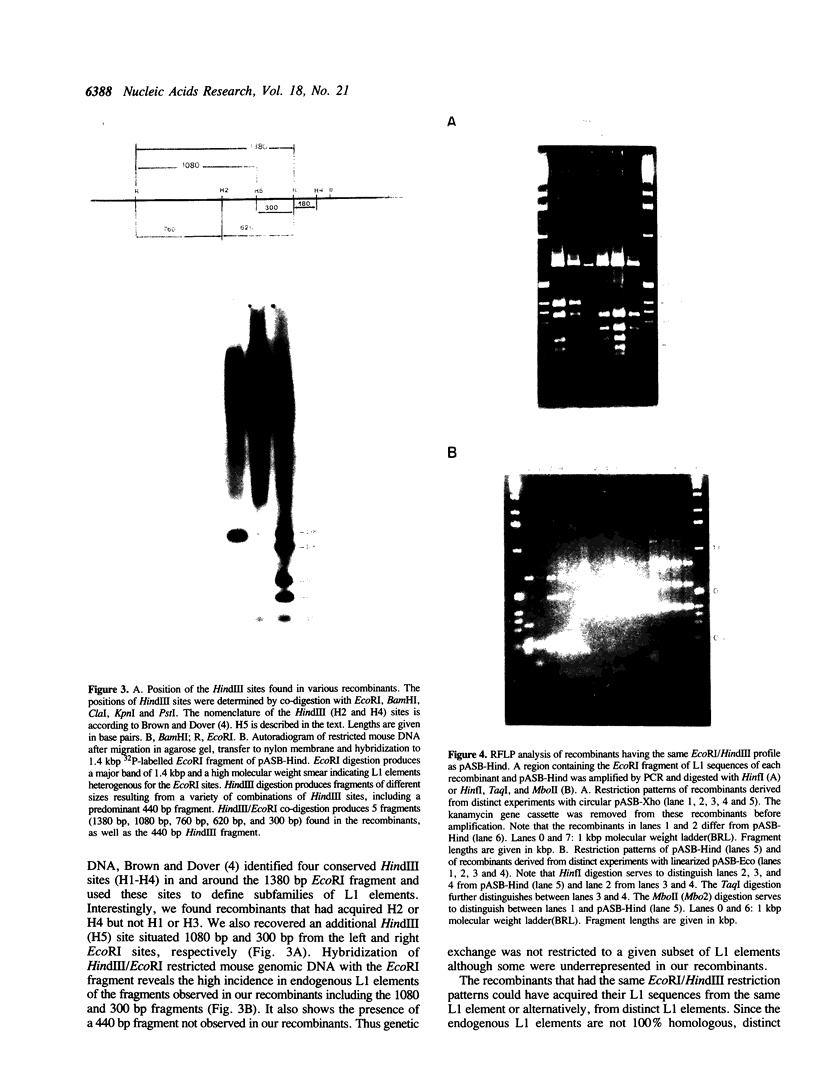



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. A., Eliason S. L. Recombination of homologous DNA fragments transfected into mammalian cells occurs predominantly by terminal pairing. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3246–3252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashman C. R., Davidson R. L. High spontaneous mutation frequency in shuttle vector sequences recovered from mammalian cellular DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2266–2272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Smith P. Mechanism of chromosomal integration of microinjected DNA. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Aug;6(4):283–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell D. D. Rapid isolation of eukaryotic DNA. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 1;162(2):463–465. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90421-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouillette S., Chartrand P. Intermolecular recombination assay for mammalian cells that produces recombinants carrying both homologous and nonhomologous junctions. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2248–2255. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Dover G. Organization and evolutionary progress of a dispersed repetitive family of sequences in widely separated rodent genomes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 25;150(4):441–466. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton F. H., Loeb D. D., Chao S. F., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Transposition of a long member of the L1 major interspersed DNA family into the mouse beta globin gene locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5071–5084. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton F. H., Loeb D. D., Voliva C. F., Martin S. L., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Conservation throughout mammalia and extensive protein-encoding capacity of the highly repeated DNA long interspersed sequence one. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Lebkowski J. S., Botchan M. R. High mutation frequency in DNA transfected into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casavant N. C., Hardies S. C., Funk F. D., Comer M. B., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Extensive movement of LINES ONE sequences in beta-globin loci of Mus caroli and Mus domesticus. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4669–4674. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Joffe S., Seidman M. M. Recombination and deletion of sequences in shuttle vector plasmids in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2265–2271. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Seidman M. M. Intramolecular recombination between transfected repeated sequences in mammalian cells is nonconservative. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2520–2526. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleaux L., D'Auriol L., Galibert F., Dujon B. Recognition and cleavage site of the intron-encoded omega transposase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6022–6026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ambrosio E., Waitzkin S. D., Witney F. R., Salemme A., Furano A. V. Structure of the highly repeated, long interspersed DNA family (LINE or L1Rn) of the rat. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):411–424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demers G. W., Matunis M. J., Hardison R. C. The L1 family of long interspersed repetitive DNA in rabbits: sequence, copy number, conserved open reading frames, and similarity to keratin. J Mol Evol. 1989 Jul;29(1):3–19. doi: 10.1007/BF02106177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou-Pachnis A., Lohse M. A., Furano A. V., Tsichlis P. N. Insertion of long interspersed repeated elements at the Igh (immunoglobulin heavy chain) and Mlvi-2 (Moloney leukemia virus integration 2) loci of rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2857–2861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J., Bernstein A. Gene targeting with retroviral vectors: recombination by gene conversion into regions of nonhomology. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1621–1627. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G., Singer M. F. LINE-1: a mammalian transposable element. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 8;910(3):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T., Singer M. The LINE-1 DNA sequences in four mammalian orders predict proteins that conserve homologies to retrovirus proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2251–2260. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Singer M. F. Members of the KpnI family of long interspersed repeated sequences join and interrupt alpha-satellite in the monkey genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):321–338. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardies S. C., Martin S. L., Voliva C. F., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. An analysis of replacement and synonymous changes in the rodent L1 repeat family. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Mar;3(2):109–125. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Hidaka S., Sakaki Y. Sequence analysis of a KpnI family member near the 3' end of human beta-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7813–7827. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Kuhara S., Takenaka O., Sakaki Y. L1 family of repetitive DNA sequences in primates may be derived from a sequence encoding a reverse transcriptase-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):625–628. doi: 10.1038/321625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin M., de Villiers J., Weber F., Schaffner W. High frequency of homologous recombination in mammalian cells between endogenous and introduced SV40 genomes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90242-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jubier-Maurin V., Dod B. J., Bellis M., Piechaczyk M., Roizes G. Comparative study of the L1 family in the genus Mus. Possible role of retroposition and conversion events in its concerted evolution. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):547–564. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90302-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzir N., Rechavi G., Cohen J. B., Unger T., Simoni F., Segal S., Cohen D., Givol D. "Retroposon" insertion into the cellular oncogene c-myc in canine transmissible venereal tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1054–1058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Wong C., Youssoufian H., Scott A. F., Phillips D. G., Antonarakis S. E. Haemophilia A resulting from de novo insertion of L1 sequences represents a novel mechanism for mutation in man. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):164–166. doi: 10.1038/332164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolewski J. J., Rush M. G. Some extrachromosomal circular DNAs containing the Alu family of dispersed repetitive sequences may be reverse transcripts. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90363-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunisada T., Yamagishi H. Sequence repetition and genomic distribution of small polydisperse circular DNA purified from HeLa cells. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90212-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmikumaran M. S., D'Ambrosio E., Laimins L. A., Lin D. T., Furano A. V. Long interspersed repeated DNA (LINE) causes polymorphism at the rat insulin 1 locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2197–2203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., DuBridge R. B., Antell E. A., Greisen K. S., Calos M. P. Transfected DNA is mutated in monkey, mouse, and human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1951–1960. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Intermolecular recombination between DNAs introduced into mouse L cells is mediated by a nonconservative pathway that leads to crossover products. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):103–112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. D., Padgett R. W., Hardies S. C., Shehee W. R., Comer M. B., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd The sequence of a large L1Md element reveals a tandemly repeated 5' end and several features found in retrotransposons. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):168–182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. L., Voliva C. F., Hardies S. C., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Tempo and mode of concerted evolution in the L1 repeat family of mice. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Mar;2(2):127–140. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Lebkowski J. S., Greisen K. S., Calos M. P. Specificity of mutations induced in transfected DNA by mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3117–3121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudgett J. S., Taylor W. D. Recombination between irradiated shuttle vector DNA and chromosomal DNA in African green monkey kidney cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):37–46. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Naujokas M. A., Hassell J. A. Isolation of large T antigen-producing mouse cell lines capable of supporting replication of polyomavirus-plasmid recombinants. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2406–2412. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Fungal recombination. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):33–58. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.33-58.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Yeast recombination: the association between double-strand gap repair and crossing-over. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4417–4421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razzaque A., Chakrabarti S., Joffee S., Seidman M. Mutagenesis of a shuttle vector plasmid in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;4(3):435–441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.3.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razzaque A., Mizusawa H., Seidman M. M. Rearrangement and mutagenesis of a shuttle vector plasmid after passage in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3010–3014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. Long interspersed sequences in mammalian DNA. Properties of newly identified specimens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 20;824(2):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. The origin and evolution of retroposons. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:187–279. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Wilson J. H. Relative rates of homologous and nonhomologous recombination in transfected DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3355–3359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaki Y., Hattori M., Fujita A., Yoshioka K., Kuhara S., Takenaka O. The LINE-1 family of primates may encode a reverse transcriptase-like protein. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):465–469. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. F., Schmeckpeper B. J., Abdelrazik M., Comey C. T., O'Hara B., Rossiter J. P., Cooley T., Heath P., Smith K. D., Margolet L. Origin of the human L1 elements: proposed progenitor genes deduced from a consensus DNA sequence. Genomics. 1987 Oct;1(2):113–125. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90003-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehee W. R., Chao S. F., Loeb D. D., Comer M. B., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Determination of a functional ancestral sequence and definition of the 5' end of A-type mouse L1 elements. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):757–767. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyman S., Weaver S. Chromosomal rearrangements associated with LINE elements in the mouse genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5085–5093. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Jones K. W. The use of heparin as a simple cost-effective means of controlling background in nucleic acid hybridization procedures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5627–5638. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J., Fanning T. G., Singer M. F. Unit-length line-1 transcripts in human teratocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1385–1397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J., Singer M. F. The abundant LINE-1 family of repeated DNA sequences in mammals: genes and pseudogenes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):457–464. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. R. Recombination between poly[d(GT).d(CA)] sequences in simian virus 40-infected cultured cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1247–1259. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Berg P. Homologous and nonhomologous recombination in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1040–1052. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S. Rescue of chromosomal T-antigen sequences onto extrachromosomally replicating, defective simian virus 40 DNA by homologous recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1320–1325. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Vernaleone F., Wilson J. H. Topological requirements for homologous recombination among DNA molecules transfected into mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2080–2089. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman A. S., Liskay R. M. Dependence of intrachromosomal recombination in mammalian cells on uninterrupted homology. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5350–5357. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. S., Zakian V. A. Telomere-telomere recombination provides an express pathway for telomere acquisition. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):456–458. doi: 10.1038/345456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods-Samuels P., Wong C., Mathias S. L., Scott A. F., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E. Characterization of a nondeleterious L1 insertion in an intron of the human factor VIII gene and further evidence of open reading frames in functional L1 elements. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90332-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng H., Wilson J. H. Gene targeting in normal and amplified cell lines. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):170–173. doi: 10.1038/344170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]