Abstract
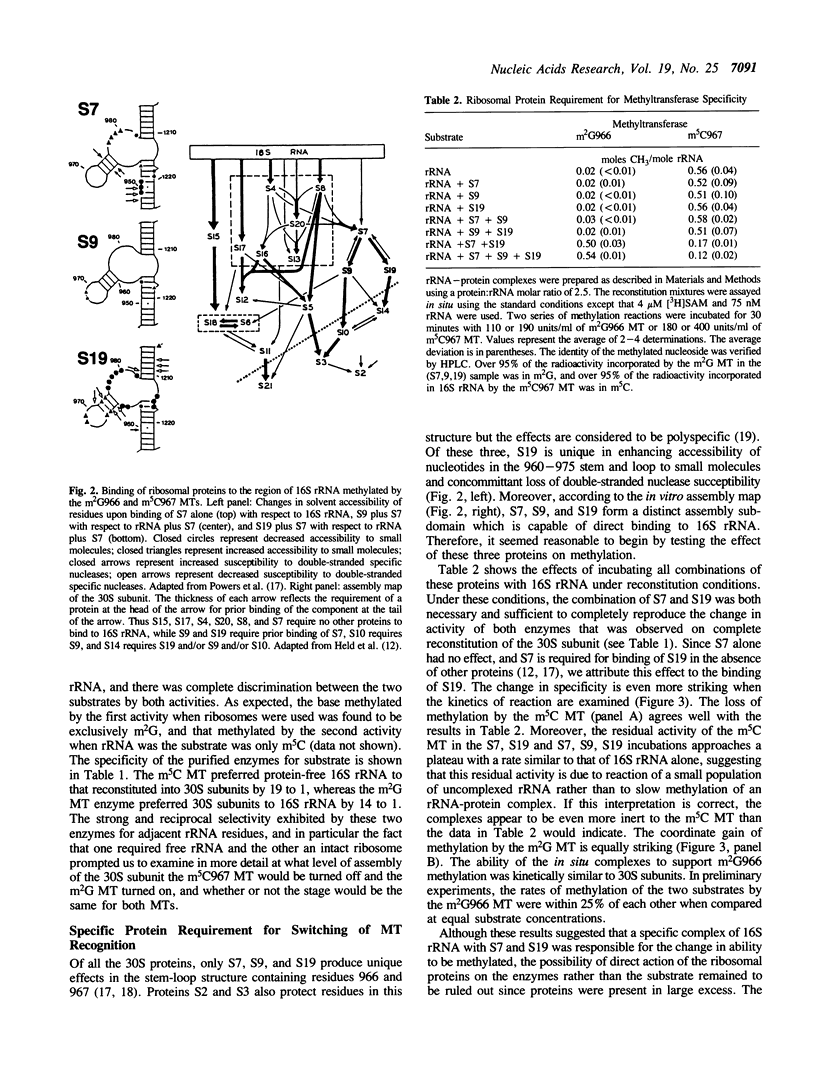
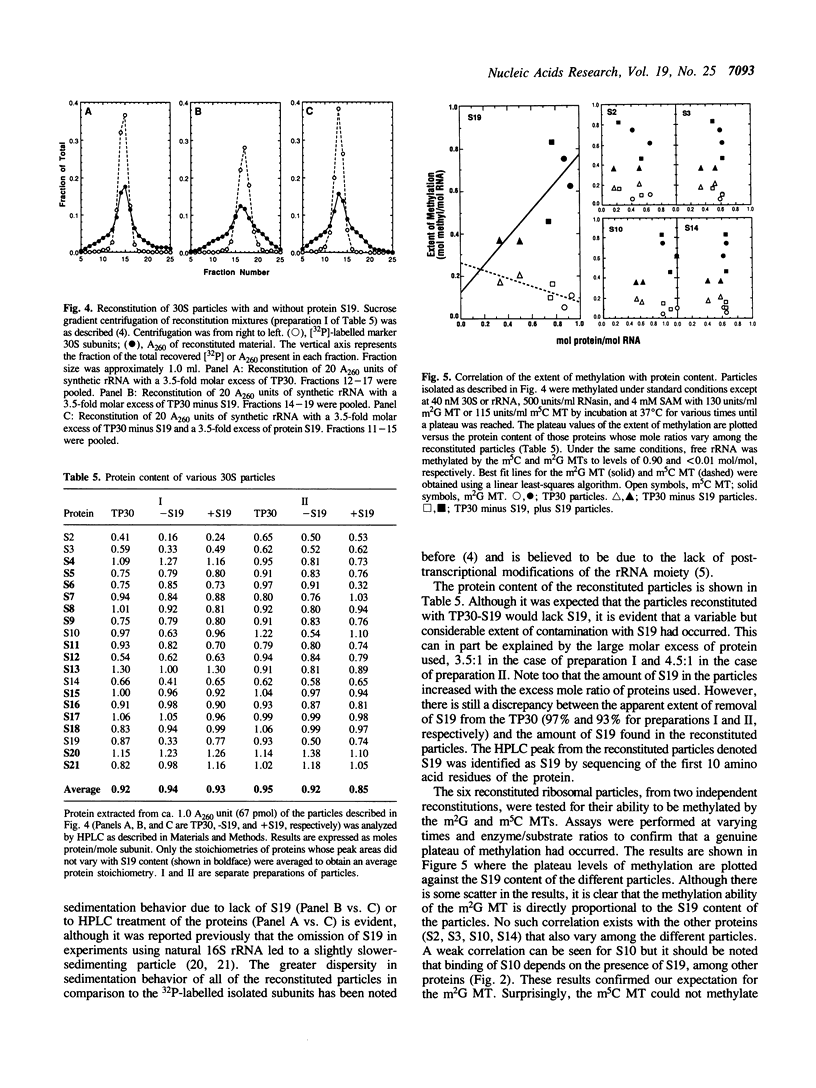
We have partially purified two 16S rRNA-specific methyltransferases, one of which forms m2G966 (m2G MT), while the other one makes m5C967 (m5C MT). The m2G MT uses unmethylated 30S subunits as a substrate, but not free unmethylated 16S rRNA, while the m5C MT functions reciprocally, using free rRNA but not 30S subunits (Nègre, D., Weitzmann, C. and Ofengand, J. (1990) UCLA Symposium: Nucleic Acid Methylation (Alan Liss, New York), pp. 1-17). We have now determined the basis for this unusual inverse specificity at adjacent nucleotides. Binding of ribosomal proteins S7, S9, and S19 to unmodified 16S rRNA individually and in all possible combinations showed that S7 plus S19 were sufficient to block methylation by the m5C MT, while simultaneously inducing methylation by the m2G MT. A purified complex containing stoichiometric amounts of proteins S7, S9, and S19 bound to 16S rRNA was isolated and shown to possess the same methylation properties as 30S subunits, that is, the ability to be methylated by the m2G MT but not by the m5C MT. Since binding of S19 requires prior binding of S7, which had no effect on methylation when bound alone, we attribute the switch in methylase specificity solely to the presence of RNA-bound S19. Single-omission reconstitution of 30S subunits deficient in S19 resulted in particles that could not be efficiently methylated by either enzyme. Thus while binding of S19 is both necessary and sufficient to convert 16S rRNA into a substrate of the m2G MT, binding of either S19 alone or some other protein or combination of proteins to the 16S rRNA can abolish activity of the m5C MT. Binding of S19 to 16S rRNA is known to cause local conformational changes in the 960-975 stem-loop structure surrounding the two methylated nucleotides (Powers, T., Changchien, L.-M., Craven, G. and Noller, H.F. (1988) J. Mol. Biol. 200, 309-319). Our results show that the two ribosomal RNA MTs studied in this work are exquisitely sensitive to this small but nevertheless functionally important structural change.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brimacombe R., Atmadja J., Stiege W., Schüler D. A detailed model of the three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA in situ in the 30 S subunit. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):115–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M. A., Cooperman B. S. Single protein omission reconstitution studies of tetracycline binding to the 30S subunit of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 5;29(22):5374–5379. doi: 10.1021/bi00474a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelbi-Alix M. K., Expert-Bezançon A., Hayes F., Alix J. H., Branlant C. Properties of ribosomes and ribosomal RNAs synthesized by Escherichia coli grown in the presence of ethionine. Normal maturation of ribosomal RNA in the absence of methylation. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(3):627–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham P. R., Weitzmann C. J., Nurse K., Masurel R., Van Knippenberg P. H., Ofengand J. Site-specific mutation of the conserved m6(2)A m6(2)A residues of E. coli 16S ribosomal RNA. Effects on ribosome function and activity of the ksgA methyltransferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):18–26. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90135-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denman R., Nègre D., Cunningham P. R., Nurse K., Colgan J., Weitzmann C., Ofengand J. Effect of point mutations in the decoding site (C1400) region of 16S ribosomal RNA on the ability of ribosomes to carry out individual steps of protein synthesis. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1012–1019. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denman R., Weitzmann C., Cunningham P. R., Nègre D., Nurse K., Colgan J., Pan Y. C., Miedel M., Ofengand J. In vitro assembly of 30S and 70S bacterial ribosomes from 16S RNA containing single base substitutions, insertions, and deletions around the decoding site (C1400). Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1002–1011. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feunteun J., Rosset R., Ehresmann C., Stiegler P., Fellner P. Abnormal maturation of precursor 16S RNA in a ribosomal assembly defective mutant of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Jan;1(1):141–147. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held W. A., Ballou B., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Assembly mapping of 30 S ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli. Further studies. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3103–3111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlavage A. R., Weitzmann C. J., Cooperman B. S. Application of high-performance liquid chromatography to the reconstitution of ribosomal subunits. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 28;317:201–212. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)91660-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzyzosiak W., Denman R., Nurse K., Hellmann W., Boublik M., Gehrke C. W., Agris P. F., Ofengand J. In vitro synthesis of 16S ribosomal RNA containing single base changes and assembly into a functional 30S ribosome. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2353–2364. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden B. E. The numerous modified nucleotides in eukaryotic ribosomal RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1990;39:241–303. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60629-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandiyan V., Tumminia S., Wall J. S., Hainfeld J. F., Boublik M. Protein-induced conformational changes in 16 S ribosomal RNA during the initial assembly steps of the Escherichia coli 30 S ribosomal subunit. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 20;210(2):323–336. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Binding of tRNA to the ribosomal A and P sites protects two distinct sets of nucleotides in 16 S rRNA. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 5;211(1):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90016-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Mizushima S., Ozaki M., Traub P., Lowry C. V. Structure and function of ribosomes and their molecular components. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:49–61. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Traub P., Guthrie C., Nashimoto H. The assembly of ribosomes. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Oct;74(2 Suppl):241+–241+. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040740428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny V., Nierhaus K. H. Assembly of the 30S subunit from Escherichia coli ribosomes occurs via two assembly domains which are initiated by S4 and S7. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):7051–7055. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nègre D., Weitzmann C., Ofengand J. In vitro methylation of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA and 30S ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4902–4906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olah T. V., Olson H. M., Glitz D. G., Cooperman B. S. Incorporation of single dinitrophenyl-modified proteins into the 30 S subunit of Escherichia coli ribosomes by total reconstitution. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4795–4800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poldermans B., Roza L., Van Knippenberg P. H. Studies on the function of two adjacent N6,N6-dimethyladenosines near the 3' end of 16 S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. III. Purification and properties of the methylating enzyme and methylase-30 S interactions. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9094–9100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers T., Changchien L. M., Craven G. R., Noller H. F. Probing the assembly of the 3' major domain of 16 S ribosomal RNA. Quaternary interactions involving ribosomal proteins S7, S9 and S19. J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 20;200(2):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers T., Stern S., Changchien L. M., Noller H. F. Probing the assembly of the 3' major domain of 16 S rRNA. Interactions involving ribosomal proteins S2, S3, S10, S13 and S14. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 20;201(4):697–716. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90468-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raué H. A., Klootwijk J., Musters W. Evolutionary conservation of structure and function of high molecular weight ribosomal RNA. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1988;51(2):77–129. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(88)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüler D., Brimacombe R. The Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal subunit; an optimized three-dimensional fit between the ribosomal proteins and the 16S RNA. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1509–1513. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02970.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Powers T., Changchien L. M., Noller H. F. RNA-protein interactions in 30S ribosomal subunits: folding and function of 16S rRNA. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):783–790. doi: 10.1126/science.2658053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Weiser B., Noller H. F. Model for the three-dimensional folding of 16 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 20;204(2):447–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90588-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Knippenberg P. H., Van Kimmenade J. M., Heus H. A. Phylogeny of the conserved 3' terminal structure of the RNA of small ribosomal subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2595–2604. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youvan D. C., Hearst J. E. A sequence from Drosophila melanogaster 18S rRNA bearing the conserved hypermodified nucleoside am psi: analysis by reverse transcription and high-performance liquid chromatography. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1723–1741. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R. A., Muto A., Fellner P., Ehresmann C., Branlant C. Location of ribosomal protein binding sites on 16S ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1282–1286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


