Abstract
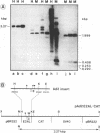
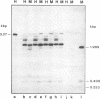
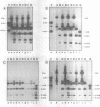
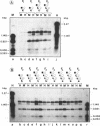
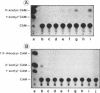
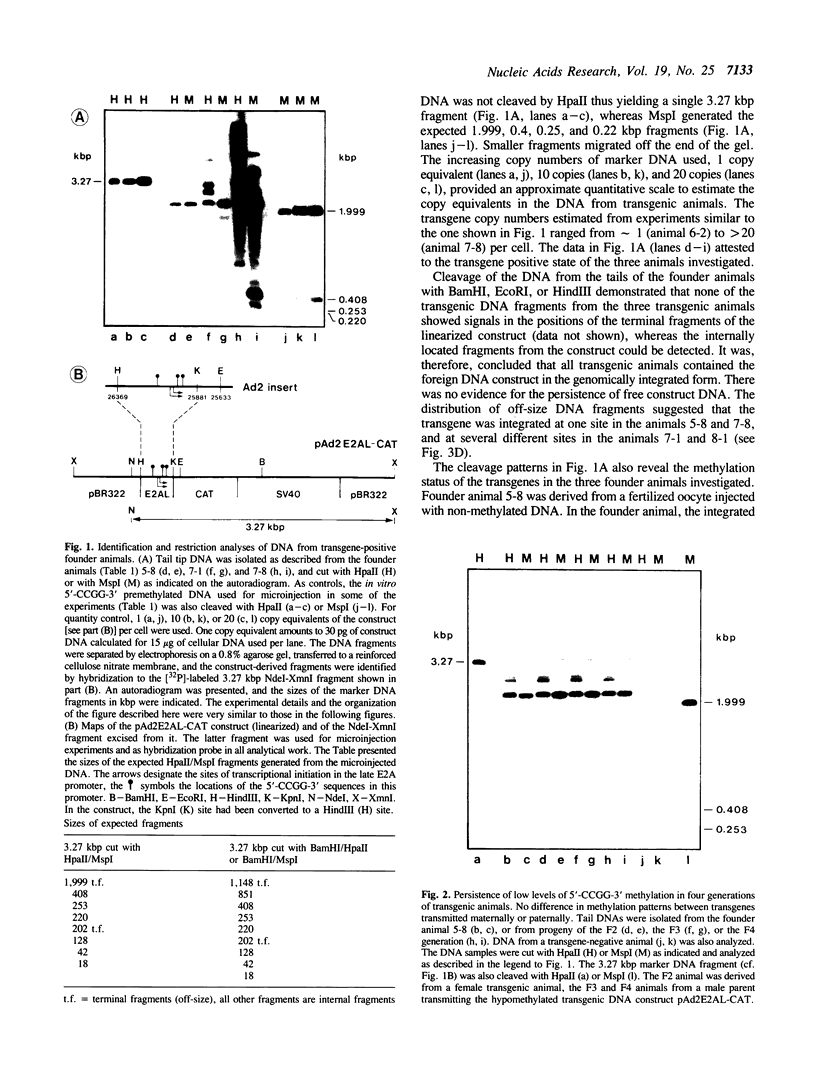
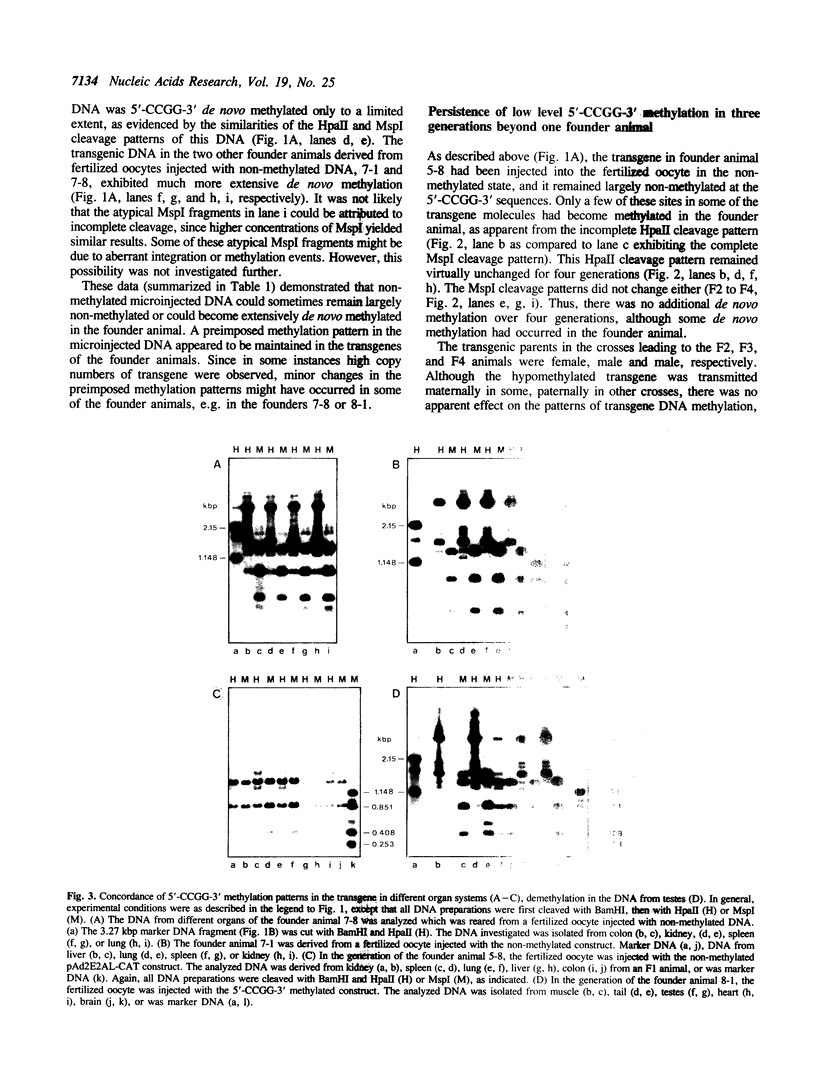
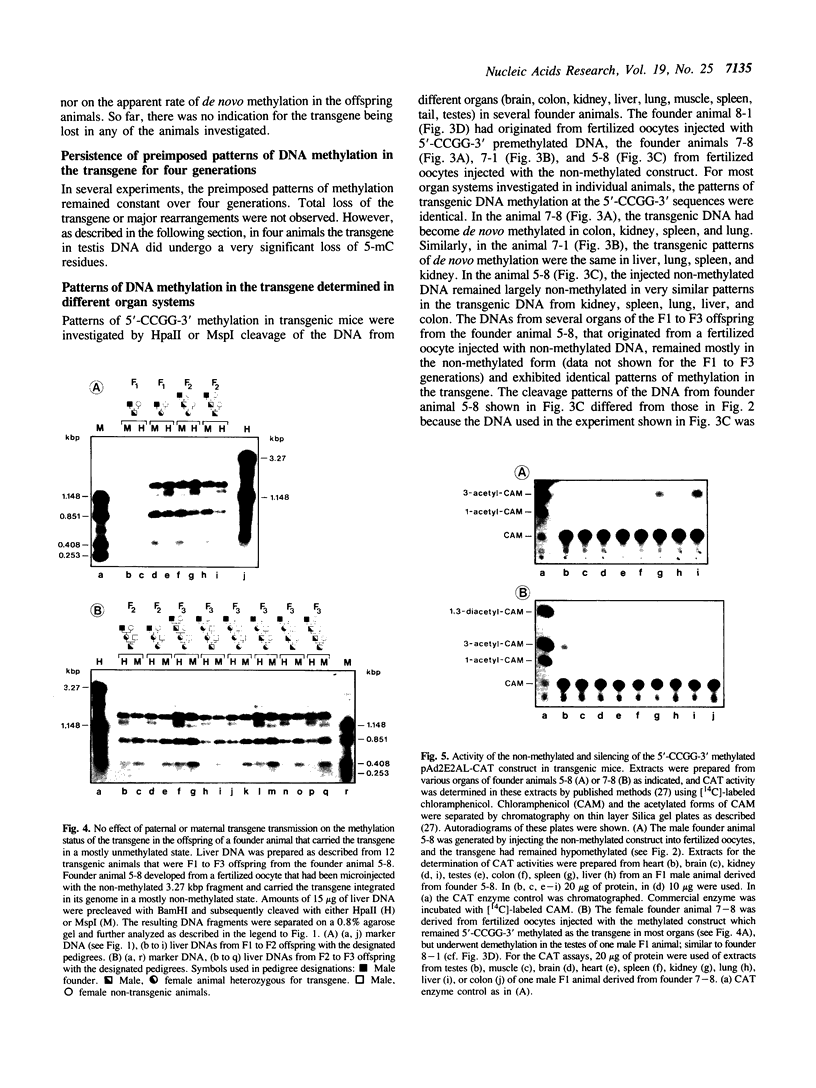
In cultured mammalian cells, foreign DNA can be integrated into the host genome. Foreign DNA is frequently de novo methylated in specific patterns with successive cell generations. The sequence-specific methylation of promoter sequences in integrated foreign DNA is associated with the long-term inactivation of eukaryotic genes. We have now extended these experiments to studies on transgenic mice. As in previous work, a construct (pAd2E2AL-CAT) has been used which consists of the late E2A promoter of adenovirus type 2 (Ad2) DNA fused to the prokaryotic gene for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT). This construct has been integrated in the non-methylated in the 5'-CCGG-3' premethylated form in the genomes of transgenic mice. DNA from various organs was analyzed by HpaII/MspI cleavage to assess the state of methylation in 5'-CCGG-3' sequences. The results demonstrate that the transgenic construct is in general stable. Non-methylated constructs have remained partly non-methylated for four generations or can become de novo methylated at all or most 5'-CCGG-3' sequences in the founder animal. Preimposed patterns of 5'-CCGG-3' methylation have been preserved for up to four generations beyond the founder animal. In the testes of two different founder animals and two F1 males, the transgenic DNA has become demethylated by an unknown mechanism. In all other organs, the transgenic DNA preserves the preimposed 5'-CCGG-3' methylation pattern. In the experiments performed so far we have not observed differences in the transmission of methylation patterns depending on whether the transgene has been maternally or paternally inherited. The 5'-CCGG-3' premethylated transgene does not catalyze CAT activity in several organs, except in one example of the testes of an animal in which the transgenic construct has become demethylated. In contrast, when the nonmethylated construct has been integrated and remained largely non-methylated, CAT activity has been detected in extracts from some of the organs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Effect of growth conditions on the formation of the relaxation complex of supercoiled ColE1 deoxyribonucleic acid and protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1135–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1135-1146.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzanski P., Hoeveler A., Doerfler W. Inactivation by sequence-specific methylations of adenovirus promoters in a cell-free transcription system. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3941–3946. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3941-3946.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation--a regulatory signal in eukaryotic gene expression. J Gen Virol. 1981 Nov;57(Pt 1):1–20. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-57-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. Patterns of DNA methylation--evolutionary vestiges of foreign DNA inactivation as a host defense mechanism. A proposal. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1991 Aug;372(8):557–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler P., Haasch D., Pinkert C. A., Doglio L., Glymour M., Brinster R., Storb U. A strain-specific modifier on mouse chromosome 4 controls the methylation of independent transgene loci. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90546-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Conkin K. F. Chromatin structure and de novo methylation of sperm DNA: implications for activation of the paternal genome. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1061–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.2986289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadchouel M., Farza H., Simon D., Tiollais P., Pourcel C. Maternal inhibition of hepatitis B surface antigen gene expression in transgenic mice correlates with de novo methylation. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):454–456. doi: 10.1038/329454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochanek S., Radbruch A., Tesch H., Renz D., Doerfler W. DNA methylation profiles in the human genes for tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta in subpopulations of leukocytes and in leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochanek S., Toth M., Dehmel A., Renz D., Doerfler W. Interindividual concordance of methylation profiles in human genes for tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8830–8834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlmann I., Doerfler W. Loss of viral genomes from hamster tumor cells and nonrandom alterations in patterns of methylation of integrated adenovirus type 12 DNA. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):631–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.631-636.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlmann I., Doerfler W. Shifts in the extent and patterns of DNA methylation upon explanation and subcultivation of adenovirus type 12-induced hamster tumor cells. Virology. 1982 Apr 15;118(1):169–180. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langner K. D., Vardimon L., Renz D., Doerfler W. DNA methylation of three 5' C-C-G-G 3' sites in the promoter and 5' region inactivate the E2a gene of adenovirus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2950–2954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langner K. D., Weyer U., Doerfler W. Trans effect of the E1 region of adenoviruses on the expression of a prokaryotic gene in mammalian cells: resistance to 5' -CCGG- 3' methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1598–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M. Genomic imprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):921–925. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Doerfler W. Fixation of the unmethylated or the 5'-CCGG-3' methylated adenovirus late E2A promoter-cat gene construct in the genome of hamster cells: gene expression and stability of methylation patterns. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3710–3720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3710-3720.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orend G., Kuhlmann I., Doerfler W. Spreading of DNA methylation across integrated foreign (adenovirus type 12) genomes in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4301–4308. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4301-4308.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P., Barros C., Whittingham D. G. Preservation of hamster oocytes to assay the fertilizing capacity of human spermatozoa. J Reprod Fertil. 1982 Sep;66(1):161–168. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0660161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Szyf M., Kafri T., Roll M., Giloh H., Scarpa S., Carotti D., Cantoni G. L. Replacement of 5-methylcytosine by cytosine: a possible mechanism for transient DNA demethylation during differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2827–2831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik W., Collick A., Norris M. L., Barton S. C., Surani M. A. Genomic imprinting determines methylation of parental alleles in transgenic mice. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):248–251. doi: 10.1038/328248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., Peterson A. C., Rossant J., Balling R. Degree of methylation of transgenes is dependent on gamete of origin. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):251–254. doi: 10.1038/328251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter D., Doerfler W. Methylation of integrated adenovirus type 12 DNA sequences in transformed cells is inversely correlated with viral gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):253–256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter D., Doerfler W. Methylation of integrated viral DNA sequences in hamster cells transformed by adenovirus 12. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):565–568. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter D., Westphal M., Doerfler W. Patterns of integration of viral DNA sequences in the genomes of adenovirus type 12-transformed hamster cells. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):569–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90243-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain J. L., Stewart T. A., Leder P. Parental legacy determines methylation and expression of an autosomal transgene: a molecular mechanism for parental imprinting. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):719–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90330-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth M., Lichtenberg U., Doerfler W. Genomic sequencing reveals a 5-methylcytosine-free domain in active promoters and the spreading of preimposed methylation patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3728–3732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toth M., Müller U., Doerfler W. Establishment of de novo DNA methylation patterns. Transcription factor binding and deoxycytidine methylation at CpG and non-CpG sequences in an integrated adenovirus promoter. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 5;214(3):673–683. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90285-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardimon L., Kressmann A., Cedar H., Maechler M., Doerfler W. Expression of a cloned adenovirus gene is inhibited by in vitro methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1073–1077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisshaar B., Langner K. D., Jüttermann R., Müller U., Zock C., Klimkait T., Doerfler W. Reactivation of the methylation-inactivated late E2A promoter of adenovirus type 2 by E1A (13 S) functions. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 20;202(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90456-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham D. G. Culture of mouse ova. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1971 Jun;14:7–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]