Abstract
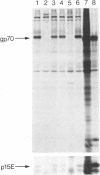
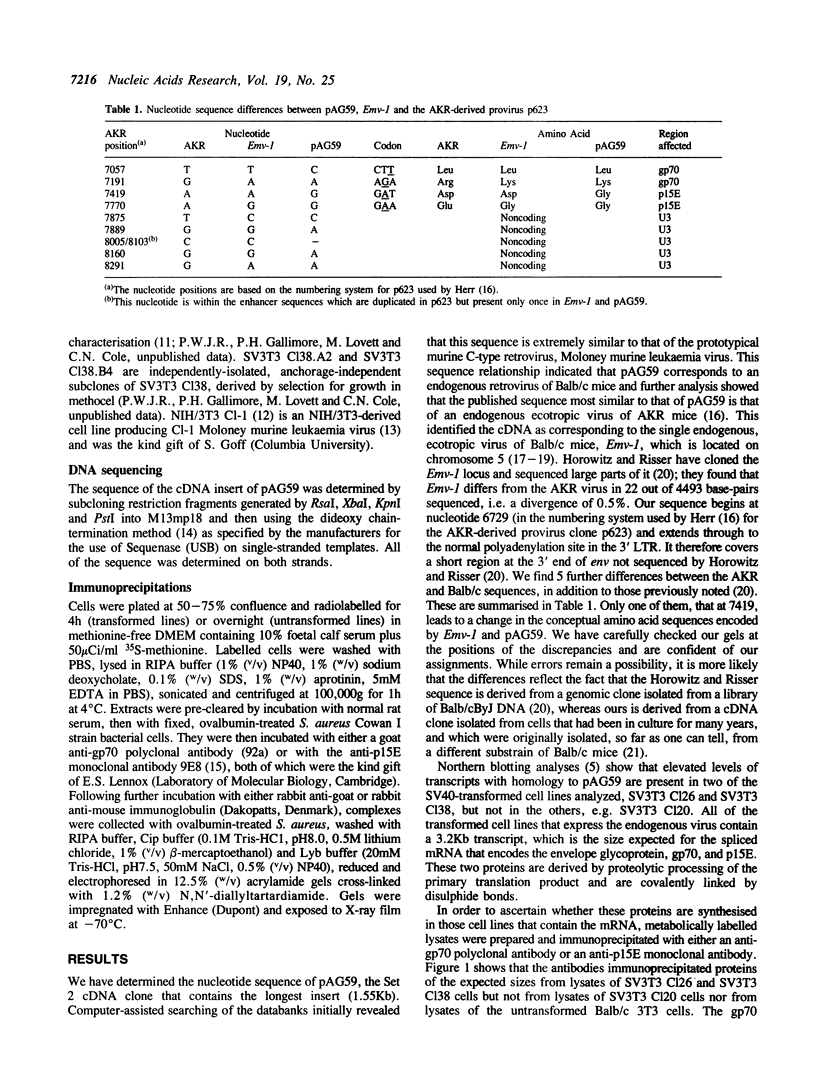
We have previously isolated a number of cDNA clones that correspond to mRNAs present at higher levels in SV40-transformed cells than in the untransformed parental cells (Scott, M.R.D., Westphal, K.-H. and Rigby, P.W.J. (1983) Cell 34, 557-567). We have now determined the nucleotide sequence of the archetypal Set 2 clone, pAG59, and can thus identify it as corresponding to the env gene of the endogenous, ecotropic C-type retrovirus of Balb/c mice, Emv-1. We have shown that in the subset of SV40-transformed cells that express the provirus both of the proteins encoded by env, gp70 and p15E, are synthesised and that the former is displayed on the cell surface. We discuss the significance of these observations for the biology of SV40 transformation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Development of 3T3-like lines from Balb-c mouse embryo cultures: transformation susceptibility to SV40. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Oct;72(2):141–148. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickell P. M., Latchman D. S., Murphy D., Willison K., Rigby P. W. Activation of a Qa/Tla class I major histocompatibility antigen gene is a general feature of oncogenesis in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):756–760. doi: 10.1038/306756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickell P. M., Latchman D. S., Murphy D., Willison K., Rigby P. W. The class I major histocompatibility antigen gene activated in a line of SV40-transformed mouse cells is H-2Dd, not Qa/Tla. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):162–163. doi: 10.1038/316162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapes S. K., Duffin D., Paulsen A. Q. Characterization of macrophage recognition and killing of SV40-transformed tumor cells that are "resistant" or "susceptible" to contact-mediated killing. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):589–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Paskind M. Measurement of the sequence complexity of cloned Moloney murine leukemia virus 60 to 70S RNA: evidence for a haploid genome. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):421–429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.421-429.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooding L. R., Taylor J. R., Laster S. M., Wehrly K., Chesebro B., Brickell P. M., Latchmann D. S., Rigby P. W. Evidence against expression of an endogenous murine leukemia virus causing cellular resistance to lysis by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):257–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Nucleotide sequence of AKV murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):471–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.471-478.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz J. M., Holland G. D., King S. R., Risser R. Germ line integration of a murine leukemia provirus into a retroviruslike sequence. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):701–707. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.701-707.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz J. M., Risser R. Molecular and biological characterization of the endogenous ecotropic provirus of BALB/c mice. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):798–806. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.798-806.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Joseph D. R., Domotor J. J., Jr Genetic linkage of C3H/HeJ and BALB/c endogenous ecotropic C-type viruses to phosphoglucomutase-1 on chromosome 5. Science. 1979 Apr 6;204(4388):71–73. doi: 10.1126/science.219476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S., Laigret F., Rodi C. P. Expression of mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia virus-related transcripts in AKR mice. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):876–882. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.876-882.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Rowe W. P. Genetic mapping of the ecotropic murine leukemia virus-inducing locus of BALB/c mouse to chromosome 5. Science. 1979 Apr 6;204(4388):69–71. doi: 10.1126/science.219475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg A. M., Khan A. S., Steinberg A. D. Multiple endogenous xenotropic and mink cell focus-forming murine leukemia virus-related transcripts are induced by polyclonal immune activators. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3545–3550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3545-3550.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mole S. E., Gannon J. V., Ford M. J., Lane D. P. Structure and function of SV40 large-T antigen. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1987 Dec 15;317(1187):455–469. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1987.0072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Chia W., Clayton C. E., Lovett M. The structure and expression of the integrated viral DNA in mouse cells transformed by simian virus 40. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Nov 19;210(1180):437–450. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg E., Donoghue D. J., Baltimore D. Analysis of a 5' leader sequence on murine leukemia virus 21S RNA: heteroduplex mapping with long reverse transcriptase products. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):435–451. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90318-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutzbank T., Robinson R., Oren M., Levine A. J. SV40 large tumor antigen can regulate some cellular transcripts in a positive fashion. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):481–490. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. R., Westphal K. H., Rigby P. W. Activation of mouse genes in transformed cells. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):557–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Carey M., Saragosti S., Botchan M. Expression of enhanced levels of small RNA polymerase III transcripts encoded by the B2 repeats in simian virus 40-transformed mouse cells. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):553–556. doi: 10.1038/314553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Saragosti S., Botchan M. Isolation of cellular genes differentially expressed in mouse NIH 3T3 cells and a simian virus 40-transformed derivative: growth-specific expression of VL30 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2590–2598. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. S., Turner S., Leong J. A., Rigby P. W. Effect of passage in culture on a clone of BALB/c 3T3 cells transformed by simian virus 40. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):146–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.146-153.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Stott D., Rigby P. W. Regulation of RNA polymerase III transcription in response to Simian virus 40 transformation. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3713–3721. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Hoffman R., Penman S. The extensive homology between mRNA sequences of normal and SV40-transformed human fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):901–907. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]