Abstract
Several neurological diseases which affect the corpus striatum are candidates for gene therapy. We have developed a defective Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV-1) vector system to introduce genes into postmitotic cells, such as neurons. The prototype vector, pHSVlac, contains a transcription unit which places the E. coli Lac Z gene under the control of the HSV-1 immediate early (IE) 4/5 promoter, a constitutive promoter. We now demonstrate that a HSV-1 vector can deliver a gene into striatal neurons. Infection of cultured rat striatal neurons with pHSVlac virus resulted in stable expression of beta-galactosidase for at least two weeks, without cell death. The potential to replace the Lac Z gene with other genes of interest, such as the gene responsible for Huntington's Disease, once it is isolated, may lead to insights about the pathogenesis of this genetic neurodegenerative disease, and may provide a method for performing gene therapy on this disease. Similarly, introduction of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene, which encodes the rate-limiting enzyme in the conversion of tyrosine to dopamine, into striatal neurons might provide a novel gene therapy approach towards treating Parkinson's Disease.
Full text
PDF

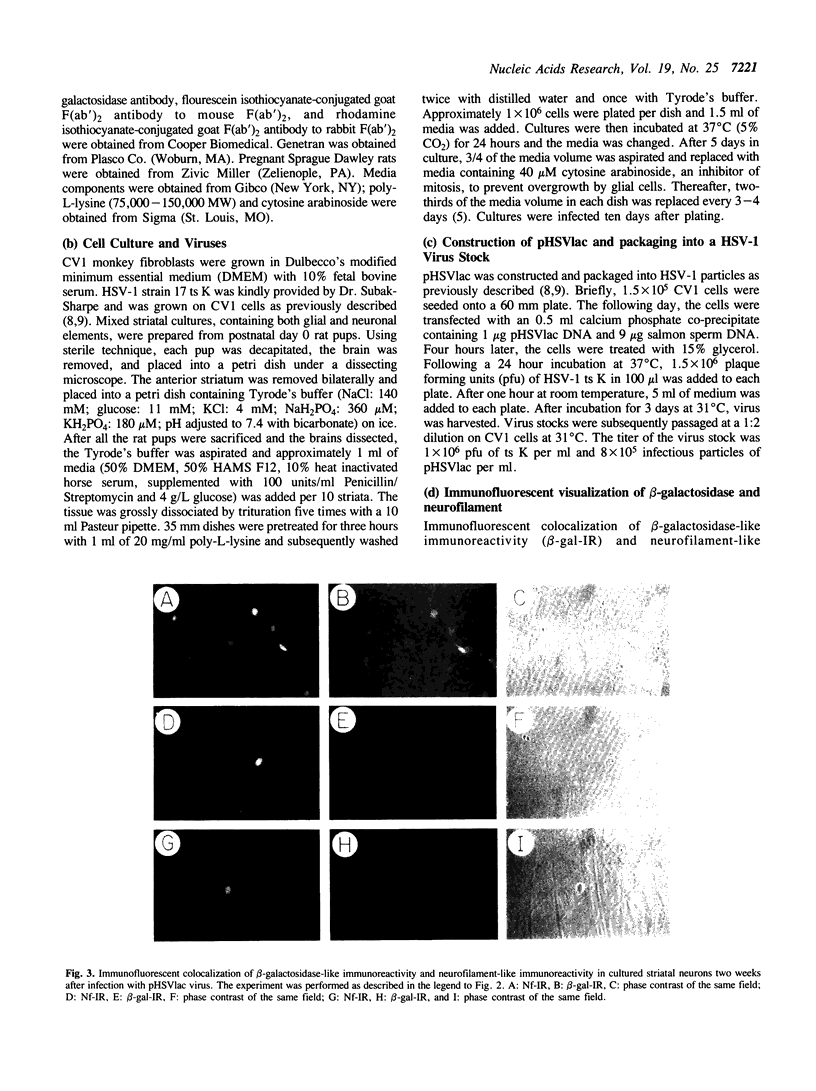


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird E. D. Chemical pathology of Huntington's disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:533–551. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohn M. C., Cupit L., Marciano F., Gash D. M. Adrenal medulla grafts enhance recovery of striatal dopaminergic fibers. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):913–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2887034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- During M. J., Freese A., Sabel B. A., Saltzman W. M., Deutch A., Roth R. H., Langer R. Controlled release of dopamine from a polymeric brain implant: in vivo characterization. Ann Neurol. 1989 Apr;25(4):351–356. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante R. J., Kowall N. W., Beal M. F., Richardson E. P., Jr, Bird E. D., Martin J. B. Selective sparing of a class of striatal neurons in Huntington's disease. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):561–563. doi: 10.1126/science.2931802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese A., DiFiglia M., Koroshetz W. J., Beal M. F., Martin J. B. Characterization and mechanism of glutamate neurotoxicity in primary striatal cultures. Brain Res. 1990 Jun 25;521(1-2):254–264. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91550-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese A., Geller A. I., Neve R. HSV-1 vector mediated neuronal gene delivery. Strategies for molecular neuroscience and neurology. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 15;40(10):2189–2199. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90711-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese A., Sabel B. A., Saltzman W. M., During M. J., Langer R. Controlled release of dopamine from a polymeric brain implant: in vitro characterization. Exp Neurol. 1989 Mar;103(3):234–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Breakefield X. O. A defective HSV-1 vector expresses Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase in cultured peripheral neurons. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1667–1669. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Freese A. Infection of cultured central nervous system neurons with a defective herpes simplex virus 1 vector results in stable expression of Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1149–1153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I. Influence of the helper virus on expression of beta-galactosidase from a defective HSV-1 vector, pHSVlac. J Virol Methods. 1991 Feb-Mar;31(2-3):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(91)90161-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Keyomarsi K., Bryan J., Pardee A. B. An efficient deletion mutant packaging system for defective herpes simplex virus vectors: potential applications to human gene therapy and neuronal physiology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8950–8954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Naylor S. L., Anderson M. A., Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Ottina K., Wallace M. R., Sakaguchi A. Y. A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington's disease. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):234–238. doi: 10.1038/306234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargraves R., Freed W. J. Chronic intrastriatal dopamine infusions in rats with unilateral lesions of the substantia nigra. Life Sci. 1987 Mar 9;40(10):959–966. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langston J. W., Ballard P., Tetrud J. W., Irwin I. Chronic Parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science. 1983 Feb 25;219(4587):979–980. doi: 10.1126/science.6823561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindvall O., Backlund E. O., Farde L., Sedvall G., Freedman R., Hoffer B., Nobin A., Seiger A., Olson L. Transplantation in Parkinson's disease: two cases of adrenal medullary grafts to the putamen. Ann Neurol. 1987 Oct;22(4):457–468. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley K. L., Anhalt M. J., Martin B. M., Kelsoe J. R., Winfield S. L., Ginns E. I. Isolation and characterization of the human tyrosine hydroxylase gene: identification of 5' alternative splice sites responsible for multiple mRNAs. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):6910–6914. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossor M. N., Watkins J., Brown M. J., Reid J. L., Dollery C. T. Plasma levodopa, dopamine and therapeutic response following levodopa therapy of Parkinsonian patients. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Jun;46(3):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahr M. D., Duvoisin R. C., Schear M. J., Barrett R. E., Hoehn M. M. Treatment of parkinsonism with levodopa. Arch Neurol. 1969 Oct;21(4):343–354. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480160015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]