Abstract
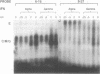
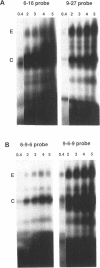
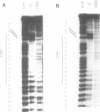
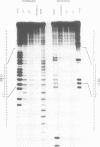
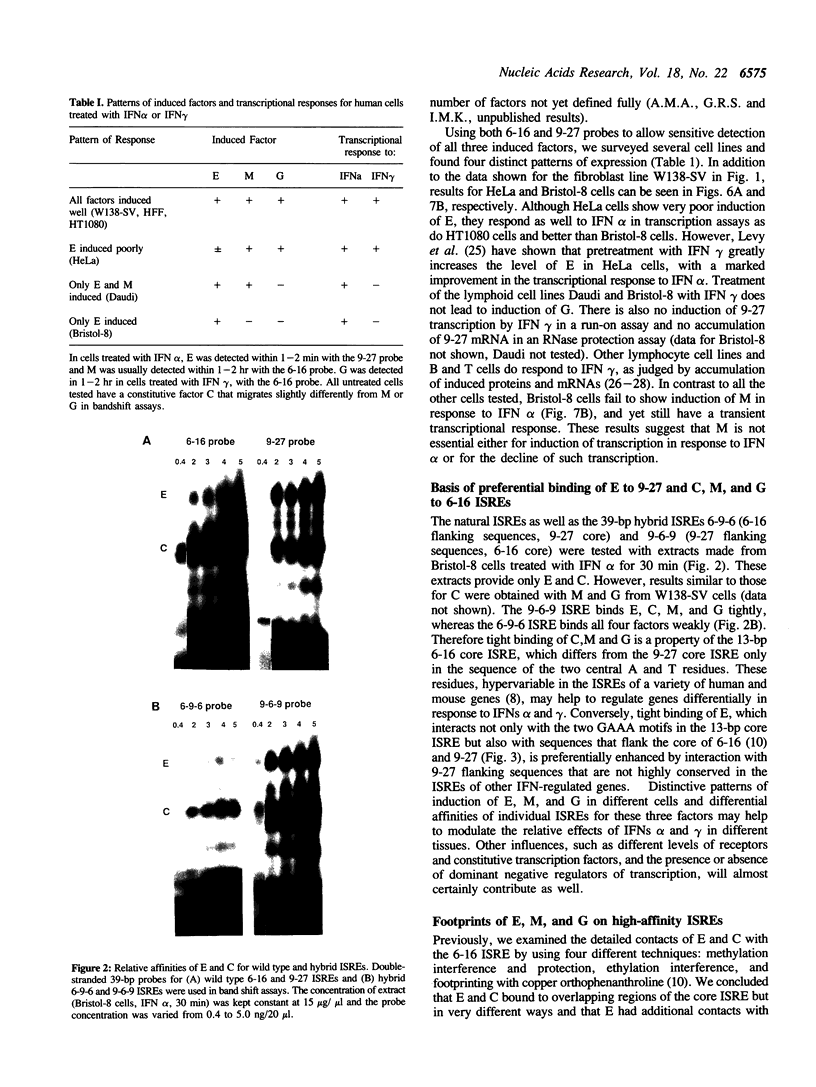
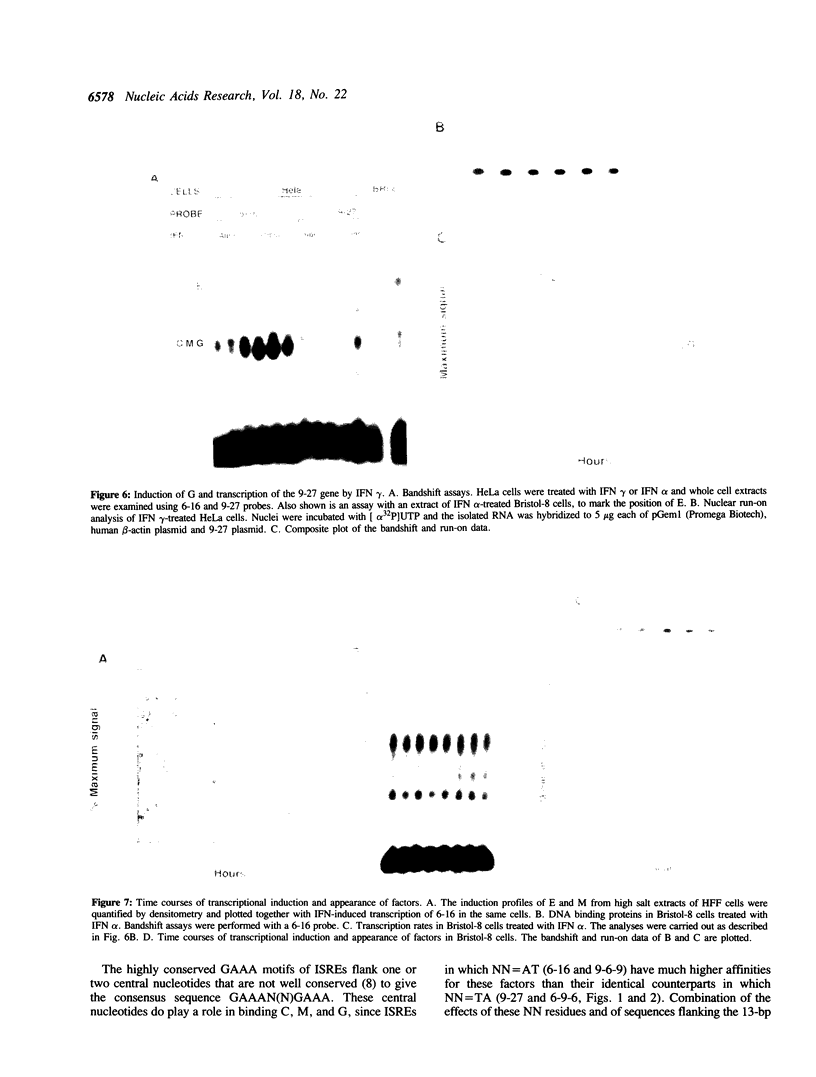
Factors induced by interferons (IFNs) bind to the IFN-stimulated response elements (ISREs) of many genes. In human cells treated with type I (alpha, beta) IFN, factor E is induced in about 1 min and factor M after about 1 hr. Factor G is induced after about 1 hr in cells treated with type II (gamma) IFN. G and M have very similar positions in bandshift assays, sensitivities to cycloheximide, footprints on an ISRE and relative affinities for different ISREs. Four different patterns of expression were observed in different cell lines: E,M and G strongly induced; M and G strongly but E weakly; only E and M induced; only E induced. Transcription in response to IFN alpha is initiated by E and probably maintained by M since, in fibroblasts, M is present maximally when transcription is most active and declines together with transcription. In Bristol-8 cells, where induction of M is not detected, transcription is still induced by IFN alpha and still declines in its continued presence, suggesting that M is not essential for either process. A variant ISRE with two G-to-C mutations binds E especially weakly but M and G strongly. The mutations don't change the response of a reporter gene to IFN gamma but do abolish its response to IFN alpha, suggesting that the binding of M is not sufficient for the latter. G probably acts positively, since its appearance correlates well with induction of transcription by IFN gamma. A 39-bp ISRE from the 9-27 gene binds E much better than M or G. Conversely, a 39-bp ISRE from the 6-16 gene binds M and G much better than E. Different patterns of expression of E, M, and G and different affinities of these factors for alternative ISREs may play a part in modulating the relative responses of genes to type I and type II IFNs in vivo.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M., Dembić Z., Merlin G. Molecular cloning and expression of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen G., Fantes K. H., Burke D. C., Morser J. Analysis and purification of human lymphoblastoid (Namalwa) interferon using a monoclonal antibody. J Gen Virol. 1982 Nov;63(Pt 1):207–212. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-1-207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Specific binding of 125I-human interferon-gamma to high affinity receptors on human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11301–11304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basta P. V., Sherman P. A., Ting J. P. Detailed delineation of an interferon-gamma-responsive element important in human HLA-DRA gene expression in a glioblastoma multiform line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8618–8622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Flavell R. A., Sharp P. A. A gamma-interferon-induced factor that binds the interferon response sequence of the MHC class I gene, H-2Kb. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1139–1144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanar M. A., Boettger E. C., Flavell R. A. Transcriptional activation of HLA-DR alpha by interferon gamma requires a trans-acting protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4672–4676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Parham P., Barnstable C. J., Crumpton M. J., Bodmer W. F. Monoclonal antibodies for analysis of the HLA system. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:3–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebath J., Merlin G., Metz R., Benech P., Revel M. Interferon-induced 56,000 Mr protein and its mRNA in human cells: molecular cloning and partial sequence of the cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1213–1226. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Imam A. M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Rapid activation by interferon alpha of a latent DNA-binding protein present in the cytoplasm of untreated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1203–1207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale T. C., Rosen J. M., Guille M. J., Lewin A. R., Porter A. G., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Overlapping sites for constitutive and induced DNA binding factors involved in interferon-stimulated transcription. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):831–839. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Cheng Y. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Interactions of alpha- and gamma-interferon in the transcriptional regulation of the gene encoding a guanylate-binding protein. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2009–2014. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finn P. W., Kara C. J., Douhan J., 3rd, Van T. T., Folsom V., Glimcher L. H. Interferon gamma regulates binding of two nuclear protein complexes in a macrophage cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):914–918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Manly S. P., McMahon M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of interferon-induced gene expression in human cells. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):745–755. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Fujita T., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Furia A., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Structurally similar but functionally distinct factors, IRF-1 and IRF-2, bind to the same regulatory elements of IFN and IFN-inducible genes. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. M., Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Characterization of a human gene inducible by alpha- and beta-interferons and its expression in mouse cells. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1601–1606. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Two interferon-induced nuclear factors bind a single promoter element in interferon-stimulated genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8521–8525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klock G., Strähle U., Schütz G. Oestrogen and glucocorticoid responsive elements are closely related but distinct. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):734–736. doi: 10.1038/329734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner A. C., Chaudhuri A., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional induction by interferon. New protein(s) determine the extent and length of the induction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):453–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecchi M., Lovisone E., Genetta C., Peruccio D., Resegotti L., Richiardi P. Gamma-IFN induces a differential expression of HLA-DR, DQ and DP antigens on peripheral blood myeloid leukemic blasts at various stages of differentiation. Leuk Res. 1989;13(3):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(89)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1362–1371. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Lew D. J., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Synergistic interaction between interferon-alpha and interferon-gamma through induced synthesis of one subunit of the transcription factor ISGF3. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1105–1111. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A., Huq A., Shan B. Beta and gamma interferons act synergistically to produce an antiviral state in cells resistant to both interferons individually. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4569–4578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4569-4578.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Harada H., Sudo Y., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen K. E., Bandu M. T. Kinetic evidence for an activation step following binding of human interferon alpha 2 to the membrane receptors of Daudi cells. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 1;134(2):355–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini S., John J., Shearer M., Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Use of a selectable marker regulated by alpha interferon to obtain mutations in the signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4605–4612. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine R., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Purification and cloning of interferon-stimulated gene factor 2 (ISGF2): ISGF2 (IRF-1) can bind to the promoters of both beta interferon- and interferon-stimulated genes but is not a primary transcriptional activator of either. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2448–2457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Darnell J. E., Jr Differential binding of interferon-induced factors to an oligonucleotide that mediates transcriptional activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3415–3424. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid L. E., Brasnett A. H., Gilbert C. S., Porter A. C., Gewert D. R., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. A single DNA response element can confer inducibility by both alpha- and gamma-interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):840–844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F., Hatat D., Abadie A., Wallach D., Revel M., Fellous M. Differential regulation of HLA-DR mRNAs and cell surface antigens by interferon. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1585–1589. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford M. N., Hannigan G. E., Williams B. R. Interferon-induced binding of nuclear factors to promoter elements of the 2-5A synthetase gene. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):751–759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02872.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman R. H., Watling D., Balkwill F. R., Trowsdale J., Kerr I. M. The ppp(A2'p)nA and protein kinase systems in wild-type and interferon-resistant Daudi cells. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(2):333–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06783.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Clark-Lewis I., McKimm-Breschkin L., Harris A. W., Schrader J. W. Interferon-gamma induces enhanced expression of Ia and H-2 antigens on B lymphoid, macrophage, and myeloid cell lines. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu-Lee L. Y., Hrachovy J. A., Stevens A. M., Schwarz L. A. Interferon-regulatory factor 1 is an immediate-early gene under transcriptional regulation by prolactin in Nb2 T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3087–3094. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimarino V., Wu C. Induction of sequence-specific binding of Drosophila heat shock activator protein without protein synthesis. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):727–730. doi: 10.1038/327727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Arnheiter H. Studies of the interferon receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 1984;24(2):259–278. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(84)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]