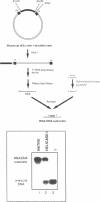
Abstract
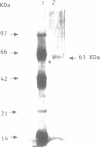
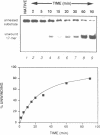
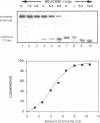
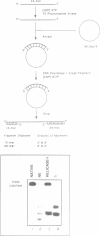
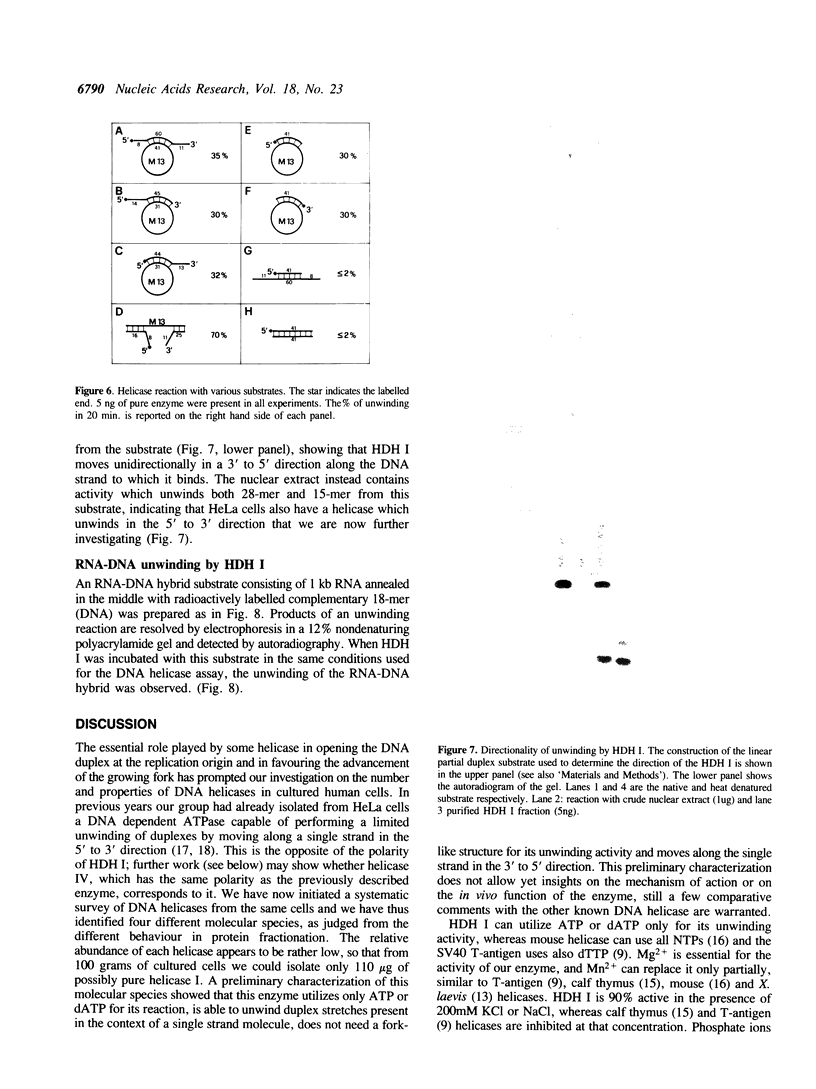
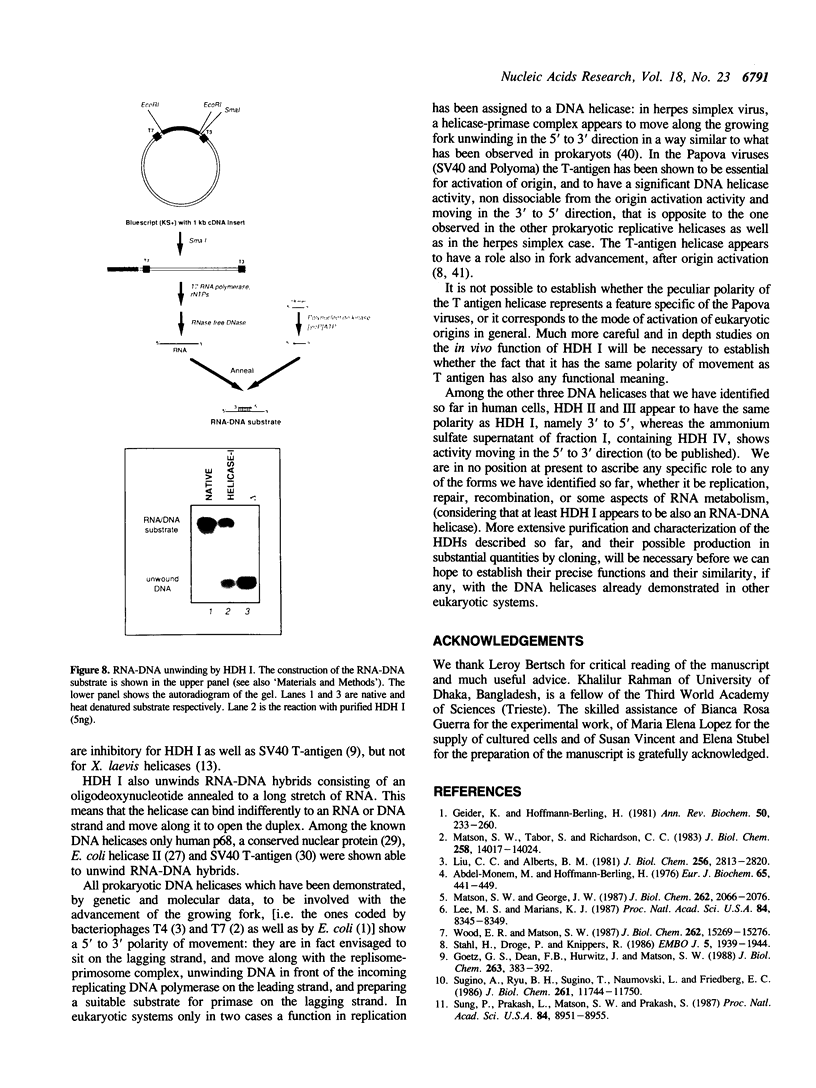
We have initiated the characterization of the DNA helicases from HeLa cells, and we have observed at least 4 molecular species as judged by their different fractionation properties. One of these only, DNA helicase I, has been purified to homogeneity and characterized. Helicase activity was measured by assaying the unwinding of a radioactively labelled oligodeoxynucleotide (17 mer) annealed to M13 DNA. The apparent molecular weight of helicase I on SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is 65 kDa. Helicase I reaction requires a divalent cation for activity (Mg2+ greater than Mn2+ greater than Ca2+) and is dependent on hydrolysis of ATP or dATP. CTP, GTP, UTP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP, ADP, AMP and non-hydrolyzable ATP analogues such as ATP gamma S are unable to sustain helicase activity. The helicase activity has an optimal pH range between pH8.0 to pH9.0, is stimulated by KCl or NaCl up to 200mM, is inhibited by potassium phosphate (100mM) and by EDTA (5mM), and is abolished by trypsin. The unwinding is also inhibited competitively by the coaddition of single stranded DNA. The purified fraction was free of DNA topoisomerase, DNA ligase and nuclease activities. The direction of unwinding reaction is 3' to 5' with respect to the strand of DNA on which the enzyme is bound. The enzyme also catalyses the ATP-dependent unwinding of a DNA:RNA hybrid consisting of a radioactively labelled single stranded oligodeoxynucleotide (18 mer) annealed on a longer RNA strand. The enzyme does not require a single stranded DNA tail on the displaced strand at the border of duplex regions; i.e. a replication fork-like structure is not required to perform DNA unwinding. The purification of the other helicases is in progress.
Full text
PDF

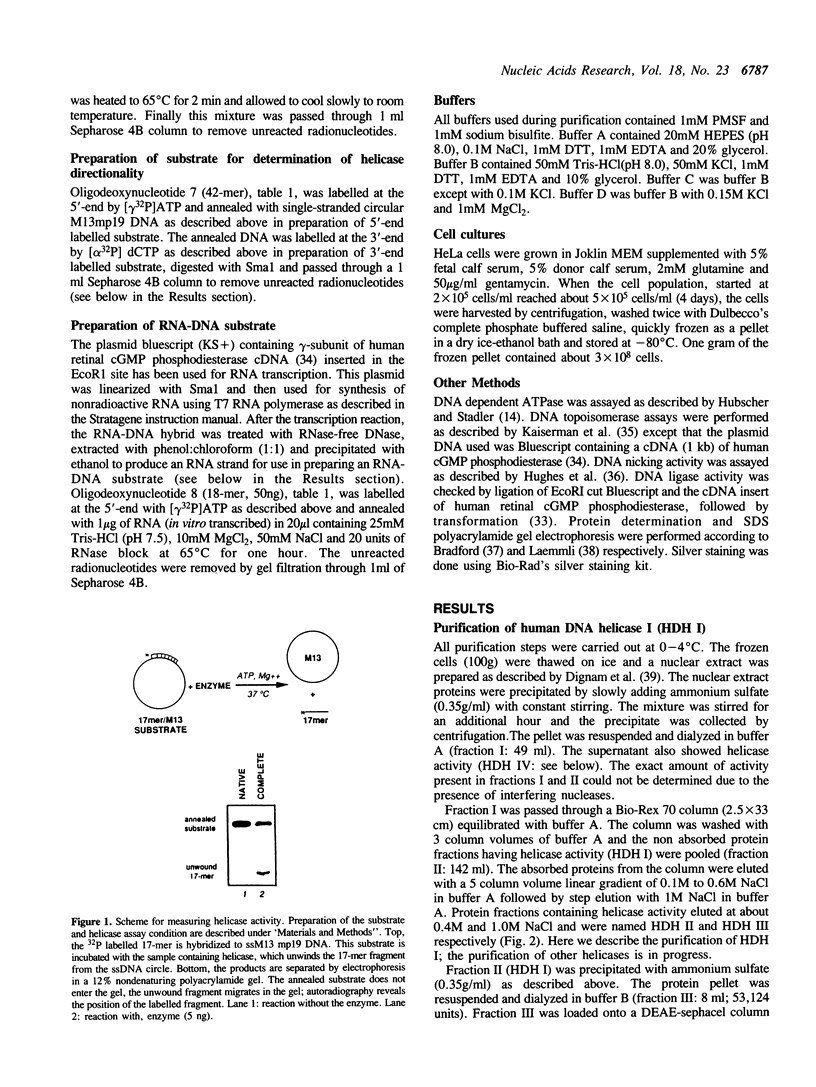
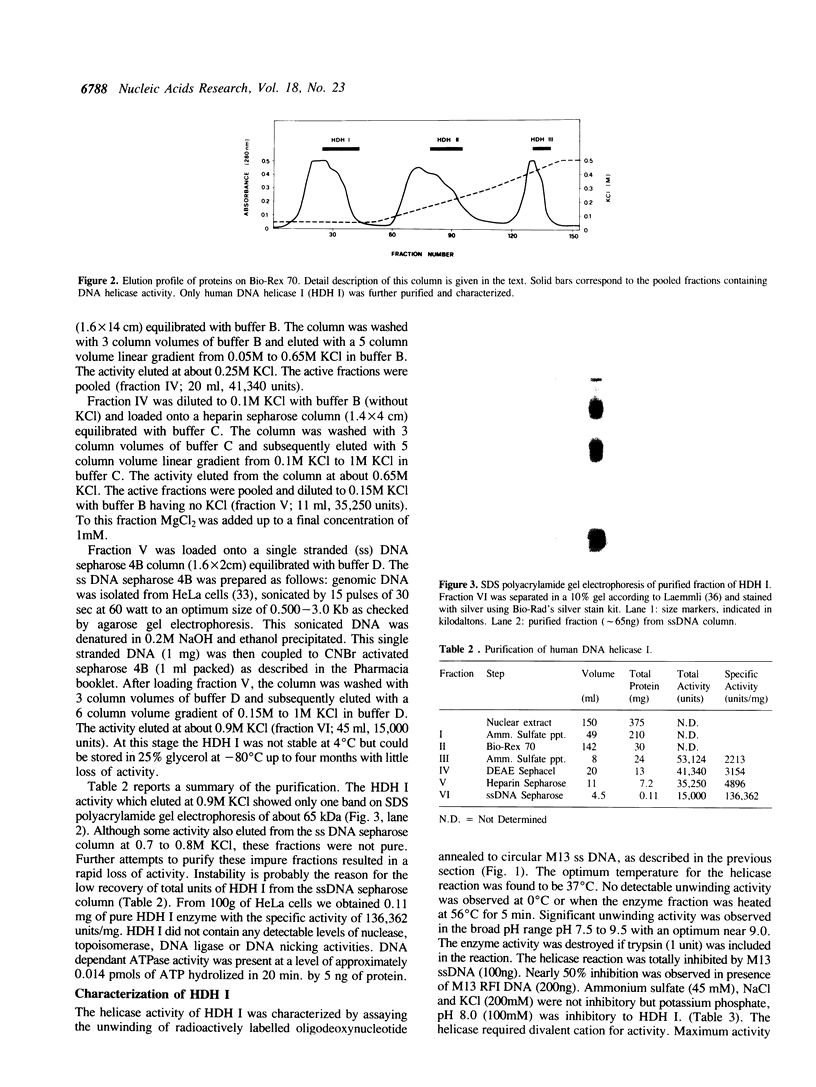
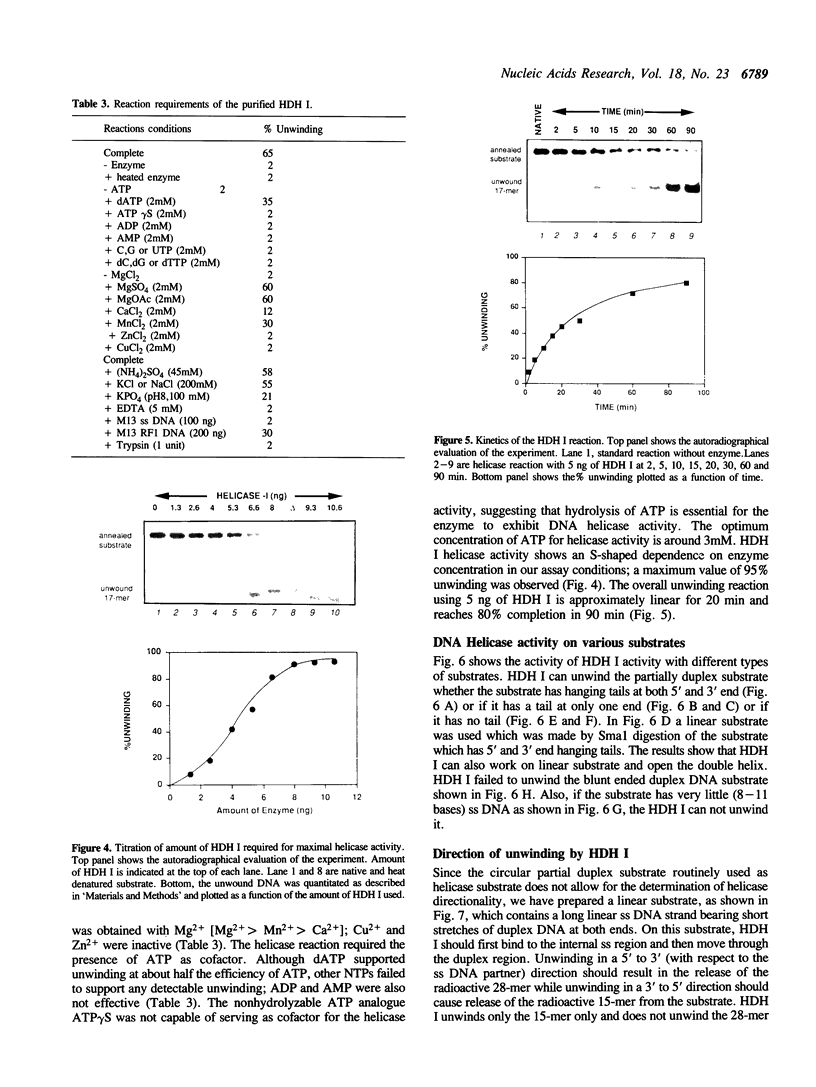

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Monem M., Dürwald H., Hoffmann-Berling H. Enzymic unwinding of DNA. 2. Chain separation by an ATP-dependent DNA unwinding enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 1;65(2):441–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Monem M., Taucher-Scholz G., Klinkert M. Q. Identification of Escherichia coli DNA helicase I as the traI gene product of the F sex factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4659–4663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan C. A., Dombroski A. J., Platt T. Transcription termination factor rho is an RNA-DNA helicase. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):945–952. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90703-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., Biamonti G., Mastromei G., Falaschi A., Riva S. A DNA dependent ATPase from HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):402–409. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90651-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., Riva S., Mastromei G., Spadari S., Pedrali-Noy G., Falaschi A. Enhancement of the rate of DNA polymerase-alpha activity on duplex DNA by a DNA-binding protein and a DNA-dependent ATPase of mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):639–647. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. M., Lehman I. R. Enzymes of general recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:229–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Tsurumi T., Zhu L. A., Weller S. K., Olivo P. D., Challberg M. D., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex virus 1 helicase-primase: a complex of three herpes-encoded gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2186–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geider K., Hoffmann-Berling H. Proteins controlling the helical structure of DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:233–260. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz G. S., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J., Matson S. W. The unwinding of duplex regions in DNA by the simian virus 40 large tumor antigen-associated DNA helicase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):383–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirling H., Scheffner M., Restle T., Stahl H. RNA helicase activity associated with the human p68 protein. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):562–564. doi: 10.1038/339562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgman T. C. A new superfamily of replicative proteins. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):22–23. doi: 10.1038/333022b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta Y., Stern H. DNA unwinding protein from meiotic cells of Lilium. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1872–1880. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M. J., Liang H. M., Jiricny J., Jost J. P. Purification and characterization of a protein from HeLa cells that binds with high affinity to the estrogen response element, GGTCAGCGTGACC. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):9137–9142. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Van Houten B., Thomas D. C., Abdel-Monem M., Sancar A. Effect of DNA polymerase I and DNA helicase II on the turnover rate of UvrABC excision nuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6774–6778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U., Stalder H. P. Mammalian DNA helicase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5471–5483. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiserman H. B., Ingebritsen T. S., Benbow R. M. Regulation of Xenopus laevis DNA topoisomerase I activity by phosphorylation in vitro. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3216–3222. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., McMacken R. The Escherichia coli dnaB replication protein is a DNA helicase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4738–4748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Marians K. J. Escherichia coli replication factor Y, a component of the primosome, can act as a DNA helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8345–8349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Lasko P. F., Ashburner M., Leroy P., Nielsen P. J., Nishi K., Schnier J., Slonimski P. P. Birth of the D-E-A-D box. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):121–122. doi: 10.1038/337121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Alberts B. M. Characterization of the DNA-dependent GTPase activity of T4 gene 41 protein, an essential component of the T4 bacteriophage DNA replication apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2813–2820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. L., Welsh K., Clark S., Su S. S., Modrich P. Repair of DNA base-pair mismatches in extracts of Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:589–596. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W. Escherichia coli DNA helicase II (uvrD gene product) catalyzes the unwinding of DNA.RNA hybrids in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4430–4434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., George J. W. DNA helicase II of Escherichia coli. Characterization of the single-stranded DNA-dependent NTPase and helicase activities. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2066–2076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., Tabor S., Richardson C. C. The gene 4 protein of bacteriophage T7. Characterization of helicase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14017–14024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poll E. H., Benbow R. M. A DNA helicase from Xenopus laevis ovaries. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8701–8706. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Lawson T. G., Kramer J. C., Cladaras M. H., Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. ATP-dependent unwinding of messenger RNA structure by eukaryotic initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7651–7658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Knippers R., Stahl H. RNA unwinding activity of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):955–963. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90334-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. F., Kornberg A. Purification of the rep protein of Escherichia coli. An ATPase which separates duplex DNA strands in advance of replication. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3292–3297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki M., Enomoto T., Hanaoka F., Yamada M. DNA-dependent adenosinetriphosphatase B from mouse FM3A cells has DNA helicase activity. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2924–2928. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Knippers R. The simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 9;910(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90088-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Ryu B. H., Sugino T., Naumovski L., Friedberg E. C. A new DNA-dependent ATPase which stimulates yeast DNA polymerase I and has DNA-unwinding activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11744–11750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Prakash L., Matson S. W., Prakash S. RAD3 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a DNA helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8951–8955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuteja N., Danciger M., Klisak I., Tuteja R., Inana G., Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Farber D. B. Isolation and characterization of cDNA encoding the gamma-subunit of cGMP phosphodiesterase in human retina. Gene. 1990 Apr 16;88(2):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90035-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood E. R., Matson S. W. Purification and characterization of a new DNA-dependent ATPase with helicase activity from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15269–15276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]