Abstract
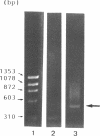
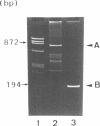
We developed a simple and sensitive method for assigning transcriptional initiation sites, and applied it to characterize the transcriptional unit of rat group II phospholipase A2 (PLA2) gene. Our method involves the primer extension reaction followed by detection of its products by hybridization. Using this method, we were able to map two transcriptional initiation sites on the nucleotide sequence of the core promoter region of PLA2 gene with one-base resolution without any difficulties.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calzone F. J., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Mapping of gene transcripts by nuclease protection assays and cDNA primer extension. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:611–632. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamley-Campbell J., Campbell G. R., Ross R. The smooth muscle cell in culture. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jan;59(1):1–61. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Kudo I., Tomita M., Inoue K. Purification and characterization of extracellular phospholipase A2 from peritoneal cavity of caseinate-treated rat. J Biochem. 1987 Jul;102(1):147–154. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Kieffer-Higgins S. Multiplex DNA sequencing. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):185–188. doi: 10.1126/science.3353714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. L., Hunsaker W. R. Improved hybridization assays employing tailed oligonucleotide probes: a direct comparison with 5'-end-labeled oligonucleotide probes and nick-translated plasmid probes. Anal Biochem. 1985 Dec;151(2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder P. K., Schmidt L. J., Ono T., Getz M. J. Specific stimulation of actin gene transcription by epidermal growth factor and cycloheximide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7476–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forst S., Weiss J., Elsbach P., Maraganore J. M., Reardon I., Heinrikson R. L. Structural and functional properties of a phospholipase A2 purified from an inflammatory exudate. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 30;25(26):8381–8385. doi: 10.1021/bi00374a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Hermanowski A. L., Ziff E. B. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growth factor activation of c-fos, c-myc, and actin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara S., Kudo I., Matsuta K., Miyamoto T., Inoue K. Amino acid composition and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of human phospholipase A2 purified from rheumatoid synovial fluid. J Biochem. 1988 Sep;104(3):326–328. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrin D. L., Schmidt G. W. Rapid, reversible staining of northern blots prior to hybridization. Biotechniques. 1988 Mar;6(3):196-7, 199-200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B. G., Frischauf A. M. Isolation of genomic DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:180–183. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaki J., Ohara O., Nakamura E., Tamaki M., Ono T., Kanda A., Yoshida N., Teraoka H., Tojo H., Okamoto M. cDNA cloning and sequence determination of rat membrane-associated phospholipase A2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1030–1036. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90777-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komada M., Kudo I., Inoue K. Structure of gene coding for rat group II phospholipase A2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):1059–1065. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91137-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Hession C., Johansen B., Hayes G., McGray P., Chow E. P., Tizard R., Pepinsky R. B. Structure and properties of a human non-pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5768–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Wold B. In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):780–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2814500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Märki F., Franson R. Endogenous suppression of neutral-active and calcium-dependent phospholipase A2 in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 14;879(2):149–156. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90097-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Ohara O., Teraoka H., Arita H. Glucocorticoids suppress group II phospholipase A2 production by blocking mRNA synthesis and post-transcriptional expression. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12745–12748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Ohara O., Teraoka H., Arita H. Group II phospholipase A2 mRNA synthesis is stimulated by two distinct mechanisms in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 12;261(1):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80663-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara O., Dorit R. L., Gilbert W. Direct genomic sequencing of bacterial DNA: the pyruvate kinase I gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6883–6887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara O., Tamaki M., Nakamura E., Tsuruta Y., Fujii Y., Shin M., Teraoka H., Okamoto M. Dog and rat pancreatic phospholipases A2: complete amino acid sequences deduced from complementary DNAs. J Biochem. 1986 Mar;99(3):733–739. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono T., Tojo H., Kuramitsu S., Kagamiyama H., Okamoto M. Purification and characterization of a membrane-associated phospholipase A2 from rat spleen. Its comparison with a cytosolic phospholipase A2 S-1. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5732–5738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Vadas P., Fornasier V. Inflammatory effect of intradermal administration of soluble phospholipase A2 in rabbits. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Apr;86(4):380–383. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12285639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata T., Nakamura E., Tsuruta Y., Tamaki M., Teraoka H., Tojo H., Ono T., Okamoto M. Presence of pancreatic-type phospholipase A2 mRNA in rat gastric mucosa and lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 23;1007(1):124–126. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Pruzanski W., Vadas P., Plant S., Miller J. A., Kloss J., Johnson L. K. Cloning and recombinant expression of phospholipase A2 present in rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5335–5338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Randall T. L., Yamanaka M., Johnson L. K. Pancreatic phospholipase A2: isolation of the human gene and cDNAs from porcine pancreas and human lung. DNA. 1986 Dec;5(6):519–527. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1986.5.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam M., Schmidt L. J., Crutchfield C. E., 3rd, Getz M. J. Negative regulation of serum-responsive enhancer elements. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):64–66. doi: 10.1038/340064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vishwanath B. S., Fawzy A. A., Franson R. C. Edema-inducing activity of phospholipase A2 purified from human synovial fluid and inhibition by aristolochic acid. Inflammation. 1988 Dec;12(6):549–561. doi: 10.1007/BF00914317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Meinkoth J. L., Kimmel A. R. Northern and Southern blots. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:572–581. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]