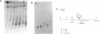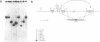Abstract
The locus responsible for the most common form of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (PKD1) is located on chromosome 16p13.3. Genetic mapping studies indicate that PKD1 is flanked on the proximal side by the DNA marker 26.6 (D16S125). Here we show that 26.6 has undergone a locus duplication and that the two loci are less than 150kb apart. One of the two loci contains a polymorphic TaqI site that has been used in genetic studies and represents the proximal boundary for the PKD1 locus. We demonstrate that the polymorphic locus is the more proximal of the two 26.6-hybridizing loci. Therefore, four cosmids isolated from the distal 26.6-hybridizing locus contain candidate sequences for the PKD1 gene. These cosmids were found to contain two CpG islands that are likely markers for transcribed regions. A third CpG island was detected and cloned by directional chromosome jumping.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuning M. H., Snijdewint F. G., Smits J. R., Dauwerse J. G., Saris J. J., van Ommen G. J. A TaqI polymorphism identified by 26-6 (D16S125) proximal to the locus affecting adult polycystic kidney disease (PKD1) on chromosome 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3106–3106. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3106-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chorney M. J., Sawada I., Gillespie G. A., Srivastava R., Pan J., Weissman S. M. Transcription analysis, physical mapping, and molecular characterization of a nonclassical human leukocyte antigen class I gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):243–253. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Drumm M. L., Cole J. L., Lockwood W. K., Vande Woude G. F., Iannuzzi M. C. Construction of a general human chromosome jumping library, with application to cystic fibrosis. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2950591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiLella A. G., Woo S. L. Cloning large segments of genomic DNA using cosmid vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:199–212. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. A., Wahl G. M. Cosmid vectors for genomic walking and rapid restriction mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:604–610. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germino G. G., Barton N. J., Lamb J., Higgs D. R., Harris P., Xiao G. H., Scherer G., Nakamura Y., Reeders S. T. Identification of a locus which shows no genetic recombination with the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease gene on chromosome 16. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 May;46(5):925–933. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberling W. J., Fain P. R., Kenyon J. B., Goldgar D., Sujansky E., Gabow P. A. Linkage heterogeneity of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 1988 Oct 6;319(14):913–918. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198810063191405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poustka A., Pohl T. M., Barlow D. P., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. Construction and use of human chromosome jumping libraries from NotI-digested DNA. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):353–355. doi: 10.1038/325353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeders S. T., Breuning M. H., Davies K. E., Nicholls R. D., Jarman A. P., Higgs D. R., Pearson P. L., Weatherall D. J. A highly polymorphic DNA marker linked to adult polycystic kidney disease on chromosome 16. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):542–544. doi: 10.1038/317542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Lawrance S. K., Gillespie G. A., Cantor C. R., Weissman S. M., Collins F. S. Strategies for mapping and cloning macroregions of mammalian genomes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;151:461–489. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)51038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]