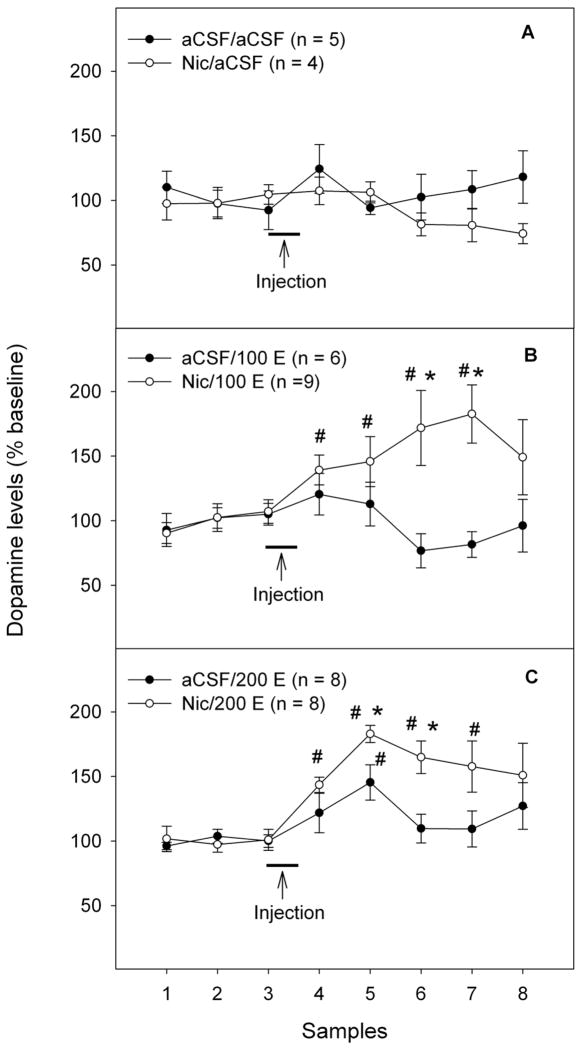
Figure 2.
Effects of challenge injections of ethanol (0, 100 or 200 mg%) into the posterior ventral tegmental area (pVTA) on extracellular dopamine levels in the nucleus accumbens shell following repeated exposure of the pVTA to either aCSF or nicotine (100 μM). ‘aCSF/aCSF’: group pretreated with aCSF and challenged with aCSF; ‘Nic/aCSF’: group pretreated with 100 μM nicotine and challenged with aCSF; ‘aCSF/100 E’: group pretreated with aCSF and challenged with 100 mg% ethanol; ‘Nic/100 E’: group pretreated with 100 μM nicotine and challenged with 100 mg% ethanol; ‘aCSF/200 E’: group pretreated with aCSF and challenged with 200 mg% ethanol; ‘Nic/200 E’: group pretreated with 100 μM nicotine and challenged with 200 mg% ethanol. * p < 0.05, significantly greater than levels in the corresponding aCSF-treated group. # p < 0.05, significantly greater than baseline levels.