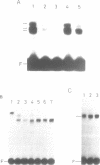
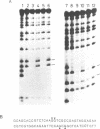
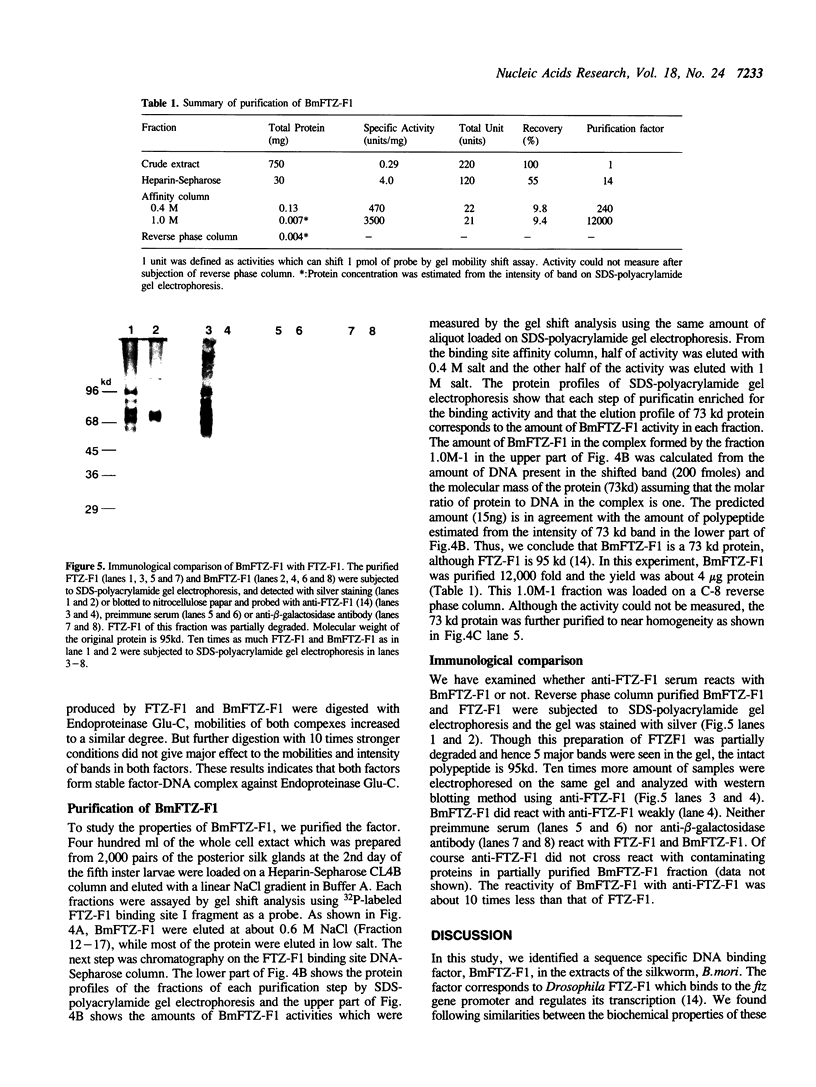
Abstract
Extracts from embryos and from posterior and middle silk glands of the silkworm, Bombyx mori contain a sequence specific DNA binding factor termed BmFTZ-F1. The factor binds to the recognition site of FTZ-F1, a positive regulator of the fushi tarazu gene in Drosophila melanogaster. BmFTZ-F1 and FTZ-F1 share the same methylation interference patterns, the same chromatographic behaviors and similar protease digestion profiles. Anti-FTZ-F1 cross reacts with BmFTZ-F1. These results indicate that BmFTZ-F1 is a B. mori homologue of FTZ-F1. The mobility of the factor-DNA complex formed in the silk gland extract changes depending on the developmental stages. Purification of BmFTZF1 to an almost homogeneous state reveals that the factor is a 73 kd protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akam M. The molecular basis for metameric pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 1987 Sep;101(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blochlinger K., Bodmer R., Jack J., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Primary structure and expression of a product from cut, a locus involved in specifying sensory organ identity in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):629–635. doi: 10.1038/333629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. B., Scott M. P. Localization of the fushi tarazu protein during Drosophila embryogenesis. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Weir M., Coulson A., Sulston J., Kenyon C. Posterior pattern formation in C. elegans involves position-specific expression of a gene containing a homeobox. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):747–756. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90131-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe C. Q., Hiromi Y., Gehring W. J., Goodman C. S. Expression and function of the segmentation gene fushi tarazu during Drosophila neurogenesis. Science. 1988 Jan 8;239(4836):170–175. doi: 10.1126/science.2892267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney M., Ruvkun G., Horvitz H. R. The C. elegans cell lineage and differentiation gene unc-86 encodes a protein with a homeodomain and extended similarity to transcription factors. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):757–769. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham P. W. The molecular genetics of embryonic pattern formation in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):25–34. doi: 10.1038/335025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo K., Aoshima Y., Hagiwara T., Ueda H., Mizuno S. Tissue-specific and periodic changes in the nuclease sensitivity of the fibroin gene chromatin in the silkworm Bombyx mori. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5271–5279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause H. M., Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Expression, modification, and localization of the fushi tarazu protein in Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):1021–1036. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Buskin J. N., Lockshon D., Davis R. L., Apone S., Hauschka S. D., Weintraub H. MyoD is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein requiring a region of myc homology to bind to the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):823–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa H., Suzuki Y. Repeated turn-off and turn-on of fibroin gene transcription during silk gland development of Bombyx mori. Dev Biol. 1980 Aug;78(2):394–406. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90343-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno K., Suzuki T., Takiya S., Suzuki Y. Complex formation with the fibroin gene enhancer through a protein-protein interaction analyzed by a modified DNA-binding assay. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4599–4604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara T., Suzuki Y. Temporal and spatial control of silk gene transcription analyzed by nuclear run-on assays. Dev Biol. 1988 Jun;127(2):384–391. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saint R., Kalionis B., Lockett T. J., Elizur A. Pattern formation in the developing eye of Drosophila melanogaster is regulated by the homoeo-box gene, rough. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):151–154. doi: 10.1038/334151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Carroll S. B. The segmentation and homeotic gene network in early Drosophila development. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):689–698. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Suzuki Y. Interaction of composite protein complex with the fibroin enhancer sequence. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5979–5986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Giza P. E. Accentuated expression of silk fibroin genes in vivo and in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov 5;107(3):183–206. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Tsuda M., Takiya S., Hirose S., Suzuki E., Kameda M., Ninaki O. Tissue-specific transcription enhancement of the fibroin gene characterized by cell-free systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9522–9526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takiya S., Suzuki Y. Factors involved in preferential transcription of the fibroin gene. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Suzuki Y. Faithful transcription initiation of fibroin gene in a homologous cell-free system reveals an enhancing effect of 5' flanking sequence far upstream. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90371-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakimoto B. T., Kaufman T. C. Analysis of larval segmentation in lethal genotypes associated with the antennapedia gene complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1981 Jan 15;81(1):51–64. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90347-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. C., Chalfie M. mec-3, a homeobox-containing gene that specifies differentiation of the touch receptor neurons in C. elegans. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):5–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90174-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wilson S., Walker B., Dawid I., Paisley T., Zimarino V., Ueda H. Purification and properties of Drosophila heat shock activator protein. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1247–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.3685975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]