Abstract
Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) of the bladder tends to remain superficial; however, in 5% to 20% of cases, it progresses to muscle invasion and, more rarely, can metastasize. TCC of the bladder primarily spreads via regional lymphatics. The most common sites of distant metastases of TCC are the liver, lung, mediastinum and bone. Long-term survival of patients with metastatic bladder cancer is rare. Patterns of pulmonary metastasis include multiple nodules, a solitary mass or interstitial micronodule. When multiple nodules are present, they are round and well-circumscribed, without calcification or cavitation. An unusual case of rapidly metastatic TCC to the lung causing large cavitary masses and nodules is presented. Imaging performed after the patient began chemotherapy revealed widespread necrosis of the metastatic cavitary masses causing moderate volume hemoptysis.
Keywords: Bladder cancer, Cavitating metastases, Chemotherapy, Hemoptysis
Abstract
Le carcinome transitionnel de la vessie a tendance à demeurer superficiel, mais dans 5 % à 20 % des cas, il envahit les muscles et, dans des cas encore plus rares, il produit des métastases. Le carcinome transitionnel de la vessie se propage surtout par les vaisseaux lymphatiques régionaux. Les principaux foyers de métastases distants sont le foie, le médiastin et les os. Peu de patients ayant un cancer métastatique de la vessie survivent à long terme. Les modèles de métastases pulmonaires incluent les nodules multiples, une masse solitaire ou un micronodule interstitiel. Les nodules multiples sont ronds et bien circonscrits, sans calcification ou formation de cavités. Est présenté un cas inhabituel de carcinome transitionnel s’étant rapidement métastasé au poumon et causant de grosses masses et de gros nodules cavitaires. L’imagerie effectuée après que le patient eût entrepris la chimiothérapie a révélé une nécrose généralisée des masses cavitaires métastasées, responsables d’une hémoptysie modérée du volume.
CASE PRESENTATION
In April 2009, a 59-year-old man presented with hematuria and flank pain. Bladder cancer was diagnosed, followed by transurethral resection. Chest imaging at presentation was unremarkable. Surgical pathology revealed a high-grade urothelial carcinoma with muscular invasion (pT3 N0 Mx). He subsequently underwent a radical cystectomy and an ileal medial bladder conduit in May 2009.
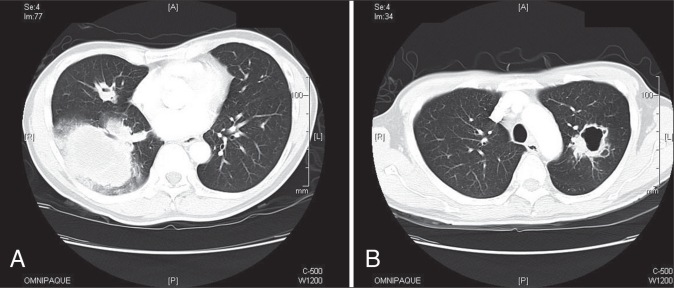
In November 2009, the patient complained of hemoptysis. A chest x-ray revealed a right lower lobe (RLL) infiltrate measuring 11.8 cm × 10.9 cm and left upper lobe cavitating mass. A computed tomography scan revealed enlarged lymph nodes and multiple cavitating lesions of varying size (Figures 1A and 1B).
Figures 1).
A and B. Computed tomography scan at time of hemoptysis presentation showing largest consolidation in the right lower lung with a mass 73 mm × 95 mm in size, with some airspace disease and some nodules in the right middle lobe, with cavitation and ring lesions
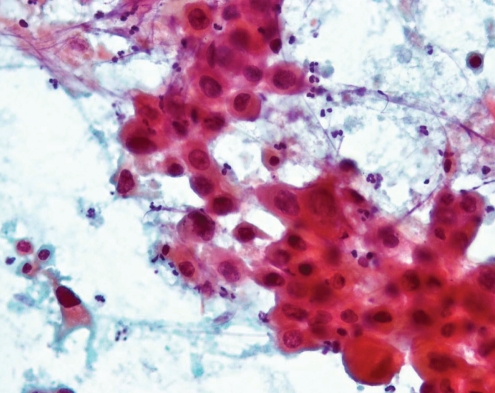
The RLL mass was new, and the differential diagnosis was tuberculosis or metastasis. A percutaneous needle biopsy revealed metastatic urothelial carcinoma (Figure 2). Sputum cytology was positive for malignancy and negative for acid-fast bacilli. His tuberculosis skin test to 5-TU protein purified derivative was negative at 48 h and 72 h.
Figure 2).
Fine-needle aspiration lung pathology using papanicolaou stain showing high-grade carcinoma. Cells were positive for cytokeratin and p63, morphologically consistent with metastatic high-grade urothelial carcinoma
The patient was treated with cisplatin and gemcitabine. Following treatment, a computed tomography scan performed after an episode of moderate hemoptysis revealed necrosis of the largest metastatic mass. At his most recent follow-up visit (February 2010), chest imaging showed decreased RLL and left upper lobe lesion sizes, and he continues gemcitabine and cisplatin, feeling subjectively well.
DISCUSSION
Muscle-invasive disease and metastases represent 30% of diagnosed cases of bladder cancer. Approximately 5% to 20% of superficial tumours will eventually progress to muscle-invasive disease (1). Rarely, low-grade superficial tumours progress directly to metastatic disease without previous evidence of muscle invasion. The two-year survival rate is lower than 15% for patients with untreated muscle-invasive disease.
Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) of the bladder primarily spreads via regional lymphatics (2). The most common sites of distant metastases of TCC, in descending order, are the following: liver, lung, mediastinum, bone and adrenal gland (2). Patterns of pulmonary metastasis include multiple nodules, a solitary mass or interstitial micronodules. When multiple nodules are present, they are characteristically round and well-circumscribed without calcification or cavitation. Approximately 4% of metastases to the lung will eventually evolve into cavitary lesions (3). Cavitation forms as a result of necrosis from an insufficient blood supply to the tumour, or via the invasion of vessels by tumour cells. The development of cavitary lesions in a patient with TCC of the bladder should raise the suspicion of a metastatic disease process (3).
Surgery
Radical cystectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy remains the gold standard treatment for muscle-invasive bladder cancer (4). The extent of lymphadenectomy has an impact on outcome. Patients undergoing radical cystectomy for urothelial carcinoma should undergo bilateral lymphadenectomy. For optimal outcomes, surgical intervention should occur within three months of diagnosis (1).
Neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy
Neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy has been explored in patients with muscle-invasive disease and is reserved for high-risk patients (5). Prospective, randomized trials (4) report a survival advantage of approximately 6.5% for patients who undergo cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy before cystectomy. Two meta-analyses (4) concluded that adjuvant therapy is associated with a modest improvement in survival over surgery alone.
Metastatic disease
Standard treatment for metastatic urothelial carcinoma is multidrug systemic chemotherapy that includes cisplatin with methotrexate, vinblastine, doxorubicin (formerly adriamycin) and cisplatin (MVAC) (4). The toxicity profile associated with this regimen is well known and includes relatively high rates of mucositis and myelosuppression. The use of these regimens is limited to patients with normal renal function (6).
Another common combination is gemcitabine and cisplatin, which has lower toxicity, and an efficiency comparable with MVAC therapy. Long-term survival in metastatic bladder cancer is rare (4). It has been suggested that resection of isolated metastases of bladder cancer contributes to long-term survival, with five-year survival rates of up to 33% (6).
CONCLUSION
An unusual case of urothelial bladder cancer with large and extensive cavitating lung metastasis was presented. When treating large metastatic masses, a physician must be prepared for the potential clinical sequelae that may result from rapid tumour necrosis, as seen in the large-volume hemoptysis of the patient described in the present report.
Footnotes
DISCLOSURES: None of the authors have personal or financial support, or author involvement with organization(s) with financial interest in the subject matter, nor do they have any conflicts of interest to declare. Additional disclosures: Dr Abraham Born holds 100 shares of Lilly & Co, 200 shares of Johnson & Johnson, and is a consultant to GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Boehringer, Nycomed and Bayer.
REFERENCES
- 1.Bischoff CJ, Clark PE. Bladder cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2009;21:272–7. doi: 10.1097/cco.0b013e328329f184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alexander PW, Sanders C, Nath H. Cavitary pulmonary metastases in transitional cell carcinoma of urinary bladder. AJR. 1990;154:493–4. doi: 10.2214/ajr.154.3.2106210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rovirosa A, Salud A, Felip E, Capdevila F, Giralt J, Bellmunt J. Cavitary pulmonary metastases in transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Urol Int. 1992;48:102–4. doi: 10.1159/000282306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Barocas DA, Clark PE. Bladder cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2008;20:307–14. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0b013e3282f8b03e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dougherty DW, Gonsorcik VK, Harpster LE, Trussell JC, Drabick JJ. Superficial bladder cancer metastatic to lungs: Two case reports and review of the literature. Urology. 2009;73:210.e3–210.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2008.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dreicer R. Locally advanced and metastatic bladder cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2001;2:431–6. doi: 10.1007/s11864-001-0048-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]