Abstract
In human volunteers, single injections of purified polyribophosphate elicited antibodies detectable by passive hemagglutination and by serum bactericidal and opsonizing activities against viable Hemophilus influenzae, type b. All three activities rose by 2 wk to maximal levels, at which they remained for at least 6 months. Doses of 1 μg elicited antibody responses in nearly all recipients; higher doses of the antigen, however, produced larger increases in titer. Booster doses of 1 μg given at 6 months did not further increase the antibody titers. A tuberculin-like response was often observed at the site of injections given intradermally.
Full text
PDF
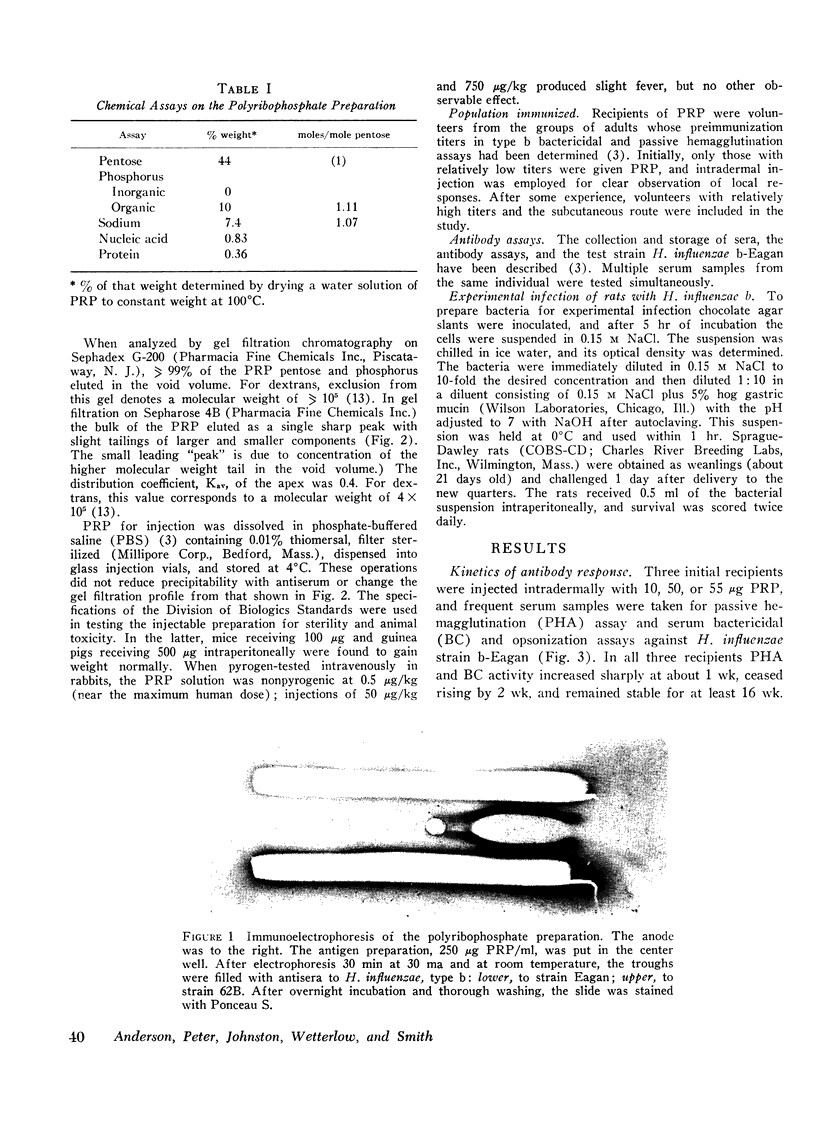




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P., Johnston R. B., Jr, Smith D. H. Human serum activities against Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):31–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI106793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artenstein M. S., Gold R., Zimmerly J. G., Wyle F. A., Branche W. C., Jr, Harkins C. Cutaneous reactions and antibody response to meningococcal group C polysaccharide vaccines in man. J Infect Dis. 1970 Apr;121(4):372–377. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.4.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artenstein M. S., Gold R., Zimmerly J. G., Wyle F. A., Schneider H., Harkins C. Prevention of meningococcal disease by group C polysaccharide vaccine. N Engl J Med. 1970 Feb 19;282(8):417–420. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197002192820803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E., Siskind G. W., Benacerraf B., Ovary Z. Secondary antibody responses in haptenic systems: cell population selection by antigen. J Immunol. 1967 Oct;99(4):760–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG E., ZAMENHOF S. Further studies on polyribophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1961 Nov;236:2845–2849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S. H. The clinical importance of Hemophilus influenzae infections in children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1970 May;17(2):415–426. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)32419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAMENHOF S., LEIDY G., FITZGERALD P. L., ALEXANDER H. E., CHARGAFF E. Polyribophosphate, the type-specific substance of Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Biol Chem. 1953 Aug;203(2):695–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



