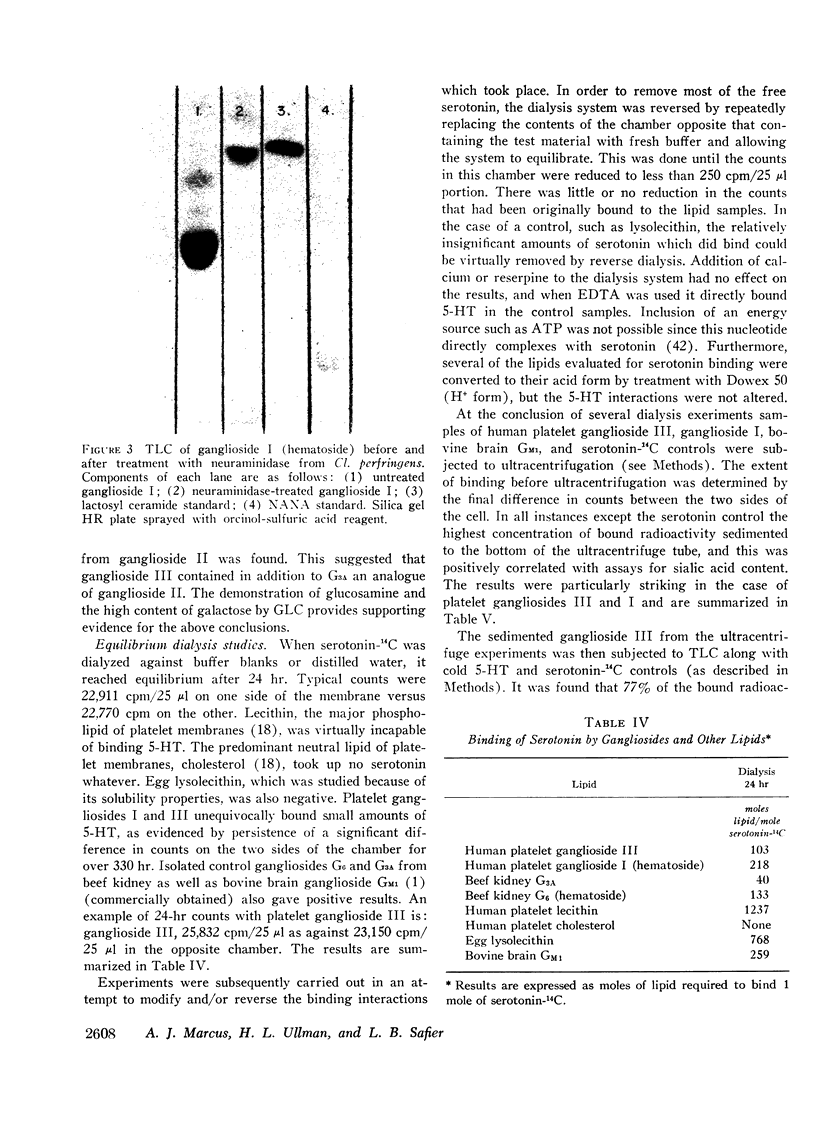
Abstract
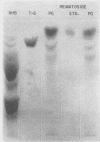
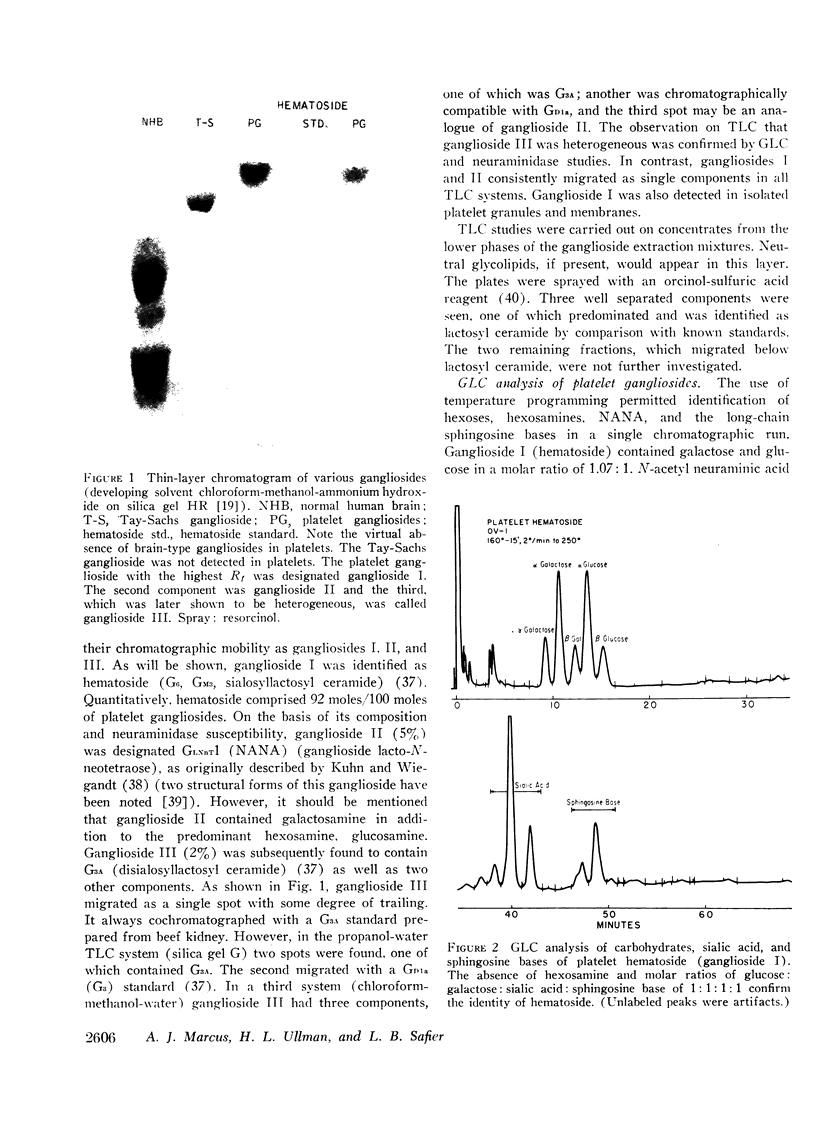
Gangliosides, glycosphingolipids which contain sialic acid, were studied in human platelets. They represented 0.5% of the platelet lipids and accounted for 6% of the total neuraminic acid content of platelets. Three major ganglioside fractions were identified and characterized. Ganglioside I was hematoside (G6) and comprised 92% of the platelet gangliosides. It contained glucose, galactose, and sialic acid in molar ratios of 1:1:1 and no hexosamine. The major fatty acid was behenate (22:0). Ganglioside I was also identified in isolated platelet granules and membranes. Ganglioside II (5%) contained glucose, galactose, sialic acid, and hexosamines (molar ratios 1:2:1:1). The hexosamines were glucosamine (72%) and galactosamine (28%). It was therefore designated as ganglioside lacto-N-neotetraose. Ganglioside III (2%) contained disialosyllactosyl ceramide (G3A) as well as two other gangliosides which could not be precisely characterized. Gangliosides I, II, and III were susceptible to the action of Clostridium perfringens neuraminidase as evidenced by full recovery of sialic acid in its free form after incubation. Neutral platelet glycolipids were qualitatively examined by thin-layer chromatography. The major component was lactosyl ceramide.
Interactions of gangliosides I and III and serotonin-14C were examined in an equilibrium dialysis system at 4°C. The gangliosides bound serotonin-14C in relatively small quantities, whereas control lipids were negative. The binding was essentially unchanged by reverse dialysis, ultracentrifugation and subsequent thin-layer chromatography. The results are comparable to the previously observed nonmetabolic interactions between whole platelets and serotonin in the cold. It is suggested that the orientation and specific distribution of platelet membrane glycolipids may be important determinants of the unique surface properties of platelets.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alivisatos S. G., Ungar F., Seth P. K., Levitt L. P., Geroulis A. J., Meyer T. S. Receptors: localization and specificity of binding of serotonin in the central nervous system. Science. 1971 Feb 26;171(3973):809–812. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3973.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V., BRICKNELL J. The uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine by blood platelets in the cold. J Physiol. 1959 Jun 23;147(1):153–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber A. J., Jamieson G. A. Isolation of glycopeptides from low- and high-density platelet plasma membranes. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 7;10(25):4711–4717. doi: 10.1021/bi00801a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner H. R., Born G. V. The relation between the 5-hydroxytryptamine content and aggregation of rabbit platelets. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):397–408. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berneis K. H., Da Prada M., Pletscher A. Micelle formation between 5-hydroxytryptamine and adenosine triphosphate in platelet storage organelles. Science. 1969 Aug 29;165(3896):913–914. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3896.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter H. E., Gaver R. C. Improved reagent for trimethylsilylation of sphingolipid bases. J Lipid Res. 1967 Jul;8(4):391–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson G. Glycosphingolipid levels in an unusual neurovisceral storage disease characterized by lactosylceramide galactosyl hydrolase deficiency: lactosylceramidosis. J Lipid Res. 1972 Mar;13(2):207–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. Molecular biology of synaptic receptors. Science. 1971 Mar 12;171(3975):963–971. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3975.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiszer S., De Robertis E. Subcellular distribution and chemical nature of the receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine in the central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1969 Aug;16(8):1201–1209. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb05967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gielen W. Uber die Funktion von ganaliosiden. Die Verbreitung des Serotonin-Receptors. Z Naturforsch B. 1968 Jan;23(1):117–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa S., Burton R. M. Lipids of retina. I. Analysis of gangliosides in beef retina by thin layer chromatography. Lipids. 1969 May;4(3):205–208. doi: 10.1007/BF02532630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand J., Stryckmans P., Stoffyn P. Neutral glycolipids in leukemic and nonleukemic leukocytes. J Lipid Res. 1971 May;12(3):361–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISHIMOTO Y., RADIN N. S. A REACTION TUBE FOR METHANOLYSIS; INSTABILITY OF HYDROGEN CHLORIDE IN METHANOL. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:435–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean E. L. Separation of gluco- and galactocerebrosides by means of borate thin-layer chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1966 May;7(3):449–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledeen R., Salsman K., Cabrera M. Gangliosides of bovine adrenal medulla. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2287–2295. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledeen R., Salsman K. Fatty acid and long chain base composition of adrenal medulla gangliosides. Lipids. 1970 Sep;5(9):751–756. doi: 10.1007/BF02531387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledeen R. The chemistry of gangliosides: a review. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1966 Feb;43(2):57–66. doi: 10.1007/BF02641015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehninger A. L. The neuronal membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1069–1080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADOFF M. A., EBBE S., BALDINI M. SIALIC ACID OF HUMAN BLOOD PLATELETS. J Clin Invest. 1964 May;43:870–877. doi: 10.1172/JCI104972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS A. J., ULLMAN H. L., SAFIER L. B., BALLARD H. S. Platelet phosphatides. Their fatty acid and aldehyde composition and activity in different clotting systems. J Clin Invest. 1962 Dec;41:2198–2212. doi: 10.1172/JCI104679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMillan V. H., Wherrett J. R. A modified procedure for the analysis of mixtures of tissue gangliosides. J Neurochem. 1969 Dec;16(12):1621–1624. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchbanks R. M. Serotonin binding to nerve ending particles and other preparations from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Dec;13(12):1481–1493. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb04309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J. Platelet function (third of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1969 Jun 12;280(24):1330–1335. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196906122802405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Ullman H. L., Safier L. B. Lipid composition of subcellular particles of human blood platelets. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):108–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Zucker-Franklin D., Safier L. B., Ullman H. L. Studies on human platelet granules and membranes. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):14–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI105318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCluer R. H. Chemistry of gangliosides. Chem Phys Lipids. 1970 Oct;5(1):220–234. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(70)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penick R. J., Meisler M. H., McCluer R. H. Thin-layer chromatographic studies of human brain gangliosides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 4;116(2):279–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puro K. Isolation of bovine kidney gangliosides. Acta Chem Scand. 1970;24(1):13–22. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.24-0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puro K., Maury P., Huttunen J. K. Qualitative and quantitative patterns of gangliosides in extraneural tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;187(2):230–235. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapport M. M., Graf L. Immunochemical reactions of lipids. Prog Allergy. 1969;13:273–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H. Cell communication, calcium ion, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):404–412. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUZUKI K. A SIMPLE AND ACCURATE MICROMETHOD FOR QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF GANGLIOSIDE PATTERNS. Life Sci. 1964 Nov;3:1227–1233. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(64)90040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF HUMAN BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. J Neurochem. 1963 Sep;10:613–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb08933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. THE GANGLIOSIDES. J Lipid Res. 1964 Apr;5:145–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Smolowe A. F., Barclay M. Separation of neutral glycosphingolipids and sulfatides by thin-layer chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1967 Jul;8(4):295–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder P. D., Jr, Desnick R. J., Krivit W. The glycosphingolipids and glycosyl hydrolases of human blood platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1857–1865. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W. Sphingolipids. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:57–82. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K. The pattern of mammalian brain gangliosides. II. Evaluation of the extraction procedures, postmortem changes and the effect of formalin preservation. J Neurochem. 1965 Jul;12(7):629–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb04256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HEYNINGEN W. E. The fixation of tetanus toxin, strychnine, serotonin and other substances by ganglioside. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jun;31:375–387. doi: 10.1099/00221287-31-3-375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance D. E., Sweeley C. C. Quantitative determination of the neutral glycosyl ceramides in human blood. J Lipid Res. 1967 Nov;8(6):621–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance W. R., Shook C. P., 3rd, McKibbin J. M. The glycolipids of dog intestine. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):435–445. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHERRETT J. R., LOWDEN J. A., WOLFE L. S. STUDIES ON BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. II. ANALYSIS OF HUMAN BRAIN GANGLIOSIDE FRACTIONS OBTAINED BY PREPARATIVE THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY. Can J Biochem. 1964 Jul;42:1057–1063. doi: 10.1139/o64-116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. B., Marsh J. B., Glick M. C., Warren L. Membranes of animal cells. VI. The glycolipids of the L cell and its surface membrane. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 10;245(15):3928–3937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegandt H. Gangliosides of extraneuronal tissue. Chem Phys Lipids. 1970 Oct;5(1):198–204. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(70)90018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegandt H. The structure and the function of gangliosides. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1968 Feb;7(2):87–96. doi: 10.1002/anie.196800871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windeler A. S., Feldman G. L. Silver acetate for stabilizing methyl galactosides after methanolysis of glycolipids. Lipids. 1969 Mar;4(2):167–168. doi: 10.1007/BF02531940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolley D. W., Gommi B. W. Serotonin receptors, VII. Activities of various pure gangliosides as the receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):959–963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]