Abstract
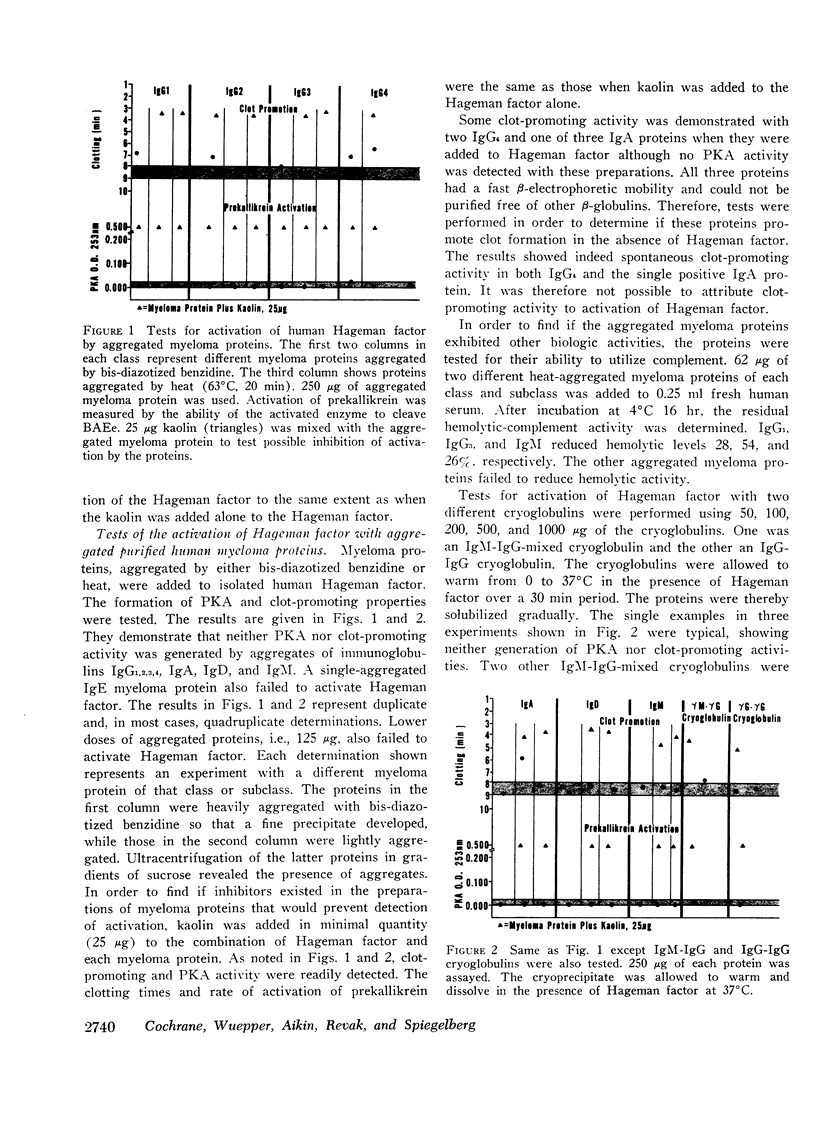
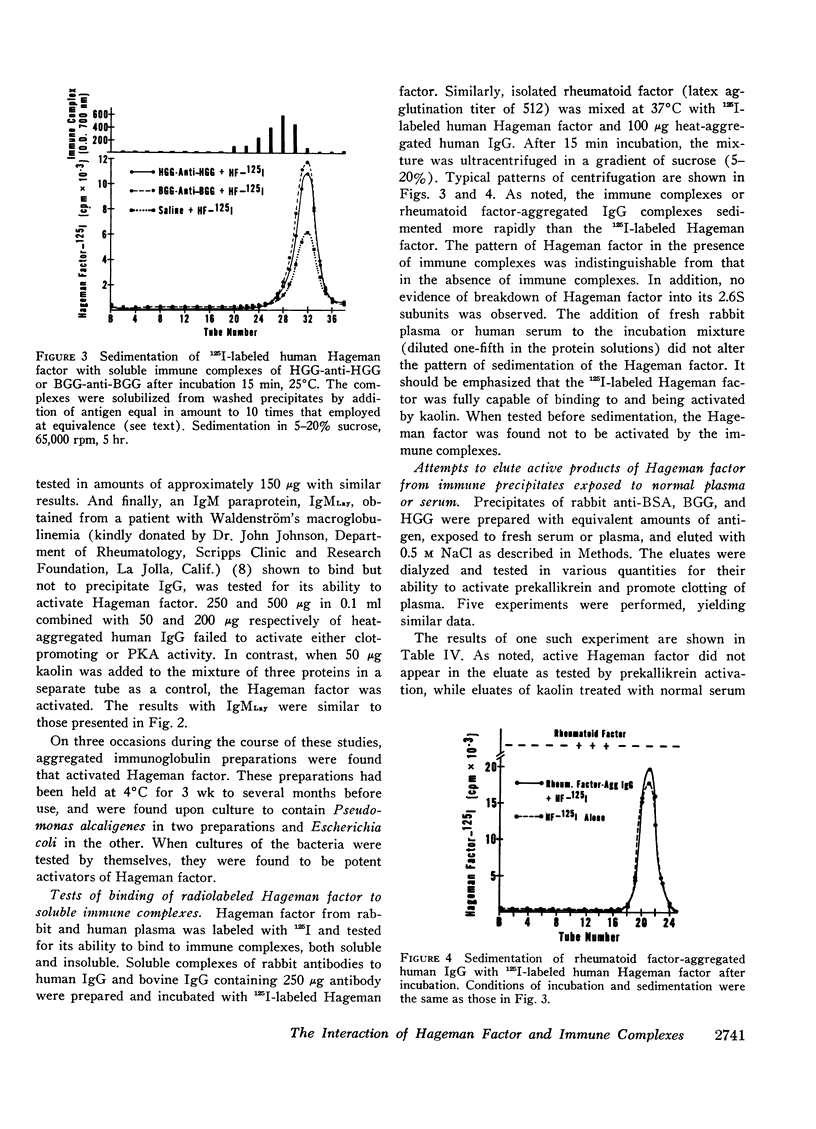
The possible interaction of Hageman factor from human or rabbit plasma with a variety of immunologic reactants was studied. Evidence of an interaction was not obtained and neither binding of radiolabeled Hageman factor to immune aggregates nor depletion of the Hageman factor from the supernate was observed. Cleavage of the labeled Hageman factor molecule into its 30,000 molecular weight-active fragments was not detectable after incubation with immune complexes.
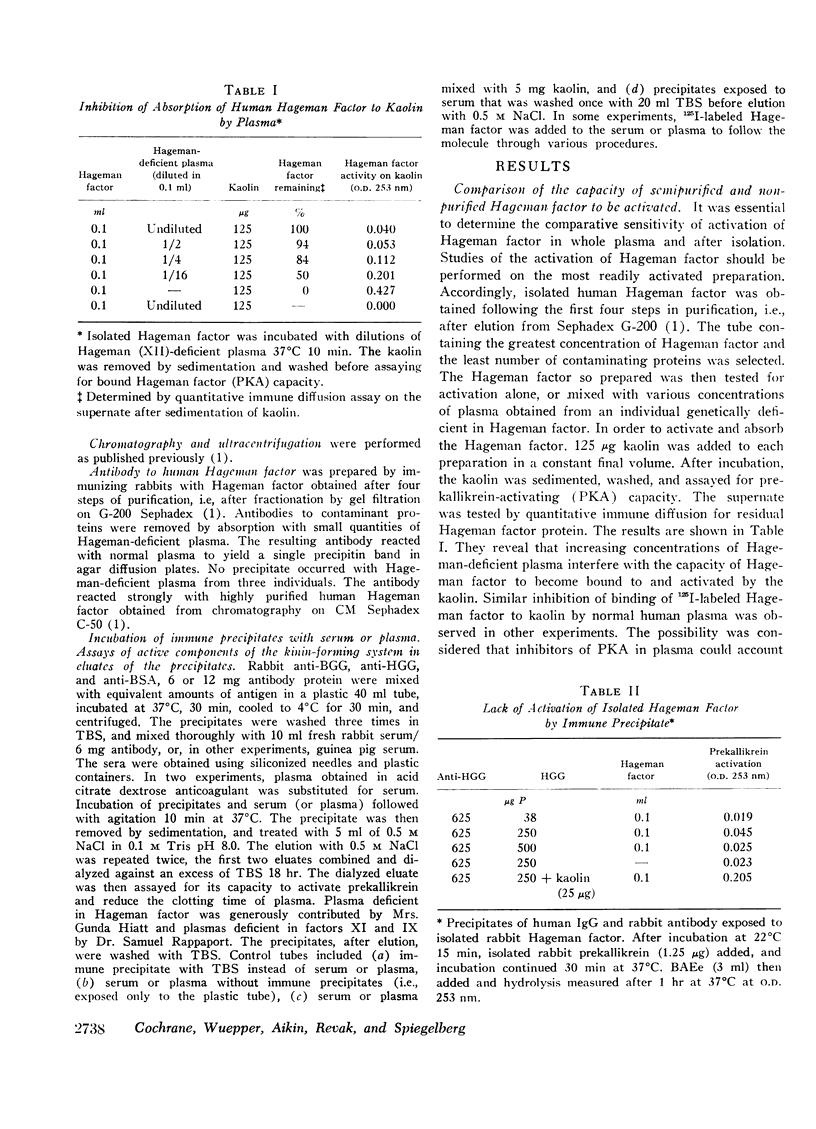
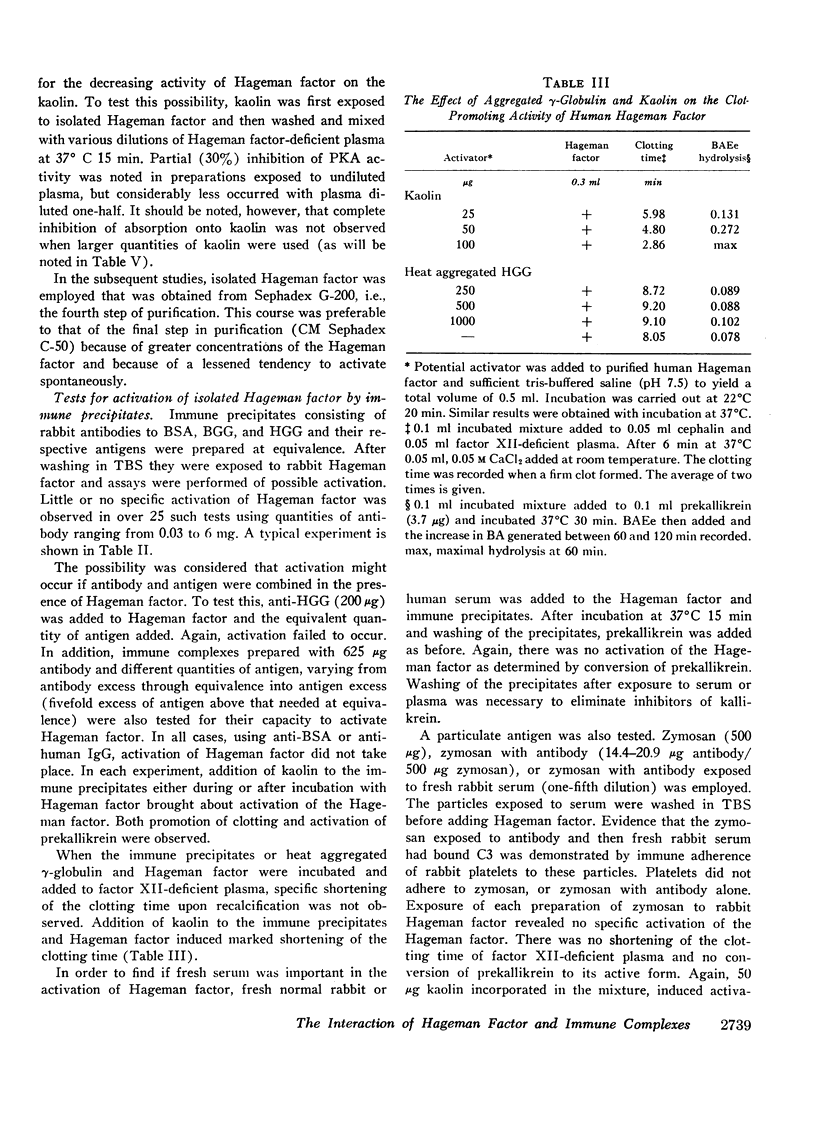
Isolated Hageman factor was far more sensitive to activation than Hageman factor in plasma or serum. There was no consistent activation of isolated Hageman factor by immunologic reactants as determined by conversion of prekallikrein to its enzymatic form or by shortening of the clotting time of factor XII-deficient plasma. A variety of immunologic stimuli were tested: (a) antigen-antibody complexes in soluble or precipitated form; (b) particulate antigen-antibody complexes, i.e., zymosan-anti-zymosan in which a surface was presented for activation; (c) human IgM-IgG and IgG-IgG (rheumatoid factor) complexes; (d) immune aggregates consisting of heat or bis-diazotized benzidine-aggregated myeloma proteins of all human immunoglobulin classes and subclasses: IgG1,2,3,4, IgA, IgD, IgM, and IgE. Absorption with immune aggregates did not reduce the quantity of Hageman factor in solution, nor was the Hageman factor bound to the precipitates. The presence of plasma or serum with immune aggregates did not generate activity of the Hageman factor.
The only preparations of immunoglobulins capable of activating Hageman factor were found to be contaminated with bacteria. These bacteria, upon isolation, activated Hageman factor.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cochrane C. G., Wuepper K. D. The first component of the kinin-forming system in human and rabbit plasma. Its relationship to clotting factor XII (Hageman Factor). J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):986–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES G. E., LOWE J. S. A permeability factor released from guinea-pig serum by antigen-antibody precipitates. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Aug;41:335–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen V., Smith H. G. Plasma kinin formation by complexes of aggregated gamma-globulin and serum proteins. Br J Exp Pathol. 1970 Jun;51(3):328–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. V., Tan M., Melmon K. L. Rheumatoid factor and kinin generation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Dec 10;168(1):173–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb43106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Salmon S., Fudenberg H. Biologic activities of aggregated gamma-globulin. 8. Aggregated immunoglobulins of different classes. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):82–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Treloar M. P., Takeuchi Y. A small molecular weight permeability factor in guinea pig serum: adsorption to antigen-antibody aggregates. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):875–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J., STETSON C. A., Jr An effect of antigen-antibody interaction on blood coagulation. J Exp Med. 1959 Jan 1;109(1):1–8. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWERT G. W., TAKENAKA Y. A spectrophotometric determination of trypsin and chymotrypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Apr;16(4):570–575. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90280-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D., Cochrane C. G. Plasma prekallikrein: isolation, characterization, and mechanism of activation. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):1–20. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



