Abstract
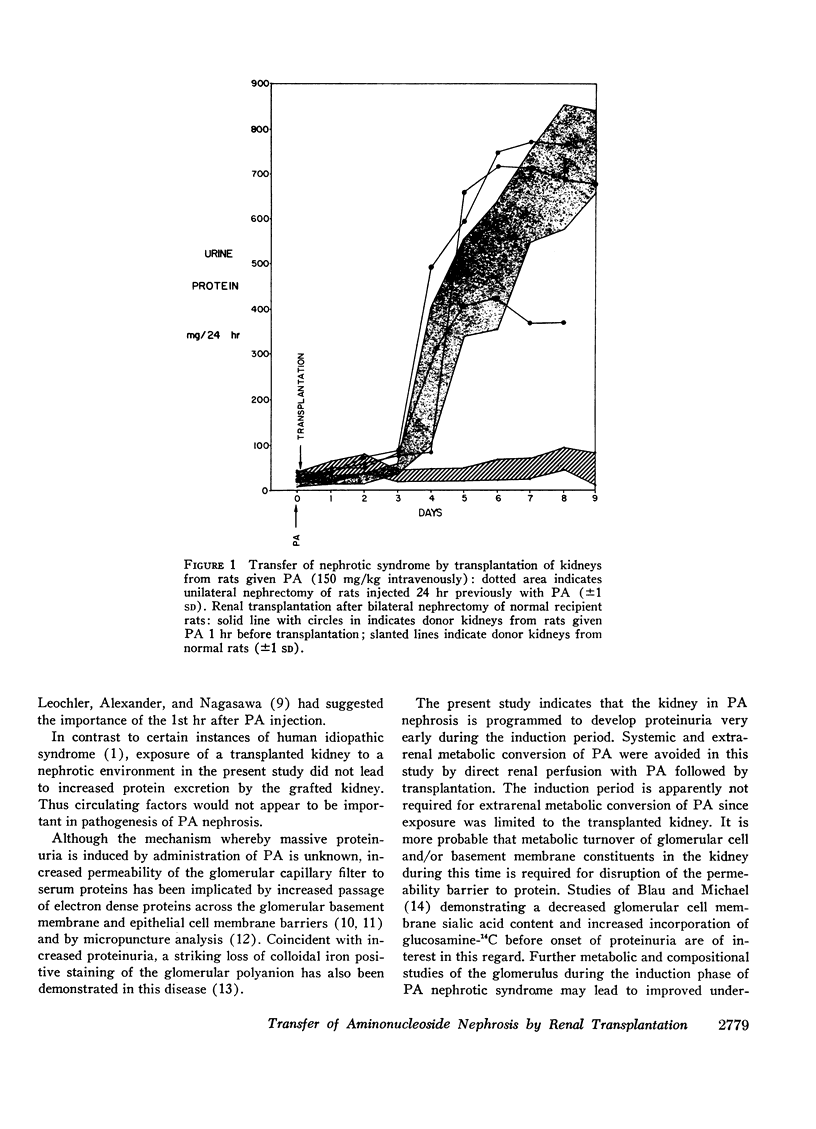
The pathogenesis of aminonucleoside of puromycin (PA) nephrotic syndrome in rats was studied using renal transplantation to separate systemic from renal factors. The nephrotic syndrome was transferred by transplantation of kidneys from rats with established proteinuria. Bilaterally nephrectomized normal rats receiving kidneys removed as early as 15 min after intravenous PA injection (100 mg/kg) of donors also developed proteinuria (602±125 mg/24 hr) and a nephrotic syndrome after the usual induction period of 4-7 days observed in this disease. Arterial perfusion of isolated kidneys with PA (50 mg/kg) followed by perfusion with isotonic saline 3 min later and then transplantation to normal bilaterally nephrectomized rats led to a nephrotic syndrome. Urine protein excretion was 494±42 mg on the 7th day after transplantation. In contrast, urine protein excretion after transplantation of normal kidneys to normal bilaterally nephrectomized rats was 40±20 mg on the 7th day. Exposure of a normal kidney to a nephrotic host environment by transplantation of a normal kidney to a unilaterally nephrectomized PA-injected rat did not transfer the disease to the normal kidney. After removal of the nephrotic kidney 11-13 days after transplantation, proteinuria of the donor kidney was normal (21±13 mg on day 15). These studies indicate that pathogenesis of aminonucleoside nephrosis involves programming of the kidney directly by PA within minutes after exposure although increased urinary protein excretion does not occur until several days later.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARNASON B. G., VAUXST-CYRC DE, RELYVELD E. H. ROLE OF THE THYMUS IN IMMUNE REACTIONS IN RATS. IV. IMMUNOGLOBULINS AND ANTIBODY FORMATION. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1964;25:206–224. doi: 10.1159/000229522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau E. B., Michael A. F. Rat glomerular glycoprotein composition and metabolism in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Oct;141(1):164–172. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derr R. F., Loechler D. K., Alexander C. S., Nagasawa H. T. Inhibition of aminonucleoside nephrosis in rats. IV. Prevention by N6-methyladenosine. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Sep;72(3):363–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., PALADE G. E. Glomerular permeability. II. Ferritin transfer across the glomerular capillary wall in nephrotic rats. J Exp Med. 1961 Nov 1;114:699–716. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. An improved technique of renal transplantation in the rat. Surgery. 1967 May;61(5):771–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARDINEY M. R., Jr, MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. MOUSE BETA-1C-GLOBULIN: PRODUCTION OF ANTISERUM AND CHARACTERIZATION IN THE COMPLEMENT REACTION. J Immunol. 1965 Jun;94:877–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael A. F., Blau E., Vernier R. L. Glomerular polyanion. Alteration in aminonucleoside nephrosis. Lab Invest. 1970 Dec;23(6):649–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael A. F., Jr, Drummond K. N., Good R. A., Vernier R. L. Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis: immune deposit disease. J Clin Invest. 1966 Feb;45(2):237–248. doi: 10.1172/JCI105336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oken D. E., Flamenbaum W. Micropuncture studies of proximal tubule albumin concentrations in normal and nephrotic rats. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1498–1505. doi: 10.1172/JCI106635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERNIER R. L., PAPERMASTER B. W., GOOD R. A. Aminonucleoside nephrosis. I. Electron microscopic study of the renal lesion in rats. J Exp Med. 1959 Jan 1;109(1):115–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachalam M. A., Cotran R. S., Karnovsky M. J. An ultrastructural study of glomerular permeability in aminonucleoside nephrosis using catalase as a tracer protein. J Exp Med. 1970 Dec 1;132(6):1168–1180. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.6.1168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



