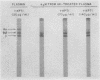
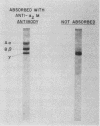
Abstract
This study demonstrates that human plasma α2-macroglobulin preparations possess an enzymic activity that degrades fibrinogen, resulting in the formation of products whose structure resembles that of circulating fibrinogen catabolites. The sequence of degradation is similar to that observed in plasmin-catalyzed digests, in that Aα-chain fragmentation precedes that of Bβ-chain. The addition of plasminogen activators to plasma induced an increase in the N-α-tosyl-l-arginine methyl ester HCl esterase and fibrinogenolytic activity associated with α2-macroglobulin purified from this plasma, indicating that the enzymic activity of the complex was preserved and could be increased in the presence of other plasma enzyme inhibitors. Immunochemical studies demonstrated that an α2-macroglobulin-plasmin complex had formed in urokinase-treated plasma. This α2-macroglobulin preparation manifested an esterolytic profile like that of a complex prepared from plasmin and purified α2-macroglobulin. After complex formation with α2-macroglobulin in plasma, plasmin retained less than 0.1% of its fibrinogenolytic activity. That plasmin expressed its activity while bound to α2-macroglobulin was suggested by immunoprecipitation of this activity with α2-macroglobulin antibody and by the demonstration that pancreatic trypsin inhibitor did not effectively inhibit its fibrinogenolytic or esterolytic activity. These results raise the possibility that, in addition to its activity as a major plasma proteolytic enzyme inhibitor, α2-macroglobulin may modulate enzyme-substrate interactions, such as those resulting in the formation of circulating fibrinogen catabolites, by providing a mechanism for the preservation and protection of a portion of the enzymic activity in the presence of other circulating inhibitors.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. xi-Aminocaproic acid: an inhibitor of plasminogen activation. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):832–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMBRUS C. M., MARKUS G. Plasmin-antiplasmin complex as a reservoir of fibrinolytic enzyme. Am J Physiol. 1960 Sep;199:491–494. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnesen H., Fagerhol M. K. 2 -Macroglobulin, 1 -antitrypsin, and antithrombin III in plasma and serum during fibrinolytic therapy with urokinase. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1972 May;29(3):259–263. doi: 10.3109/00365517209080240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyde T. R. The interaction between alpha-2-macroglobulin and cationic aspartate aminotransferase. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(1):59–61. doi: 10.1042/bj1110059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Mattler L., Sherry S. Studies on the prekallikrein (kallikreinogen)--kallikrein enzyme system of human plasma. I. Isolation and purification of plasma kallikreins. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):11–22. doi: 10.1172/JCI105959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlayson J. S., Mosesson M. W., Bronzert T. J., Pisano J. J. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. II. Cross-linking capacity of high solubility catabolic intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5220–5222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Beck E. A. Plasmic degradation of human fibrinogen. I. Structural characterization of degradation products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 18;263(3):631–644. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O. Inhibition of plasmin activity by alpha-2-macroglobulin. Clin Chim Acta. 1967 May;16(2):328–329. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(67)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. A sensitive colorimetric method for the measurement of serum C1 inactivator using the substrate N-alpha-acetyl-L-lysine methyl ester. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):1024–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin. An inhibitor of plasma kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):329–352. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Separation of plasma thromboplastin antecedent from kallikrein by the plasma 2 -macroglobulin, kallikrein inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2084–2090. doi: 10.1172/JCI106702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Studies on the interaction between collagen and a plasma kallikrein-like activity. Evidence for a surface-active enzyme system. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1813–1822. doi: 10.1172/JCI106983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanchantin G. F., Plesset M. L., Friedmann J. A., Hart D. W. Dissociation of esterolytic and clotting activities of thrombin by trypsin-binding macroglobulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Feb;121(2):444–449. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEHL J. W., O'CONNELL W., DEGROOT J. MACROGLOBULIN FROM HUMAN PLASMA WHICH FORMS AN ENZYMATICALLY ACTIVE COMPOUND WITH TRYPSIN. Science. 1964 Aug 21;145(3634):821–822. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3634.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSESSON M. W., FINLAYSON J. S. SUBFRACTIONS OF HUMAN FIBRINOGEN; PREPARATION AND ANALYSIS. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Oct;62:663–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSESSON M. W. The preparation of human fibrinogen free of plasminogen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Feb 26;57:204–213. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)91112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell D. J. Inhibitors of kallikrein in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1611–1623. doi: 10.1172/JCI106962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D., Karpatkin S. Heterogeneity of human fibrinogen: possible relation to proteolysis by thrombin and plasmin as studies by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 13;40(1):206–211. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D., Karpatkin S. The initial macromolecular derivatives of human fibrinogen produced by plasmin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 22;271(1):163–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Alkjaersig N., Sweet B., Sherry S. Human fibrinogen of relatively high solubility. Comparative biophysical, biochemical, and biological studies with fibrinogen of lower solubility. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3279–3287. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S., Umfleet R. A., Galanakis D. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. I. Structural and related studies of plasma fibrinogens which are high solubility catabolic intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5210–5219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Sherry S. The preparation and properties of human fibrinogen of relatively high solubility. Biochemistry. 1966 Sep;5(9):2829–2835. doi: 10.1021/bi00873a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN P. S., HILL B. M. Studies of the plasmin system. III. Physical properties of the two plasmin inhibitors in plasma. J Exp Med. 1958 Nov 1;108(5):639–649. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.5.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Han B. H., Sugihara H., Suzuki T. Studies on alpha 2-macroglobulin in bovine plasma. II. Interaction of alpha2-macroglobulin and trypsin. J Biochem. 1970 Jun;67(6):821–832. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Rubin H., Drillings M., Hsieh R. Inhibition of Hageman factor activation. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1172–1180. doi: 10.1172/JCI105806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzo S. V., Schwartz M. L., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. The effect of plasmin on the subunit structure of human fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):636–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H., Geokas M. C. Role for a 2 -macroglobulin in haemostatic balance. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 27;239(91):116–117. doi: 10.1038/newbio239116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Summaria L. An immunochemical study of human plasminogen and plasmin. Immunochemistry. 1966 Jan;3(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90279-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SGOURIS J. T., INMAN J. K., McCALL K. B., HYNDMAN L. A., ANDERSON H. D. The preparation of human fibrinolysin (plasmin). Vox Sang. 1960 Jul;5:357–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1960.tb03750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L. A., Fletcher A. P., Sherry S. In vivo transformation between fibrinogens of varying ethanol solubilities: a pathway of fibrinogen catabolism. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Apr;73(4):574–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L. A., Mosesson M. W., Sherry S. Isolation and characterization of the clottable low molecular weight fibrinogen derived by limited plasmin hydrolysis of human fraction I-4. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1515–1523. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry S., Alkjaersig N., Fletcher A. P. Comparative activity of thrombin on substituted arginine and lysine esters. Am J Physiol. 1965 Sep;209(3):577–583. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.3.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry S., Alkjaersig N., Fletcher A. P. [Activity of plasmin and streptokinase-activator on substituted arginine and lysine esters]. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 Jul 31;16(1):18–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbuch M., Blatrix C. H., Josso F. Action anti-protéase de l'gamma2-macroglobuline. II. Son role d'antithrombine progressive. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1968 Feb;13(2):179–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]