Abstract
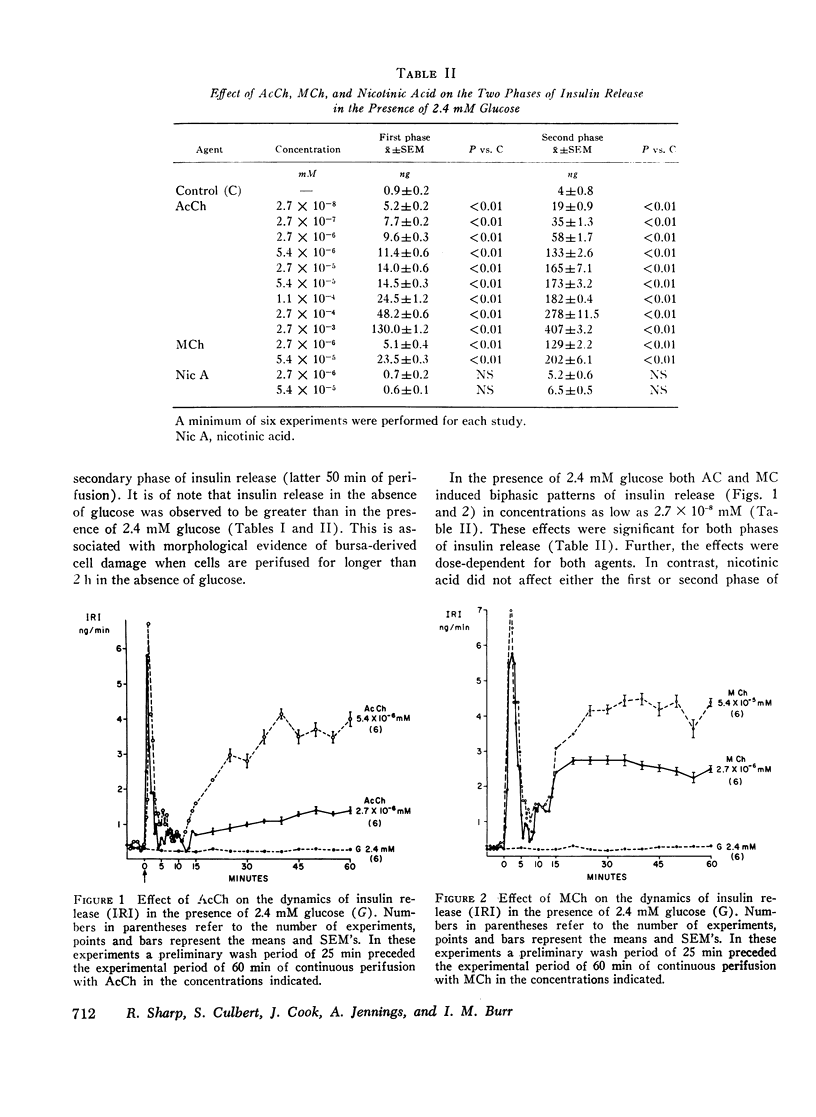
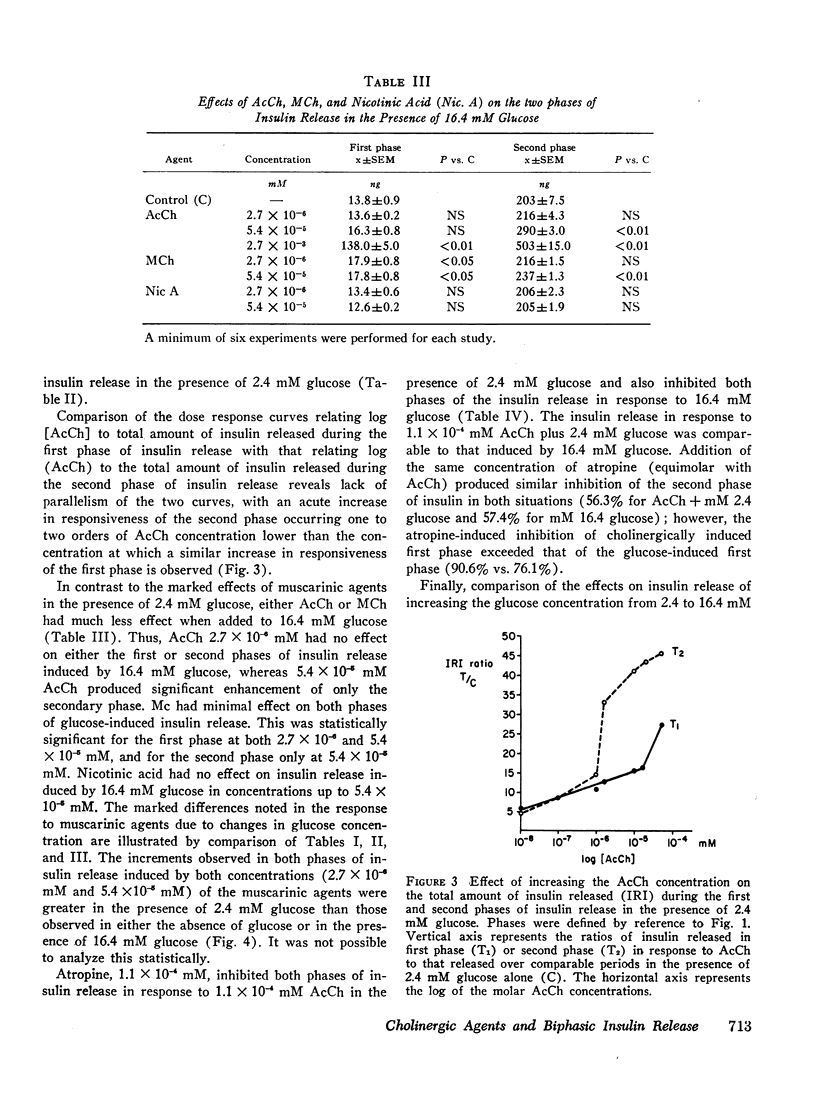
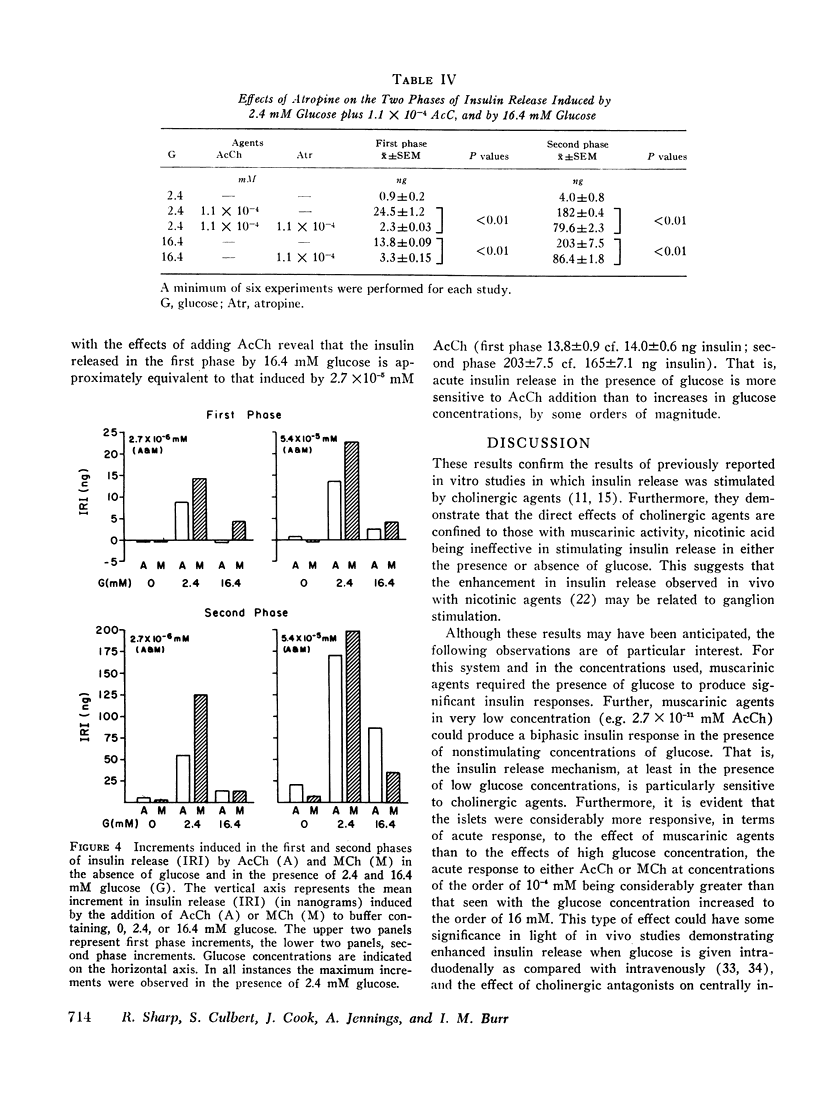
An in vitro system for perifusion of rat pancreatic islets has been utilized to define the effects of cholinergic agents on the dynamics of insulin release. In the absence of glucose the effects of either acetylcholine or acetyl-β-methylcholine were minimal at concentrations up to 10−5 mM. In the presence of low glucose concentration (2.4 mM), both of the muscarinic agents produced dose-dependent biphasic insulin release. Under these conditions significant insulin release was observed over both phases at concentrations of the muscarinic agents as low as 10−8 mM. Further, the dose response curves relating muscarinic concentration to the total amount of insulin released in each of the two phases showed lack of parallelism between the curves. Nicotinic acid in concentrations up to 10−5 mM had no effect on insulin release in the presence of 2.4 mM glucose. When the glucose concentration was increased to 16.4 mM, the effects of the muscarinic agents were significantly less than those observed in the presence of 2.4 mM glucose. This held true whether the effect was defined as absolute increment due to the muscarinic agent or as percentage of enhancement. Atropine inhibited insulin release induced by both acetylcholine and by 16.4 mM glucose. These data indicate that cholinergic stimulation can play a significant role in modifying insulin release patterns.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burr I. M., Balant L., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. Adrenergic modification of glucose-induced biphasic insulin release from perifused rat pancreas. Eur J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;1(4):216–224. doi: 10.1111/eci.1971.1.4.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Balant L., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. Perifusion of rat pancreatic tissue in vitro: substrate modification of theophylline-induced biphasic insulin release. J Clin Invest. 1970 Nov;49(11):2097–2105. doi: 10.1172/JCI106427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Marliss E. B., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. Diazoxide effects on biphasic insulin release: "adrenergic" suppression and enhancement in the perifused rat pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1444–1450. doi: 10.1172/JCI106628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Marliss E. B., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. Differential effect of ouabain on glucose-induced biphasic insulin release in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1971 Sep;221(3):943–947. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.3.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Renold A. E., Stauffacher W., Grodsky G. M., Balant L. [Regulation of insulin release in perifused pancreatic tissue]. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1969 Sep;6 (Suppl 1):580–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Taft H. P., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. On the role of cyclic AMP in insulin release: II. Dynamic aspects and relations to adrenergic receptors in the perfused pancreas of adult rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 30;185:245–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb45253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I., Hudson W., Page D., Taft H. P. Observations on the effect of a ganglion blocking agent on responses to intravenous glucose infusion. Diabetologia. 1970 Oct;6(5):467–472. doi: 10.1007/BF01211885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coore H. G., Randle P. J. Regulation of insulin secretion studied with pieces of rabbit pancreas incubated in vitro. Biochem J. 1964 Oct;93(1):66–78. doi: 10.1042/bj0930066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Grodsky G. M. Dynamics of insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology. 1968 Sep;83(3):572–584. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-3-572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELRICK H., STIMMLER L., HLAD C. J., Jr, ARAI Y. PLASMA INSULIN RESPONSE TO ORAL AND INTRAVENOUS GLUCOSE ADMINISTRATION. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Oct;24:1076–1082. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-10-1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer U., Hommel H., Ziegler M., Michael R. The mechanism of insulin secretion after oral glucose administration. I. Multiphasic course of insulin mobilization after oral administration of glucose in conscious dogs. Differences to the behaviour after intravenous administration. Diabetologia. 1972 Apr;8(2):104–110. doi: 10.1007/BF01235634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman L. A., Ezdinli E. Z., Javid R. Effect of vagotomy and vagal stimulation on insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1967 Jul;16(7):443–448. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.7.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Abraira C., Gruenewald D., Goldstein M. S. Plasma insulin levels during imaginary food ingestion under hypnosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jan;133(1):274–276. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES C. N., RANDLE P. J. Immunoassay of insulin with insulin-antibody precipitate. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0880137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel H., Fischer U., Retzlaff K., Knöfler H. The mechanism of insulin secretion after oral glucose administration. II. Reflex insulin secretion in conscious dogs bearing fistulas of the digestive tract by sham-feeding of glucose or tap water. Diabetologia. 1972 Apr;8(2):111–116. doi: 10.1007/BF01235635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajinuma H., Kaneto A., Kuzuya T., Nakao K. Effects of methacholine on insulin secretion in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Sep;28(9):1384–1388. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-9-1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto A., Kajinuma H., Kosaka K., Nakao K. Stimulation of insulin secretion by parasympathomimetic agents. Endocrinology. 1968 Oct;83(4):651–658. doi: 10.1210/endo-83-4-651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto A., Kosaka K., Nakao K. Effects of stimulation of the vagus nerve on insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1967 Mar;80(3):530–536. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-3-530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kris A. O., Miller R. E., Wherry F. E., Mason J. W. Inhibition of insulin secretion by infused epinephrine in rhesus monkeys. Endocrinology. 1966 Jan;78(1):87–97. doi: 10.1210/endo-78-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Mayhew D. A possible role for the adenylcyclase system in insulin secretion. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1724–1734. doi: 10.1172/JCI105663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W., Malaisse-Lagae F., Wright P. H., Ashmore J. Effects of adrenergic and cholinergic agents upon insulin secretion in vitro. Endocrinology. 1967 May;80(5):975–978. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-5-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre N., Holdsworth C. D., Turner D. S. Intestinal factors in the control of insulin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1317–1324. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen T. A., Taskinen M. R., Pelkonen R., Nikkilä E. A. Glucose tolerance and plasma insulin in man during acute and chronic administration of nicotinic acid. Acta Med Scand. 1969 Oct;186(4):247–253. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1969.tb01473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague W., Cook J. R. The role of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in the regulation of insulin release by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;122(1):115–120. doi: 10.1042/bj1220115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M. J., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to oral and intravenous glucose: studies in normal and diabetic sujbjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1954–1962. doi: 10.1172/JCI105685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr A receptor mechanism for the inhibition of insulin release by epinephrine in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):86–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI105514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr Beta adrenergic stimulation of insulin release in man. Diabetes. 1967 Mar;16(3):150–155. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.3.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Girardier L., Seydoux J., Kanazawa Y., Posternak J. Neural regulation of insulin secretion in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):210–214. doi: 10.1172/JCI107168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Robertson R. P. Control of insulin secretion by catecholamines, stress, and the sympathetic nervous system. Fed Proc. 1973 Jul;32(7):1792–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer H. S., Allen E. W., Herron A. L., Jr, Brennan M. T. Insulin secretion in response to glycemic stimulus: relation of delayed initial release to carbohydrate intolerance in mild diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Mar;46(3):323–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI105534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. C. Conditioned hypoglycemia: effect of vagotomy and pharmacological blockade. Am J Physiol. 1972 Dec;223(6):1424–1427. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.6.1424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


