Abstract
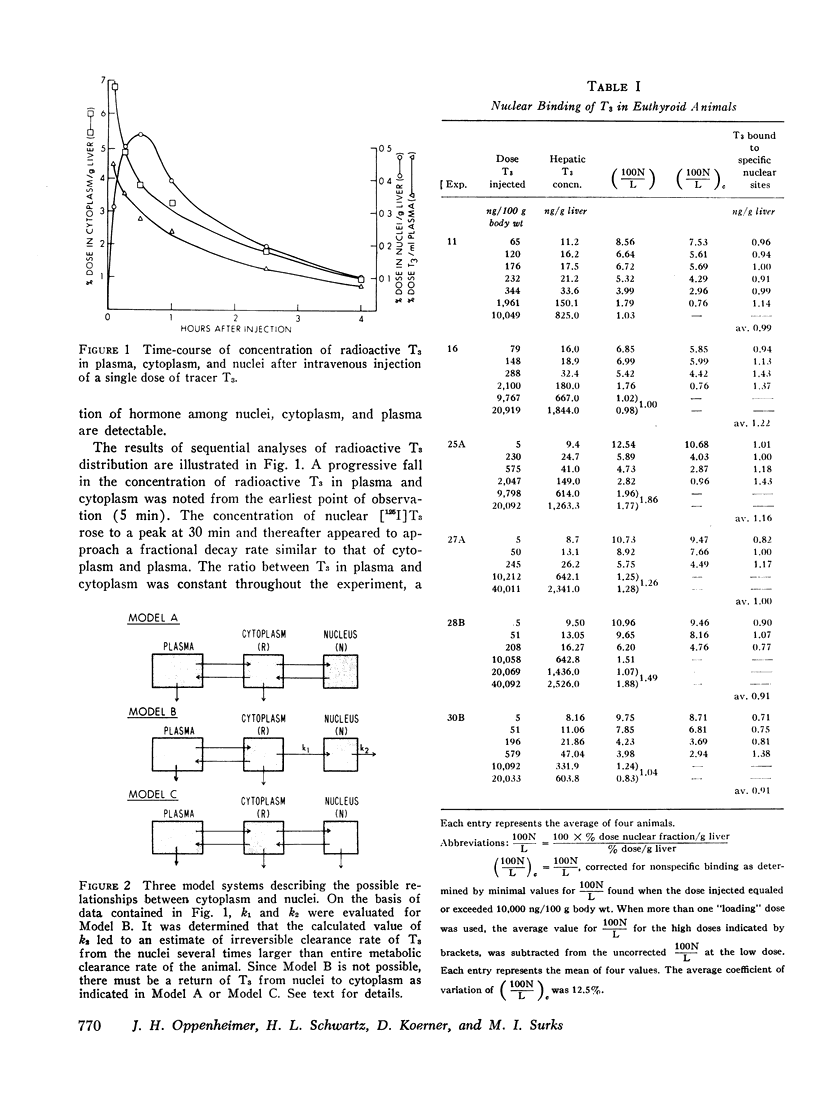
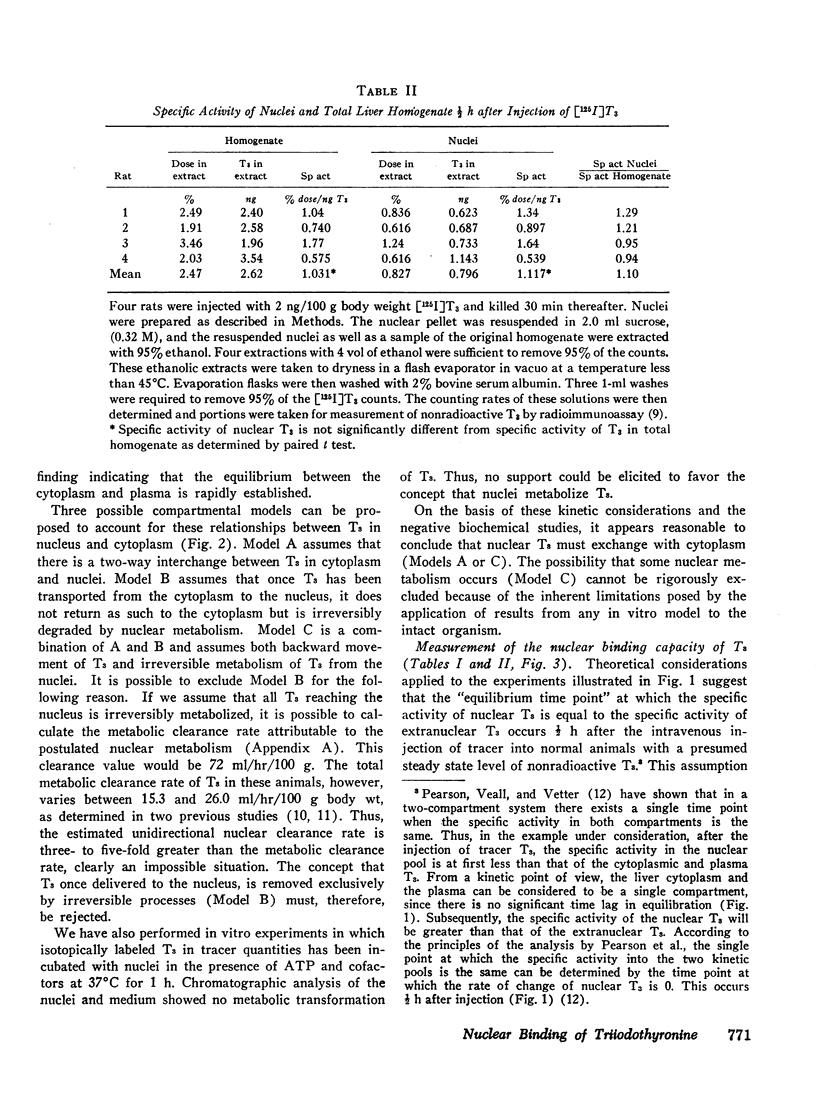
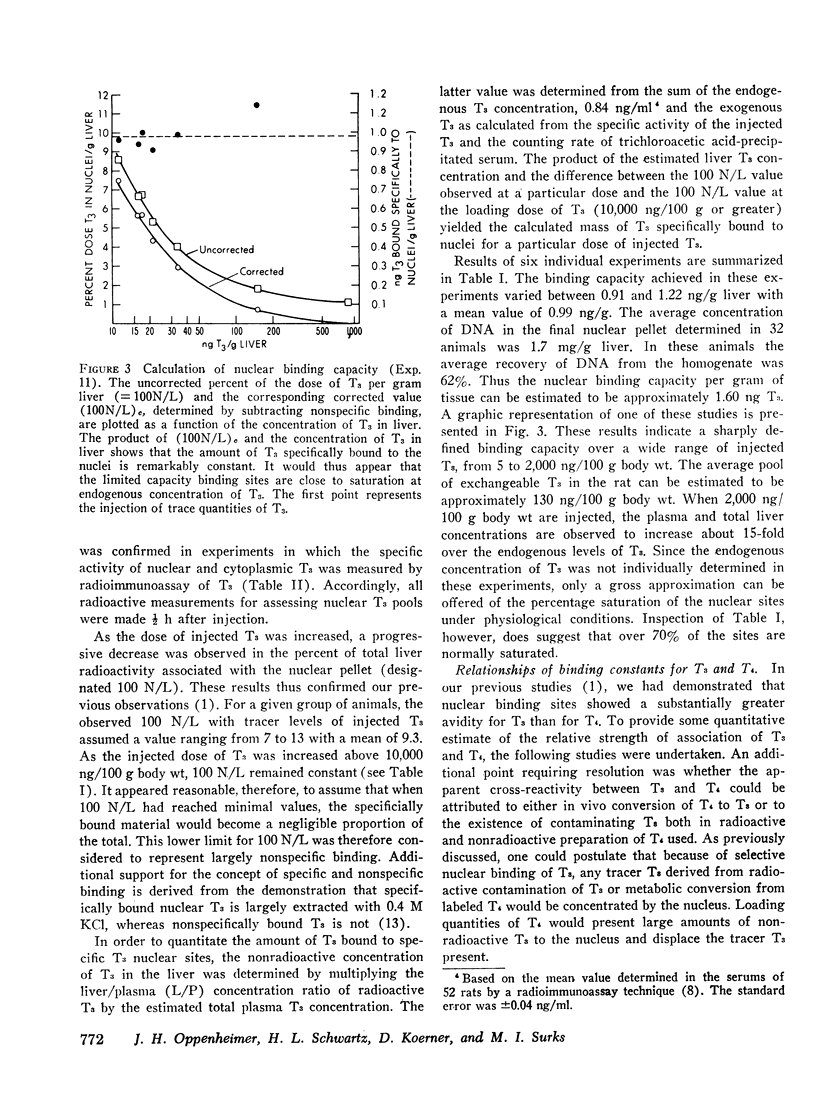
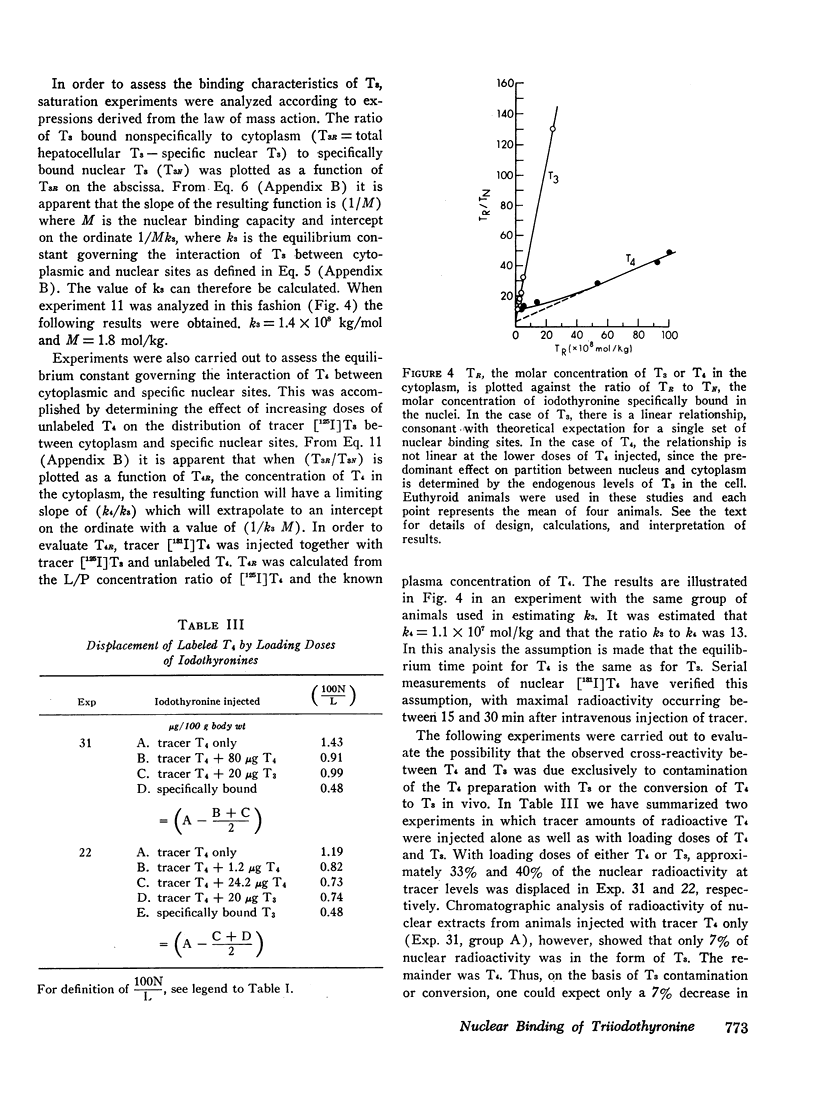
Further studies have been performed to define the kinetic characteristics of nuclear triiodothyronine (T3) binding sites in rat liver (J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1972. 35: 330). Sequential determination of labeled T3 associated with nuclei and cytoplasm over a 4-h period allowed analysis of the relationship of T3 in nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments. A rapid interchange of hormone between nuclei and cytoplasm was demonstrated, and in vitro incubation experiments with nuclei yielded no evidence favoring metabolic transformation of T3 by the nuclei. In vivo displacement experiments were performed by subcellular fractionation of liver ½ h after injection of [125I]T3 with increasing quantities of unlabeled T3. The nuclear binding capacity for T3 could be defined (0.52 ng/mg DNA). Analysis of these experiments also allowed an estimation of the association constant of nuclear sites for T3 (4.7 × 1011M−1). The affinity of these sites for T3 was estimated to be 20-40 fold greater than for thyroxine (T4). Chromatographic analysis of the nuclear radioactivity after injection of labeled T4 indicated that the binding of T4 by the nucleus could not be attributed to in vivo conversion of T4 to T3 but reflected intrinsic cross-reactivity of the two iodothyronines at the nuclear binding sites.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellabarba D., Peterson R. E., Sterling K. An improved method for chromatography of iodothyronines. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Feb;28(2):305–307. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-2-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein G., Artz S. A., Hasen J., Oppenheimer J. H. Hepatic accumulation of 125I-thyroxine in the rat: augmentation by phenobarbital and chlordane. Endocrinology. 1968 Feb;82(2):406–409. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-2-406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman L. E., Ingbar S. H., Sterling K. Conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3) in athyreotic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):855–864. doi: 10.1172/JCI106304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman D., Funder J. W., Edelman I. S. Subcellular mechanisms in the action of adrenal steroids. Am J Med. 1972 Nov;53(5):545–560. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., PITT-RIVERS R. The identification of 3:5:3'-L-triiodothyronine in human plasma. Lancet. 1952 Mar 1;1(6705):439–441. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)91952-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griswold M. D., Fischer M. S., Cohen P. P. Temperature-dependent intracellular distribution of thyroxine in amphibian liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1486–1489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSITER W. R., STANBURY J. B. The in vivo conversion of thyroxine to 3:5:3'triiodothyronine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Aug;18(8):903–906. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-8-903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEUCHTENBERGER C., VENDRELY R., VENDRELY C. A comparison of the content of desoxyribosenucleic acid (DNA) in isolated animal nuclei by cytochemical and chemical methods. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1951 Jan;37(1):33–38. doi: 10.1073/pnas.37.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Shapiro H. C., Bernstein G., Surks M. I. Differences in primary cellular factors influencing the metabolism and distribution of 3,5,3'-L-triiodothyronine and L-thyroxine. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):1016–1024. doi: 10.1172/JCI106301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Propylthiouracil inhibits the conversion of L-thyroxine to L-triiodothyronine. An explanation of the antithyroxine effect of propylthiouracil and evidence supporting the concept that triiodothyronine is the active thyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2493–2497. doi: 10.1172/JCI107063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON J. D., VEALL N., VETTER H. A practical method for plasma albumin turnover studies. Strahlentherapie. 1958;107(SONDERBD):290–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Quantitation of extrathyroidal conversion of L-thyroxine to 3,5,3'-triiodo-L-thyronine in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1124–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI106584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel E., Tobias C. A. End-organ effects of thyroid hormones: subcellular interactions in cultured cells. Science. 1966 Aug 12;153(3737):763–765. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3737.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Koerner D., Dillman W., Oppenheimer J. H. Limited capacity binding sites for L-triiodothyronine in rat liver nuclei. Localization to the chromatin and partial characterization of the L-triiodothyronine-chromatin complex. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7066–7072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Schadlow A. R., Oppenheimer J. H. A new radioimmunoassay for plasma L-triiodothyronine: measurements in thyroid disease and in patients maintained on hormonal replacement. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3104–3113. doi: 10.1172/JCI107137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Schadlow A. R., Stock J. M., Oppenheimer J. H. Determination of iodothyronine absorption and conversion of L-thyroxine (T 4 ) to L-triiodothyronine (T 3 ) using turnover rate techniques. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):805–811. doi: 10.1172/JCI107244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Widnell C. C. Ribonucleic acid synthesis during the early action of thyroid hormones. Biochem J. 1966 Feb;98(2):604–620. doi: 10.1042/bj0980604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpert E. M., Martinez M., Oppenheimer J. H. Radioiodinated impurities in commercial preparations of 131-I-thyroxine and their effect on the measurement of free thyroxine in human serum by equilibrium dialysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Mar;27(3):421–428. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-3-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. A procedure for the isolation of enzymically active rat-liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):313–317. doi: 10.1042/bj0920313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



