Abstract
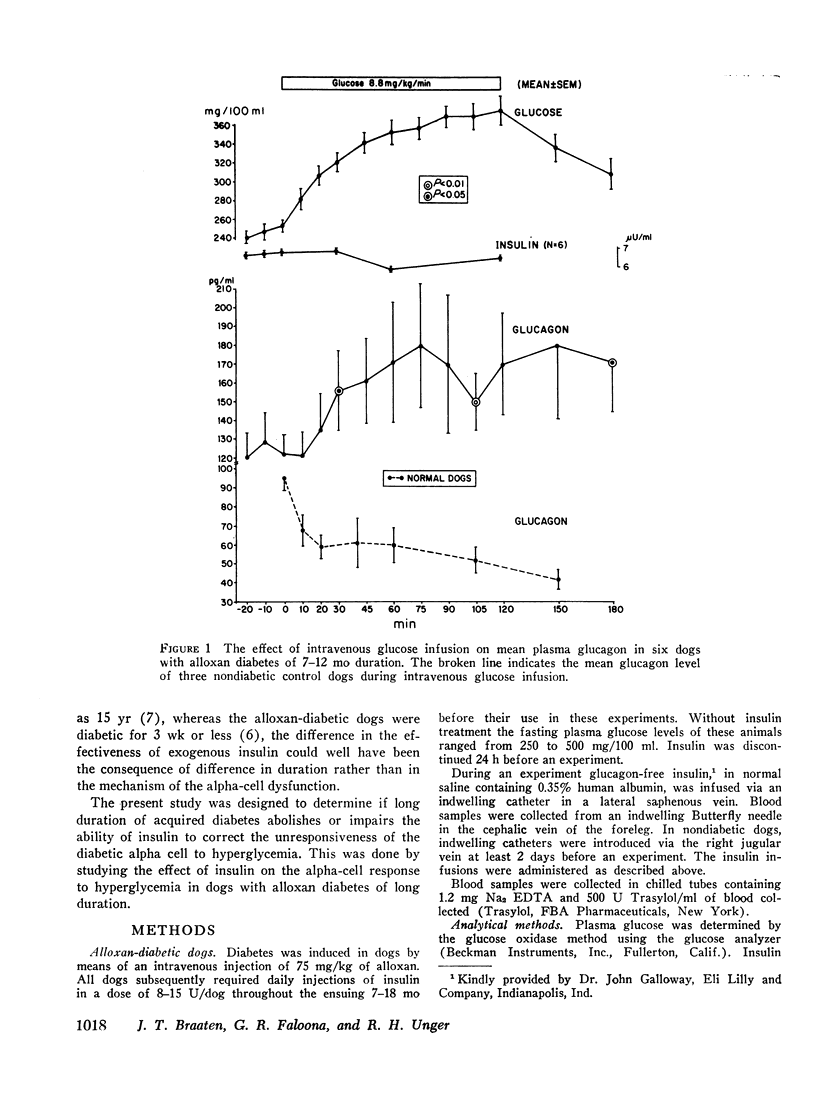
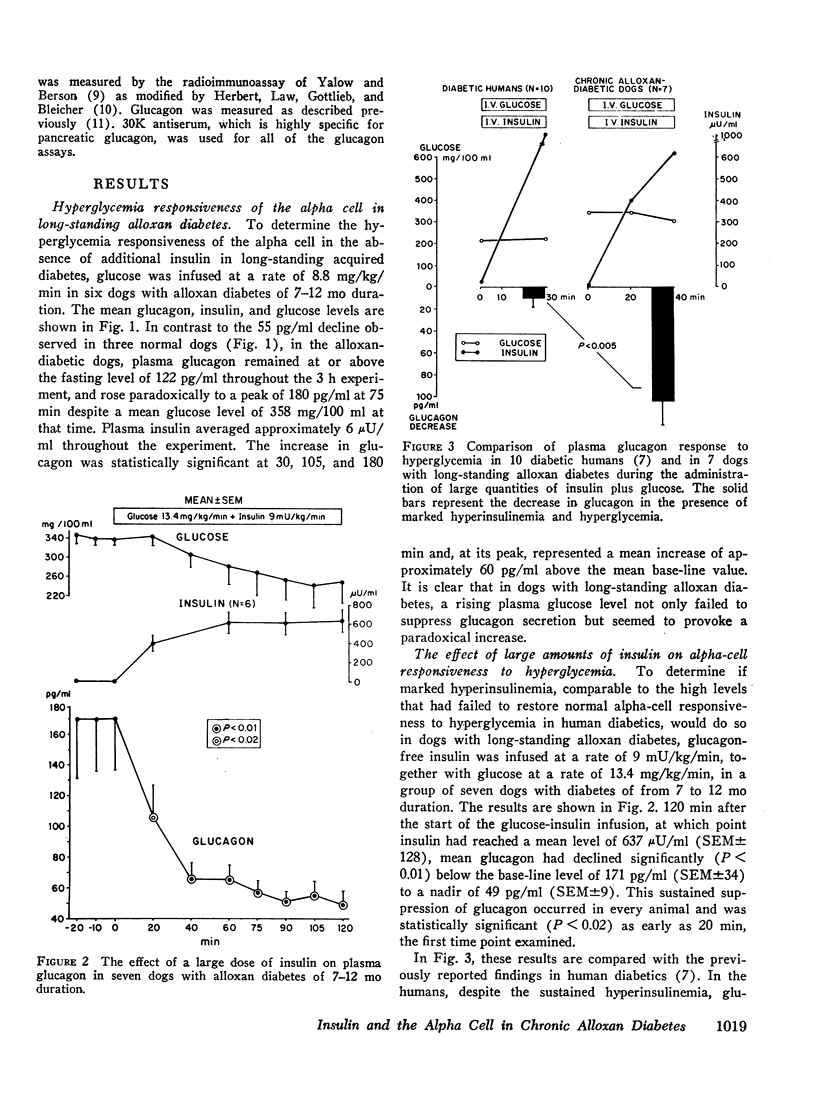
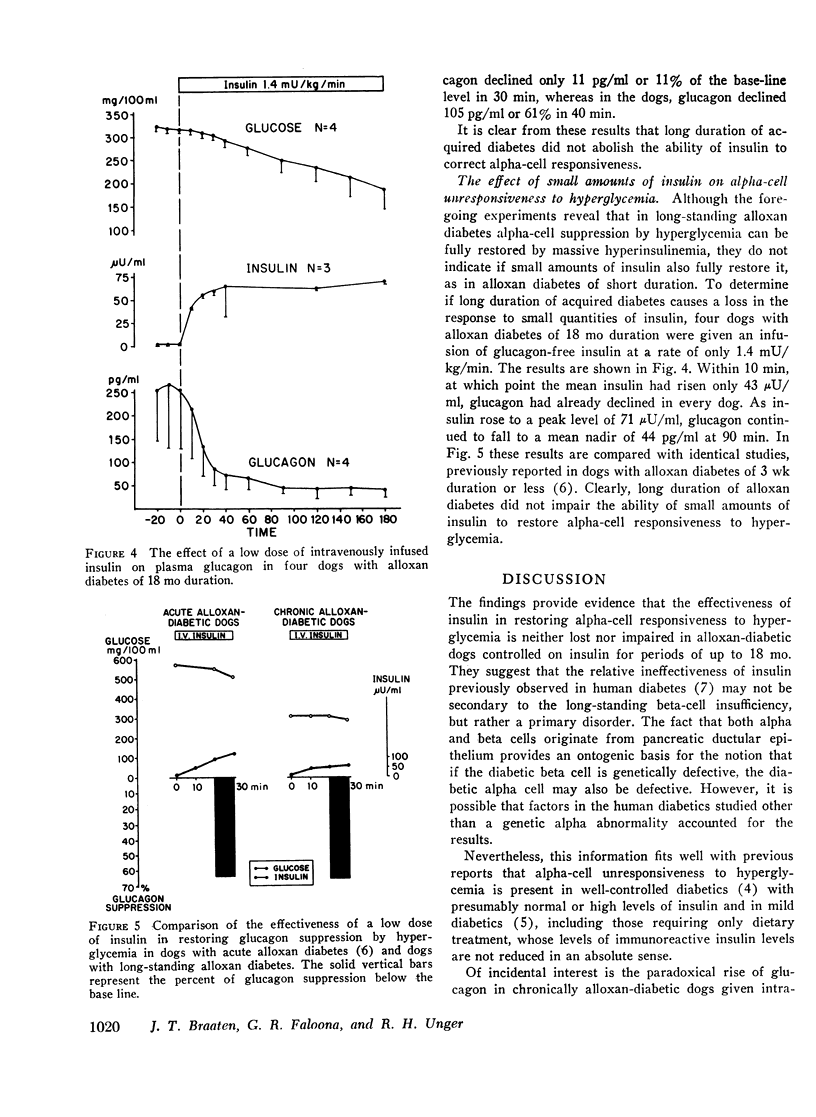
In acute experimental diabetes in animals, alpha-cell unresponsiveness to hyperglycemia can be promptly corrected by insulin, but in human diabetes, even massive doses of insulin have little effect. To determine if this inability of insulin to correct the alpha-cell abnormality in man is merely the consequence of the long duration of the diabetic state (rather than of a difference in mechanism), the effect of insulin was studied in alloxan diabetes of long duration. Alloxan-diabetic dogs were maintained for 7-18 mo and treated daily with insulin. When glucose was infused without insulin, glucagon did not decline but rose paradoxically. However, when insulin was infused at a rate of 9 mU/kg/min together with glucose, a prompt decline in glucagon from a base-line average of 171 pg/ml SEM±34 to a nadir of 41 pg/ml SEM±9 was observed. This decline indicated that alpha-cell responsiveness to hyperglycemia is completely restored by large quantities of insulin. To determine if small amounts of insulin would similarly restore alpha-cell responsiveness in long-standing experimental diabetes, 1.4 mU/kg/min was infused. By the time the mean insulin level had risen 43 μU/ml, glucagon had declined significantly and ultimately fell to a nadir of 44 pg/ml. It is concluded from these studies that alpha-cell responsiveness to hyperglycemia can be fully restored in long-standing alloxandiabetic dogs as readily as in acutely diabetic dogs. Its ineffectiveness in restoring alpha-cell responsiveness to hyperglycemia in human diabetes may not, therefore, be related to duration of the diabetic state, and may reflect a primary alpha-cell defect.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguilar-Parada E., Eisentraut A. M., Unger R. H. Pancreatic glucagon secretion in normal and diabetic subjects. Am J Med Sci. 1969 Jun;257(6):415–419. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196906000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan K. D., McCarroll A. M. Abnormalities of glucagon metabolism in untreated diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1972 Dec 30;2(7792):1394–1395. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92964-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. A., Faloona G. R., Aguilar-Parada E., Unger R. H. Abnormal alpha-cell function in diabetes. Response to carbohydrate and protein ingestion. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jul 16;283(3):109–115. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197007162830301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. A., Faloona G. R., Unger R. H. The effect of experimental insulin deficiency on glucagon secretion. J Clin Invest. 1971 Sep;50(9):1992–1999. doi: 10.1172/JCI106691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNGER R. H., EISENTRAUT A. M., McCALL M. S., MADISON L. L. Measurements of endogenous glucagon in plasma and the influence of blood glucose concentration upon its secretion. J Clin Invest. 1962 Apr;41:682–689. doi: 10.1172/JCI104525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Aguilar-Parada E., Müller W. A., Eisentraut A. M. Studies of pancreatic alpha cell function in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):837–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI106297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



