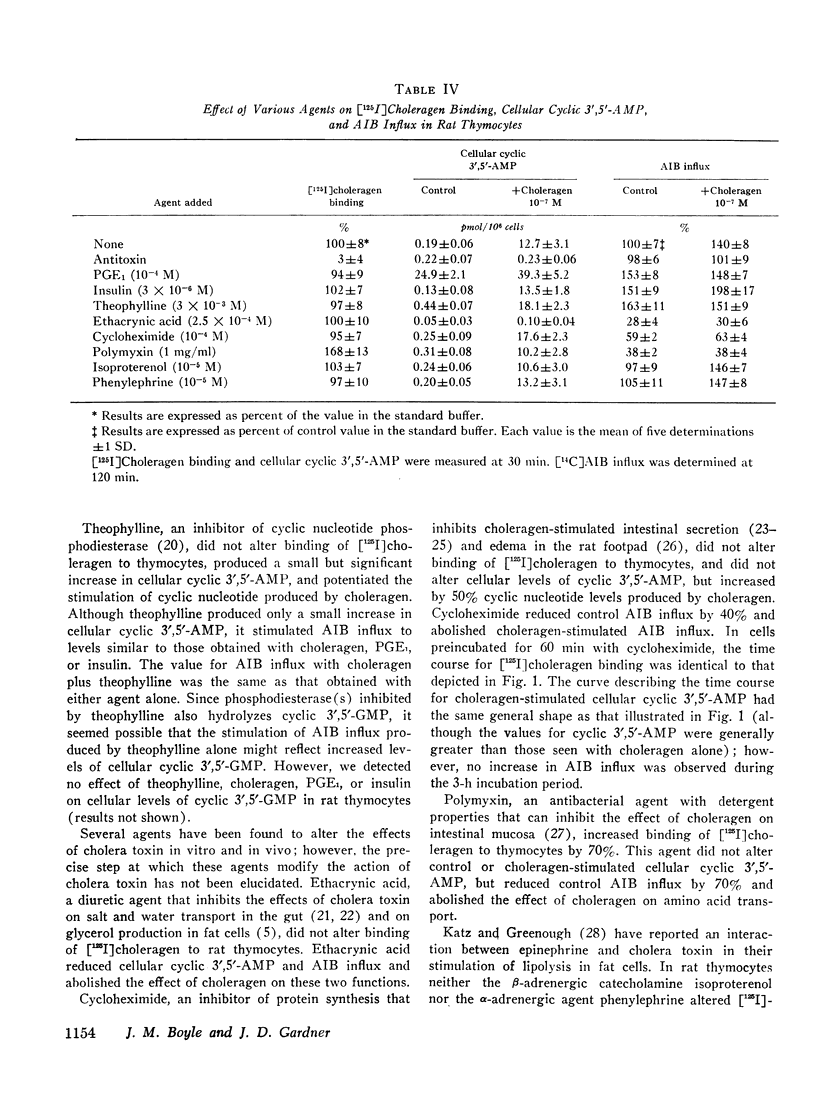
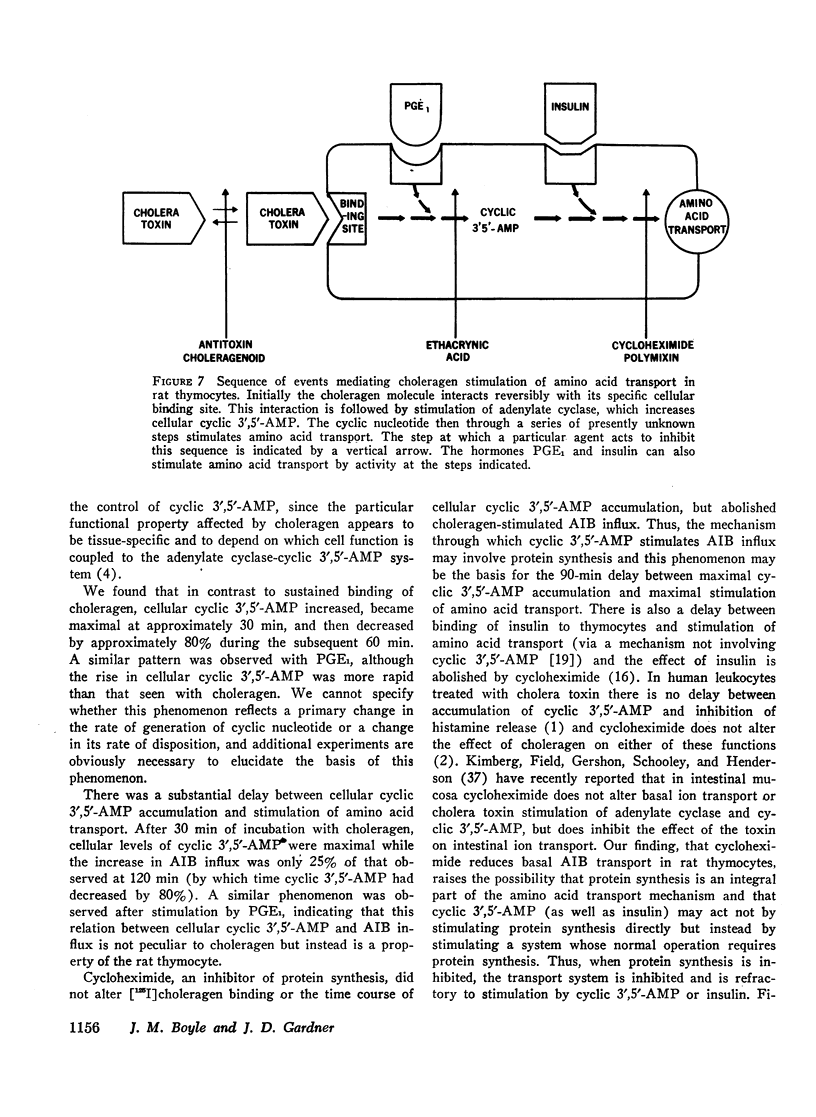
Abstract
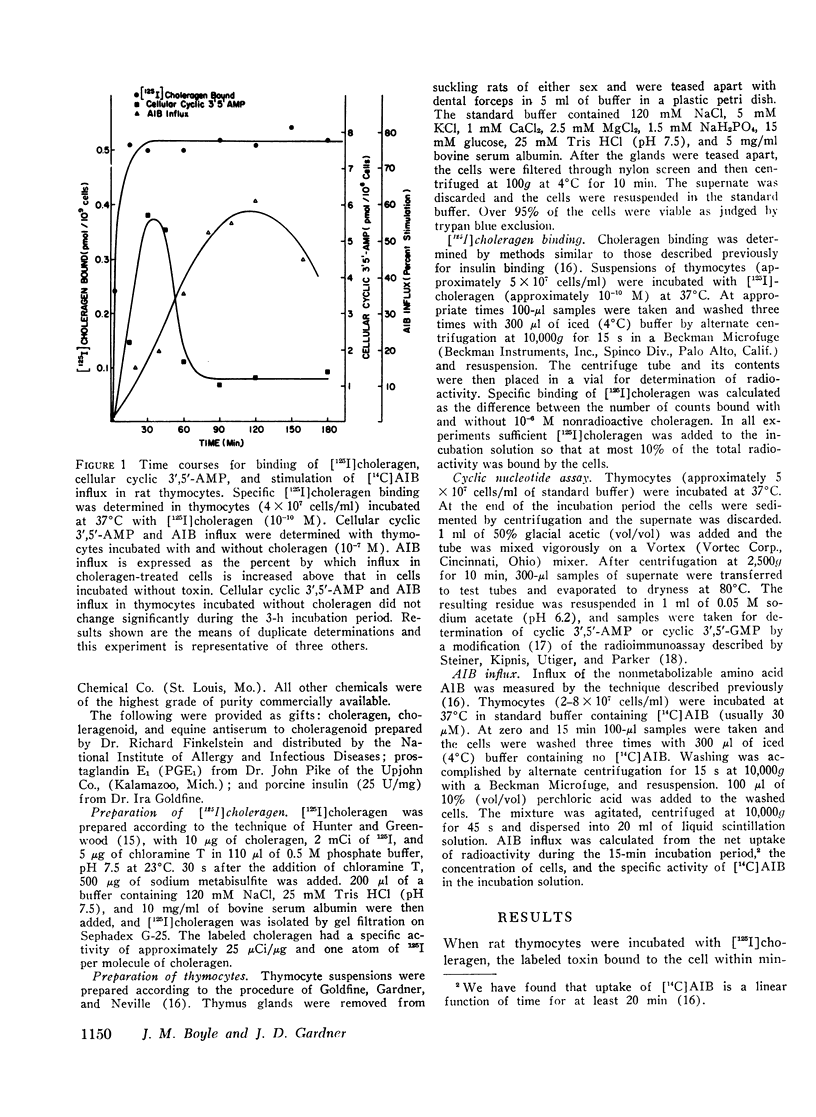
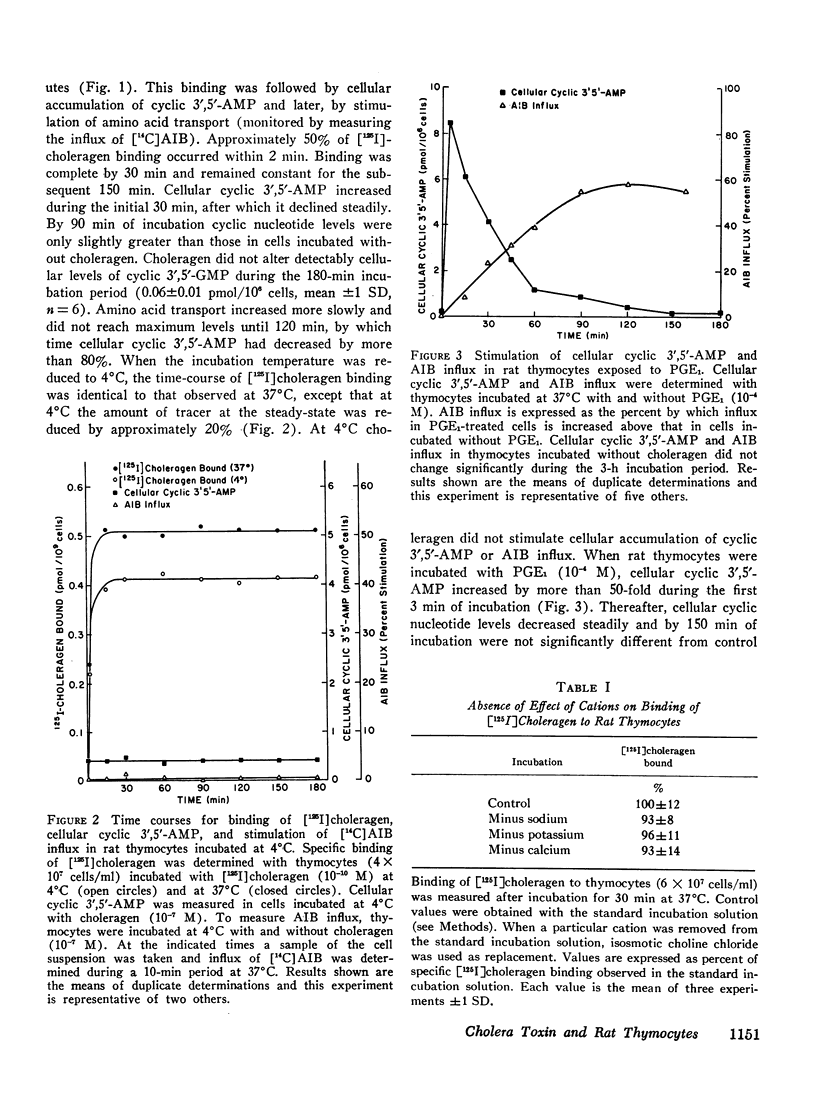
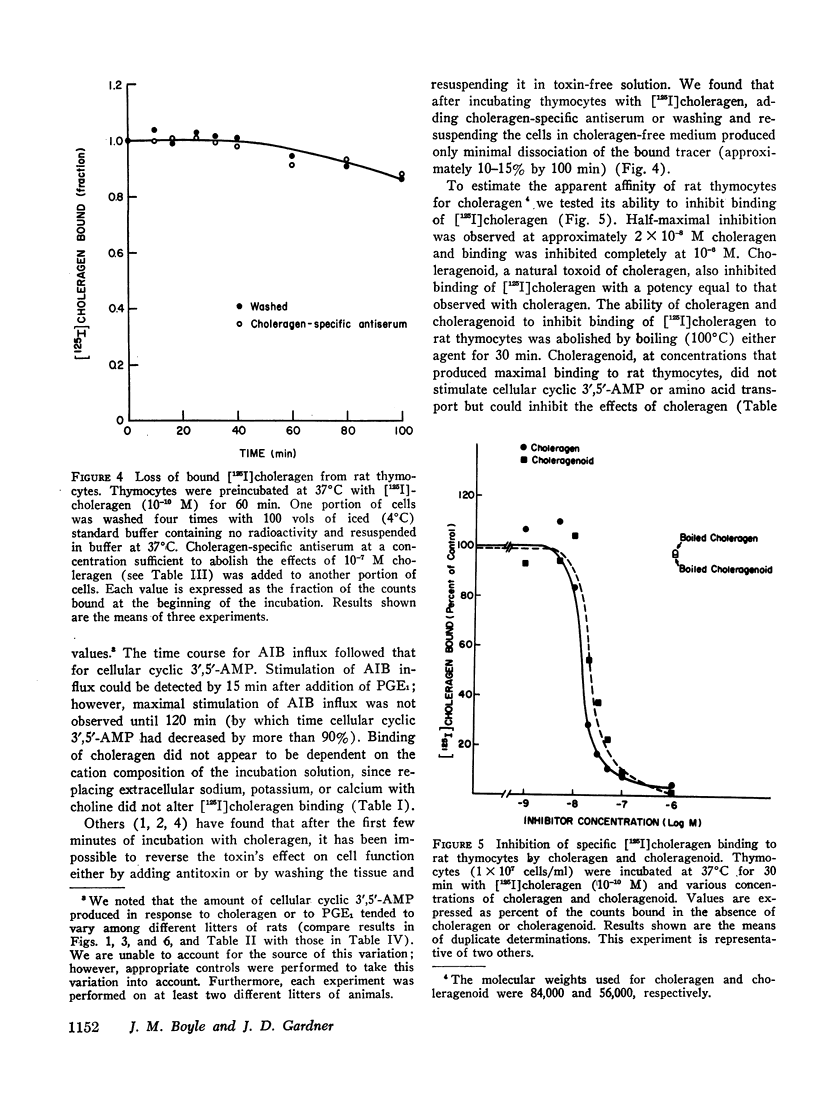
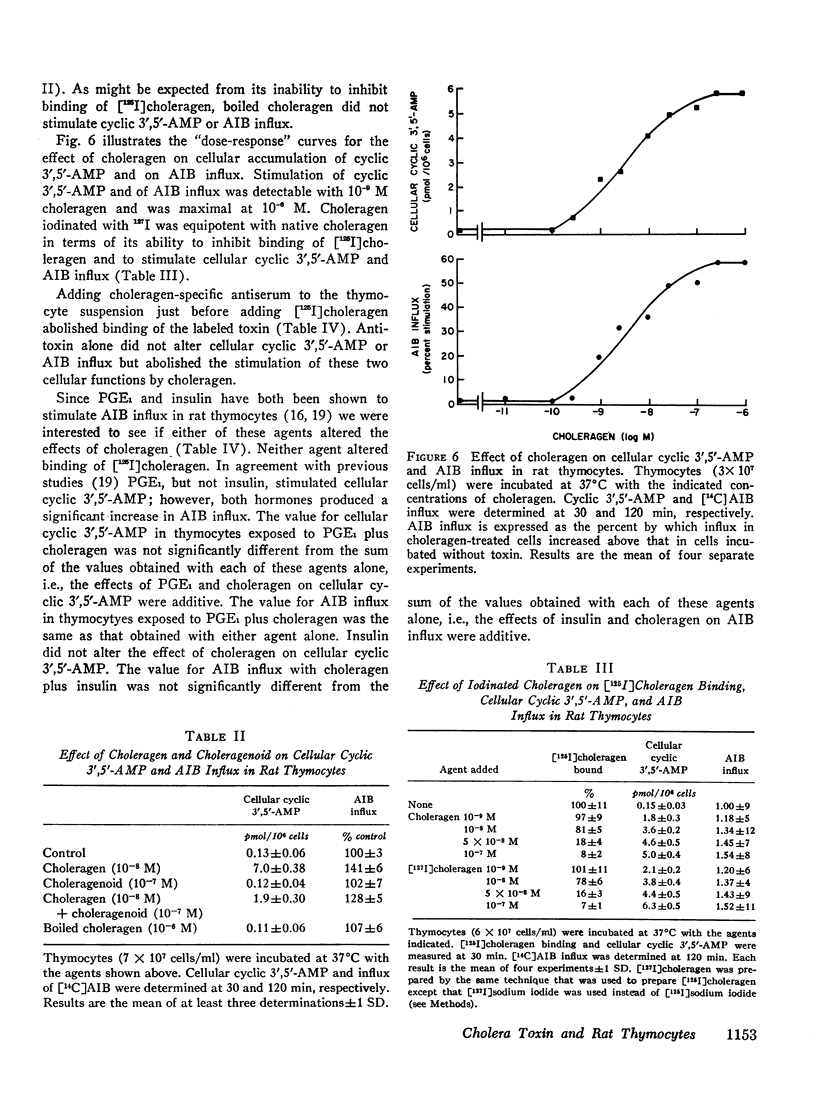
We have found that in rat thymocytes binding of [125I]choleragen is followed by cellular accumulation of cyclic 3′,5′-AMP which, in turn, is followed by stimulation of amino acid transport. Binding of cholera toxin was complete by 30 min and remained constant for the subsequent 150 min. After stimulation by choleragen, cellular cyclic 3′,5′-AMP became maximal by 30 min, after which it declined steadily so that by 90 min of incubation, cellular cyclic nucleotide levels were only 20% of those seen at 30 min. Stimulation of amino acid transport, although detectable by 15 min, did not become maximal until 120 min (by which time cellular cyclic 3′,5′-AMP had decreased by more than 80%). We have also used this system to delineate the step at which various pharmacologic agents and hormones act to alter the sequence of events mediating the response of rat thymocytes to cholera toxin. The ability of cycloheximide to abolish choleragen-stimulated amino acid influx without reducing [125I]choleragen binding or cellular cyclic 3′,5′-AMP suggests that cyclic nucleotide stimulation of amino acid transport includes a step involving protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bilezikian J. P., Aurbach G. D. A beta-adrenergic receptor of the turkey erythrocyte. I. Binding of catecholamine and relationship to adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5577–5583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilezikian J. P., Aurbach G. D. A beta-adrenergic receptor of the turkey erythrocyte. II. Characterization and solubilization of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5584–5589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Pohl S. L., Rodbell M., Sundby F. The glucagon-sensitive adenylate cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. VII. Hormonal stimulation: reversibility and dependence on concentration of free hormone. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2038–2043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Lehrer R. I., Lichtenstein L. M., Weissmann G., Zurier R. Effects of cholera enterotoxin on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and neutrophil function. Comparison with other compounds which stimulate leukocyte adenyl cyclase. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):698–708. doi: 10.1172/JCI107231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. C., Curlin G. T., Greenough W. B. Response of canine Thiry-Vella jejunal loops to cholera exotoxin and its modification by ethacrynic acid. J Infect Dis. 1969 Sep;120(3):332–338. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.3.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. C., Rohde J. E., Sharp G. W. Intestinal adenyl-cyclase activity in human cholera. Lancet. 1971 May 8;1(7706):939–941. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91443-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. C., Rohde J. E., Sharp G. W. Properties of adenyl cyclase from human jejunal mucosa during naturally acquired cholera and convalescence. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):731–740. doi: 10.1172/JCI106867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Cholera toxin-fat cell interaction and the mechanism of activation of the lipolytic response. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3567–3577. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Gangliosides and membrane receptors for cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3558–3566. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin with cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3547–3558. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Vibrio cholerae choleragenoid. Mechanism of inhibition of cholera toxin action. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3577–3581. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Aurbach G. D. Use of polyethylene glycol to separate free and antibody-bound peptide hormones in radioimmunoassays. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Nov;33(5):732–738. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-5-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. R. The effect of cycloheximide on membrane transport in Euglena. A comparative study with nigericin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6144–6151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., al-Awqati Q., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effect of cholera enterotoxin on ion transport across isolated ileal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):796–804. doi: 10.1172/JCI106874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: observations with purified antigens and the ligated ileal loop model. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):464–467. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.464-467.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., LaRue M. K., LoSpalluto J. J. Properties of the cholera exo-enterotoxin: effects of dispersing agents and reducing agents in gel filtration and electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):934–944. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.934-944.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Klaeveman H. L., Bilezikian J. P., Aurbach G. D. Effect of beta-adrenergic catecholamines on sodium transport in turkey erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5590–5597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Gardner J. D., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin action in isolated rat thymocytes. I. Binding of 125 I-insulin and stimulation of -aminoisobutyric acid transport. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6919–6926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Sherline P. Insulin action in isolated rat thymocytes. II. Independence of insulin and cyclic adenosine monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6927–6931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayer D. T., Serebro H. A., Iber F. L., Hendrix T. R. Effect of cycloheximide on unidirectional sodium fluxes in the jejunum after cholera exotoxin exposure. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jun;58(6):815–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Chen L. C., Sharp G. W. Intestinal adenyl-cyclase activity in canine cholera: correlation with fluid accumulation. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):377–381. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper D. T., Jr, Yardley J. H., Hendrix T. R. Reversal of cholera exotoxin-induced jejunal secretion by cycloheximide. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1970 May;126(5):258–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstein H. D., Feeley J. C., Richardson S. H. Titration of cholera antitoxin levels by passive hemagglutination tests using fresh and formalinized sheep erythrocytes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jan;133(1):120–124. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Gershon E., Schooley R. T., Henderson A. Effects of cycloheximide on the response of intestinal mucosa to cholera enterotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1376–1383. doi: 10.1172/JCI107310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein L. M., Henney C. S., Bourne H. R., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effects of cholera toxin on in vitro models of immediate and delayed hypersensitivity. Further evidence for the role of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):691–697. doi: 10.1172/JCI107230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson D. K., Ebel H., DiBona D. R., Sharp G. W. Localization of the action of cholera toxin on adenyl cyclase in mucosal epithelial cells of rabbit intestine. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2292–2298. doi: 10.1172/JCI107039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W., LoSpalluto J. J., Finkelstein R. A. Localization of cholera toxin in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):617–628. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Carpenter C. C., Jr, Elliott H. L., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effects of prostaglandins, theophylline, and cholera exotoxin upon transmucosal water and electrolyte movement in the canine jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jan;60(1):22–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Greenough W. B., 3rd, Carpenter C. C., Jr Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin and its mode of action. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Mar;35(1):1–13. doi: 10.1128/br.35.1.1-13.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow A. Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Sep;17(3):265–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer D. E., Lust W. D., Sircar B., Goldberg N. D. Elevated concentration of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in intestinal mucosa after treatment with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):851–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serebro H. A., Iber F. L., Yardley J. H., Hendrix T. R. Inhibition of cholera toxin action in the rabbit by cycloheximide. Gastroenterology. 1969 Mar;56(3):506–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by cholera toxin. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):266–269. doi: 10.1038/229266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Kipnis D. M., Utiger R., Parker C. Radioimmunoassay for the measurement of adenosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):367–373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan M., Pierce N. F., Greenough W. B., 3rd Stimulation of glycerol production in fat cells by cholera toxin. Nature. 1970 May 16;226(5246):658–659. doi: 10.1038/226658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



