Abstract
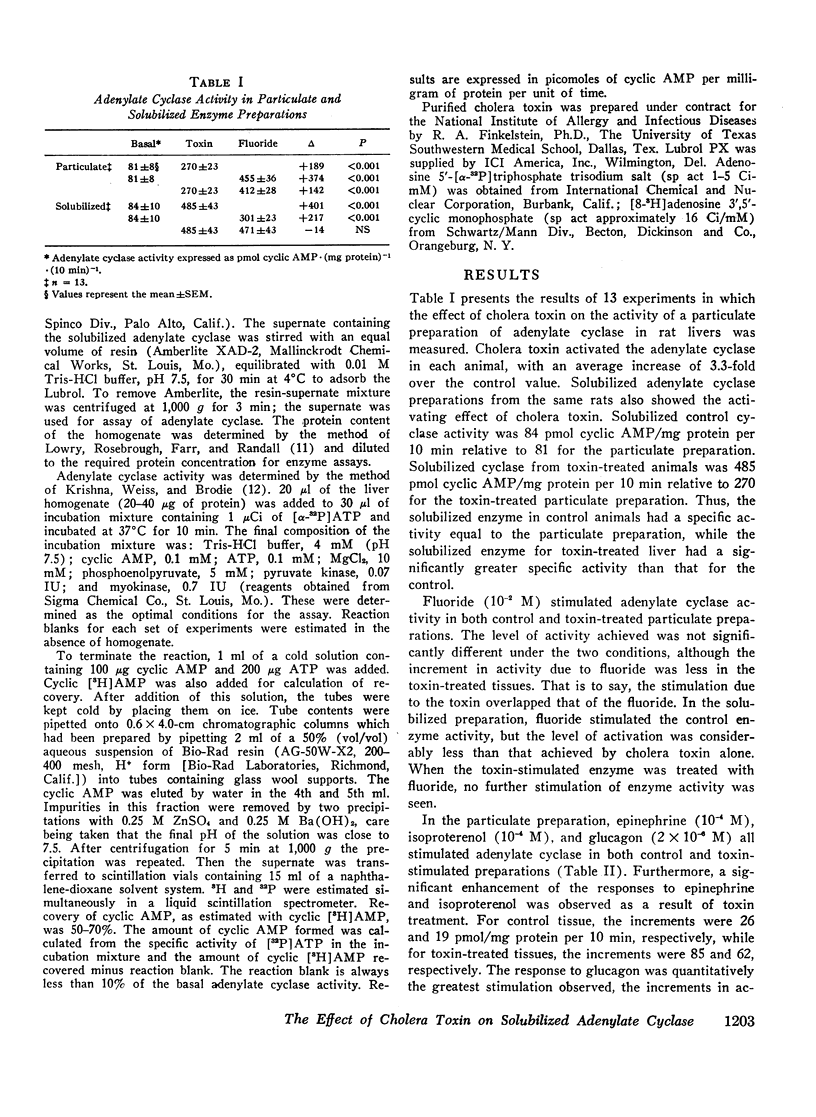
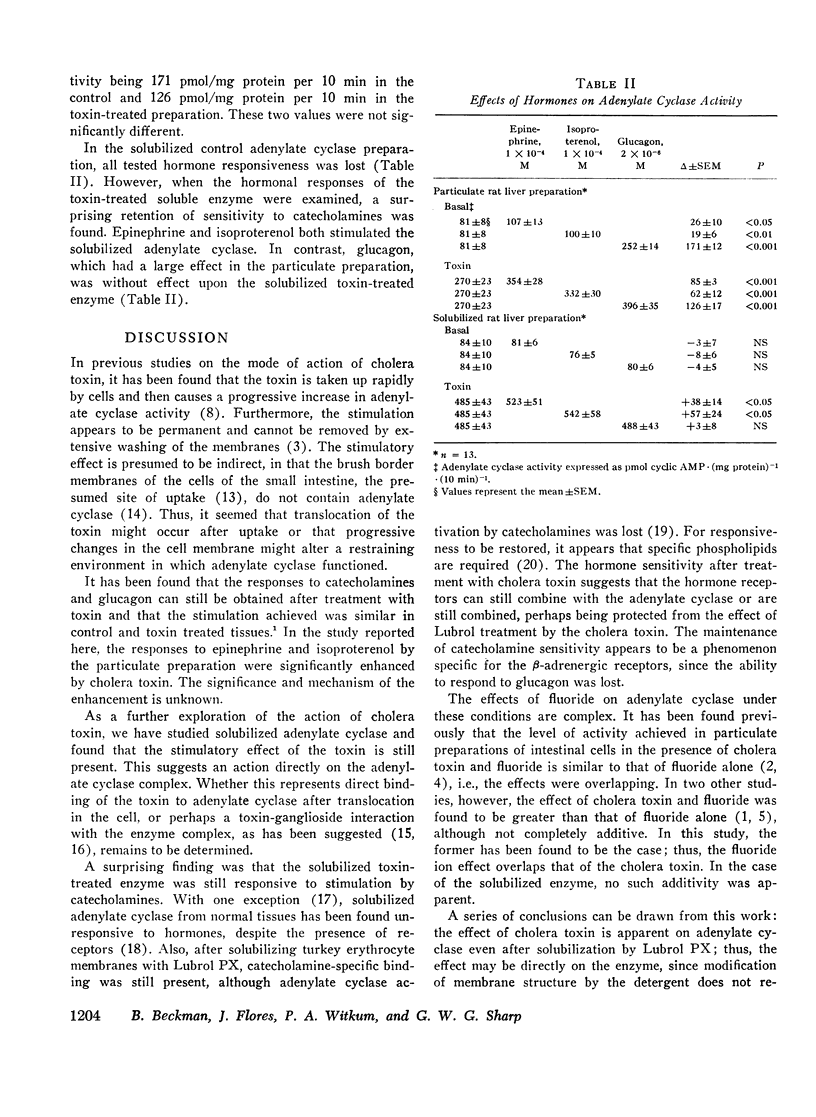
To gain further insight into the mechanism of action of cholera toxin, solubilized preparations of adenylate cyclase from control and toxin-treated rat livers were studied. Adenylate cyclase activity was measured in both particulate and solubilized form in rat liver under control conditions and after intravenous injection of cholera toxin. Cholera toxin caused a 3.3-fold activation of adenylate cyclase in the particulate preparation and a 5.8-fold increase in the solubilized preparation. Thus, the ability of cholera toxin to stimulate adenylate cyclase is present even when the enzyme membrane environment is disrupted. Furthermore, the solubilized enzyme, after treatment with cholera toxin, retained its ability to respond to catecholamines, but not to glucagon. In contrast, the control enzyme lost its responsiveness to catecholamines and glucagon after solubilization.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bilezikian J. P., Aurbach G. D. A beta-adrenergic receptor of the turkey erythrocyte. I. Binding of catecholamine and relationship to adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 25;248(16):5577–5583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. C., Rohde J. E., Sharp G. W. Intestinal adenyl-cyclase activity in human cholera. Lancet. 1971 May 8;1(7706):939–941. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91443-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Gangliosides and membrane receptors for cholera toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3558–3566. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curlin G. T., Craig J. P., Subong A., Carpenter C. C. Antitoxic immunity in experimental canine cholera. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):463–470. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Chen L. C., Sharp G. W. Intestinal adenyl-cyclase activity in canine cholera: correlation with fluid accumulation. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):377–381. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna G., Weiss B., Brodie B. B. A simple, sensitive method for the assay of adenyl cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Oct;163(2):379–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Haber E., O'Hara D. Identification of the cardiac beta-adrenergic receptor protein: solubilization and purification by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2828–2832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey G. S. Solubilization of myocardial adenyl cyclase: less of hormone responsiveness and activation by phospholipids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 30;185:449–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb45272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lospalluto J. J., Finkelstein R. A. Chemical and physical properties of cholera exo-enterotoxin (choleragen) and its spontaneously formed toxoid (choleragenoid). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):158–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90265-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J. Vasopressin-responsive, soluble adenylate cyclase from the rat renal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3742–3744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson D. K., Ebel H., DiBona D. R., Sharp G. W. Localization of the action of cholera toxin on adenyl cyclase in mucosal epithelial cells of rabbit intestine. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2292–2298. doi: 10.1172/JCI107039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. W., LoSpalluto J. J., Finkelstein R. A. Localization of cholera toxin in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):617–628. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Carpenter C. C., Jr, Elliott H. L., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effects of prostaglandins, theophylline, and cholera exotoxin upon transmucosal water and electrolyte movement in the canine jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jan;60(1):22–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. G., Bowser A. M., Feingold D. S. Partial purification and properties of UDPG dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 12;293(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90369-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S., Lipson L. C., Parkinson D. K. Action of cholera toxin to stimulate adenyl cyclase. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1971;84:200–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by cholera toxin. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):266–269. doi: 10.1038/229266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heyningen W. E., Carpenter C. C., Pierce N. F., Greenough W. B., 3rd Deactivation of cholera toxin by ganglioside. J Infect Dis. 1971 Oct;124(4):415–418. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



