Abstract
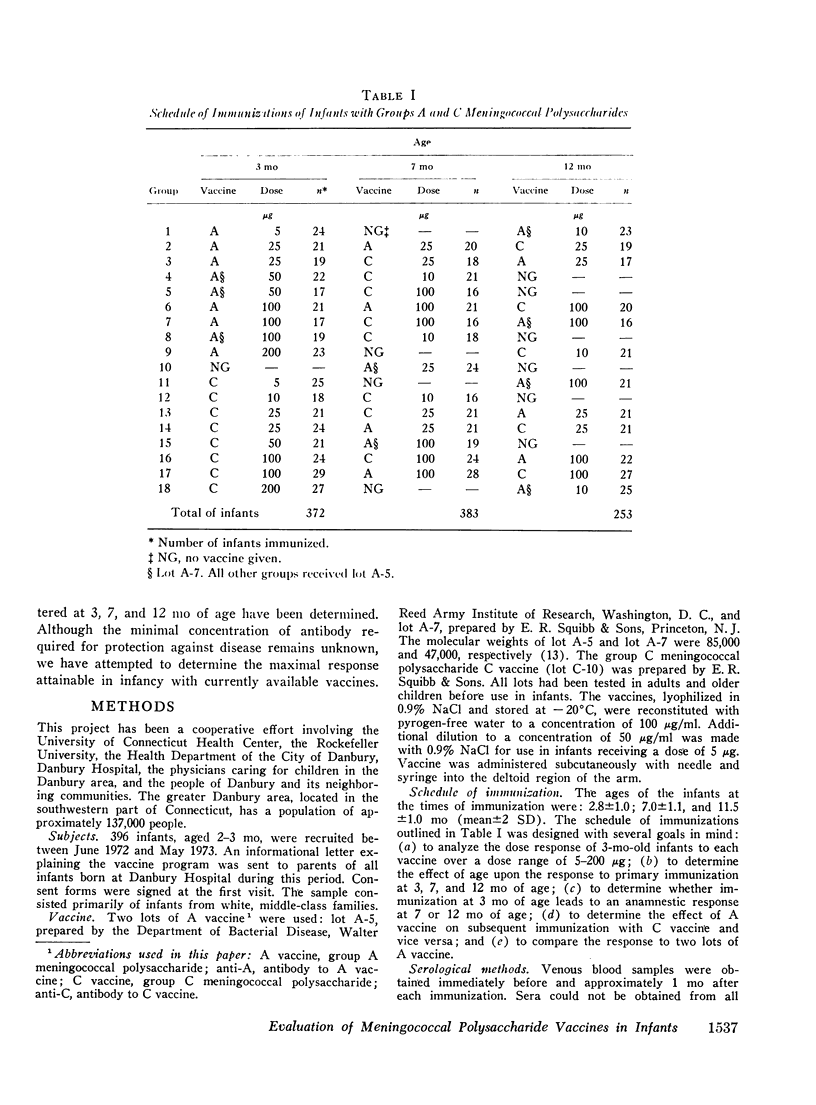
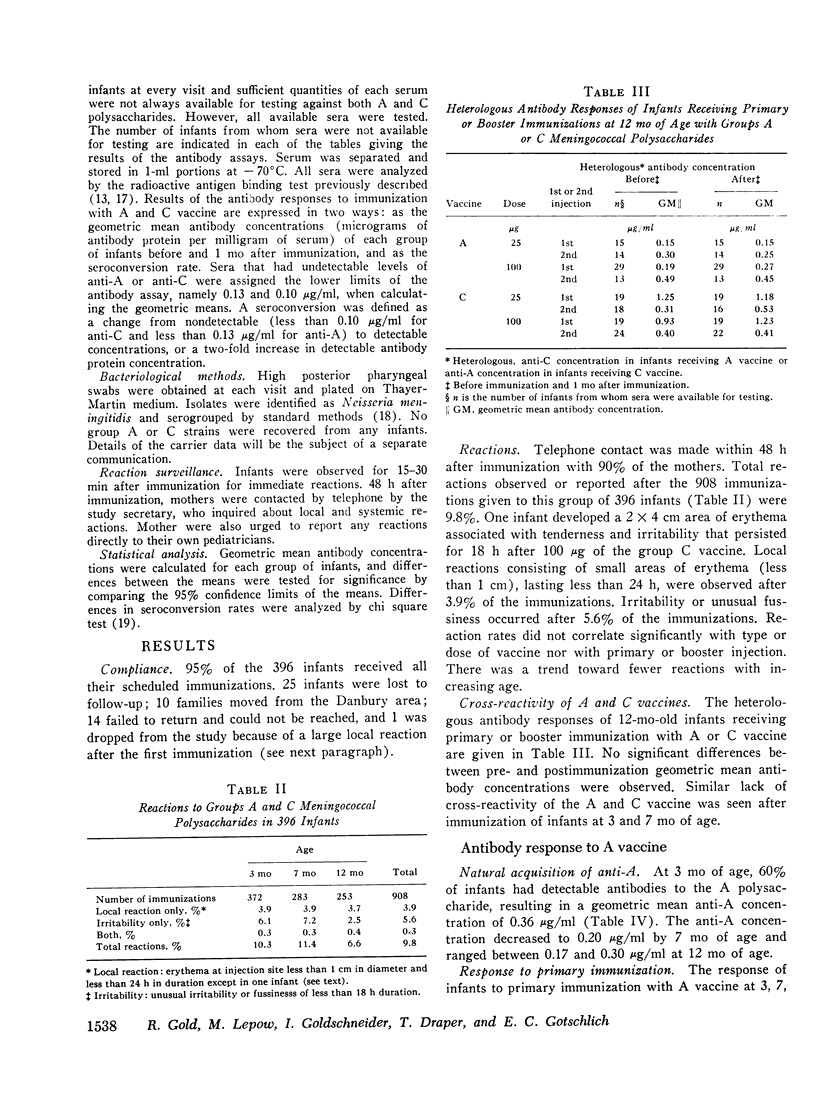
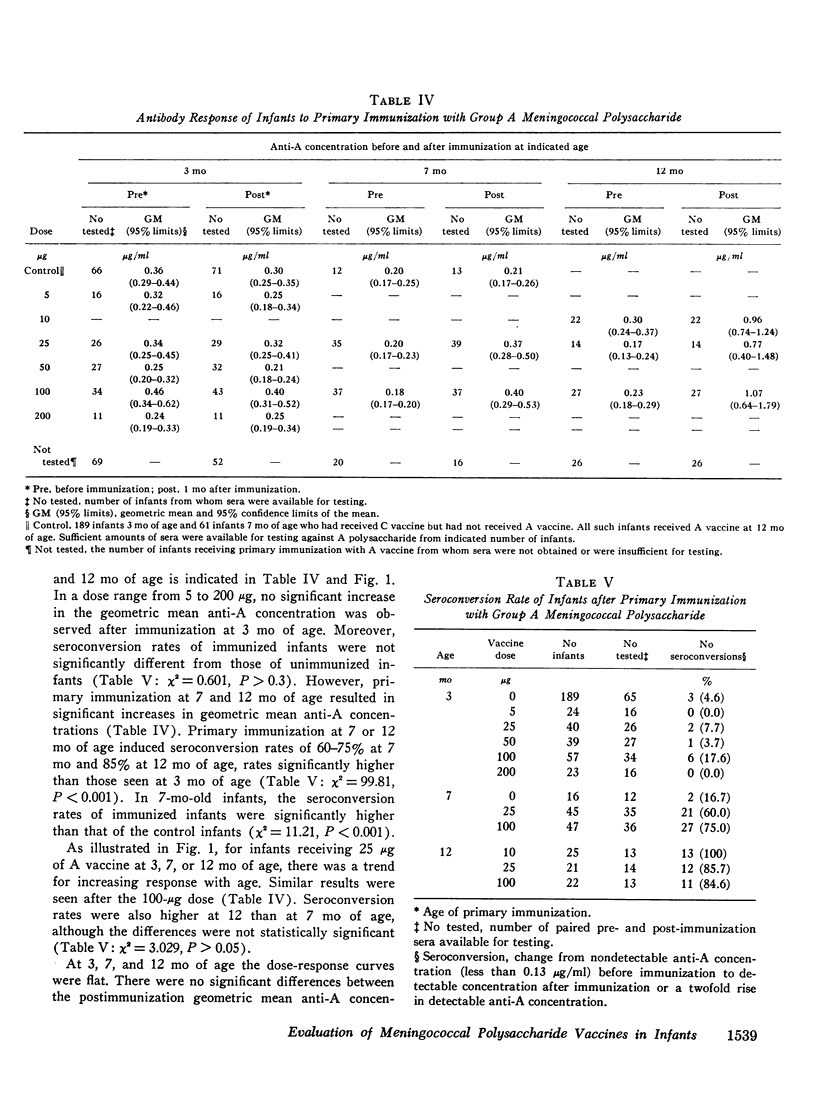
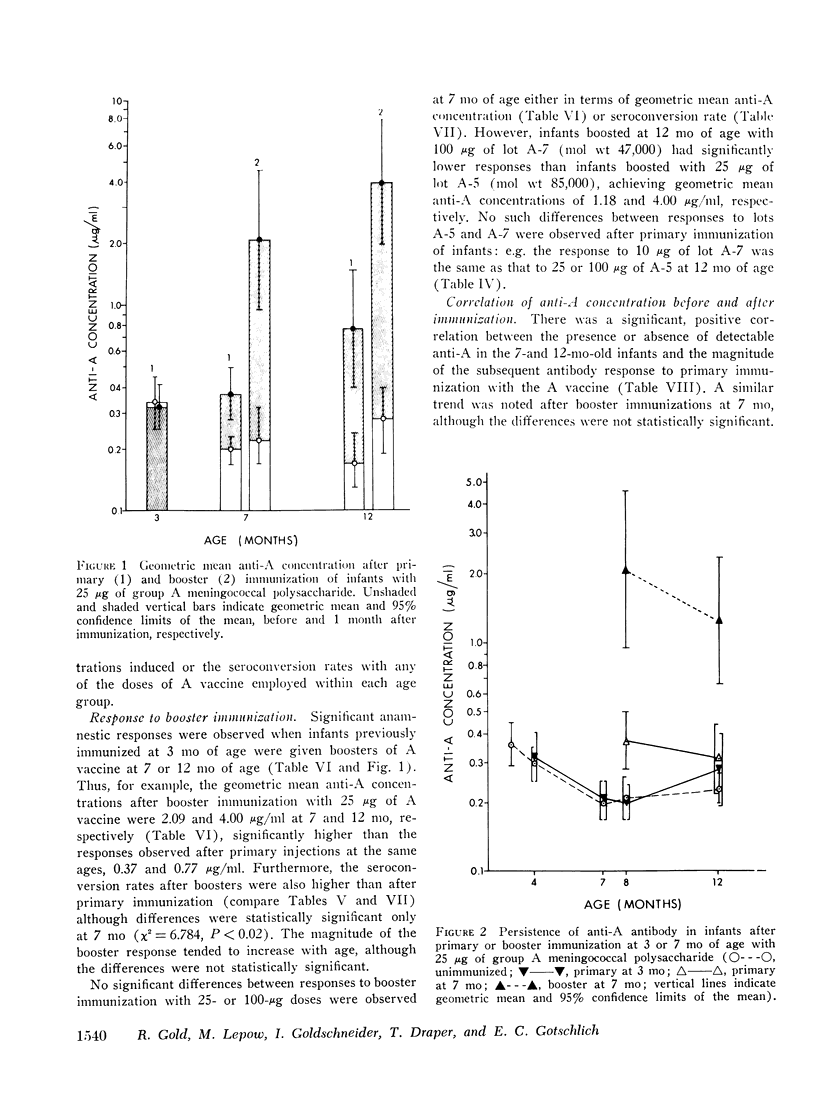
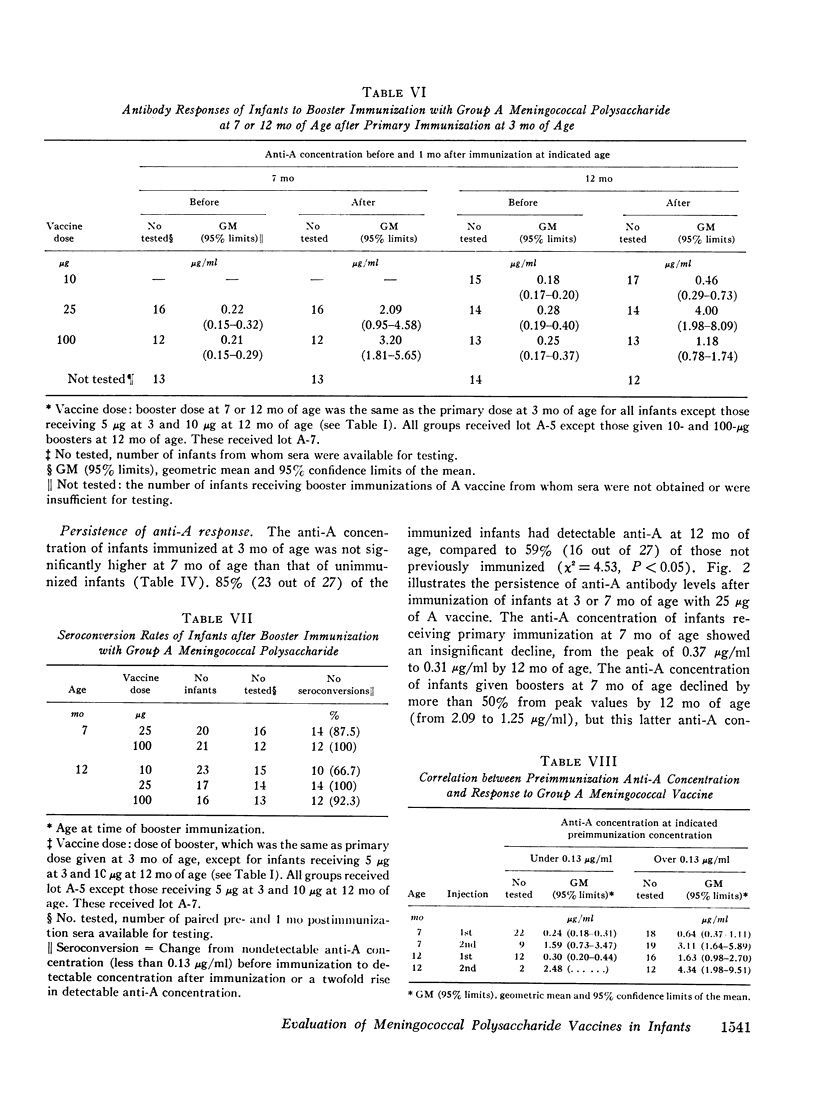
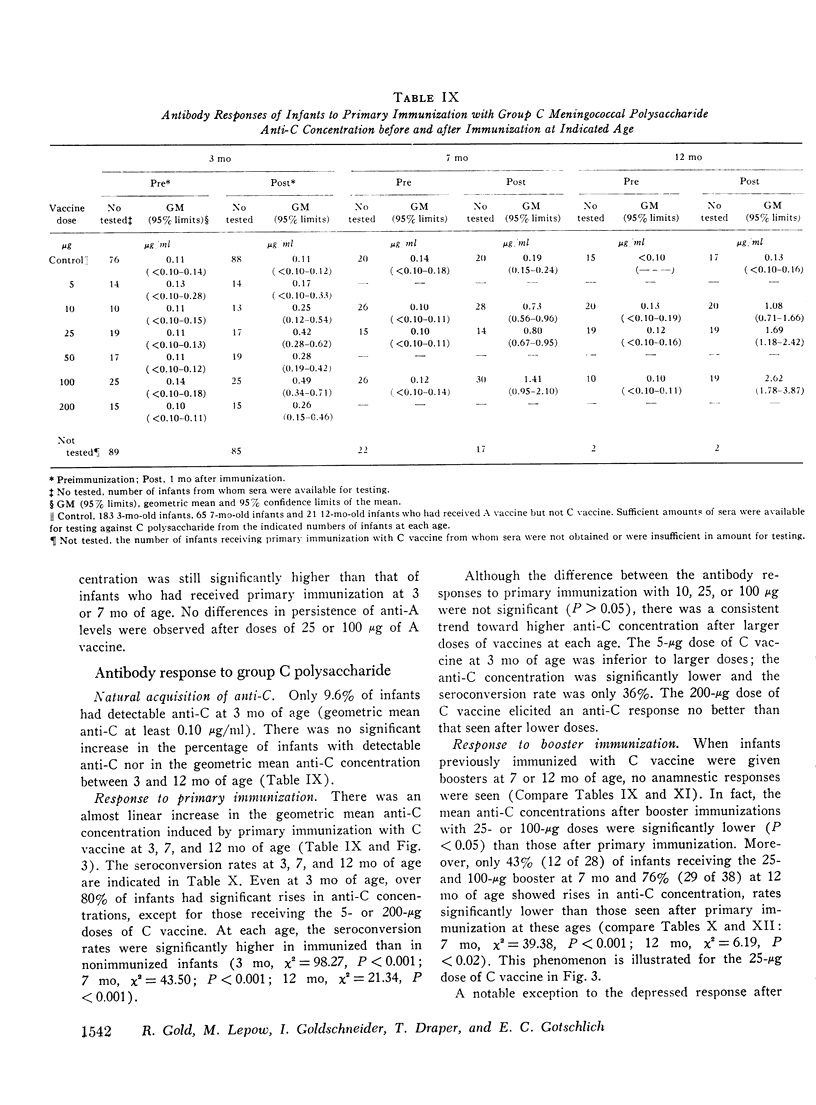
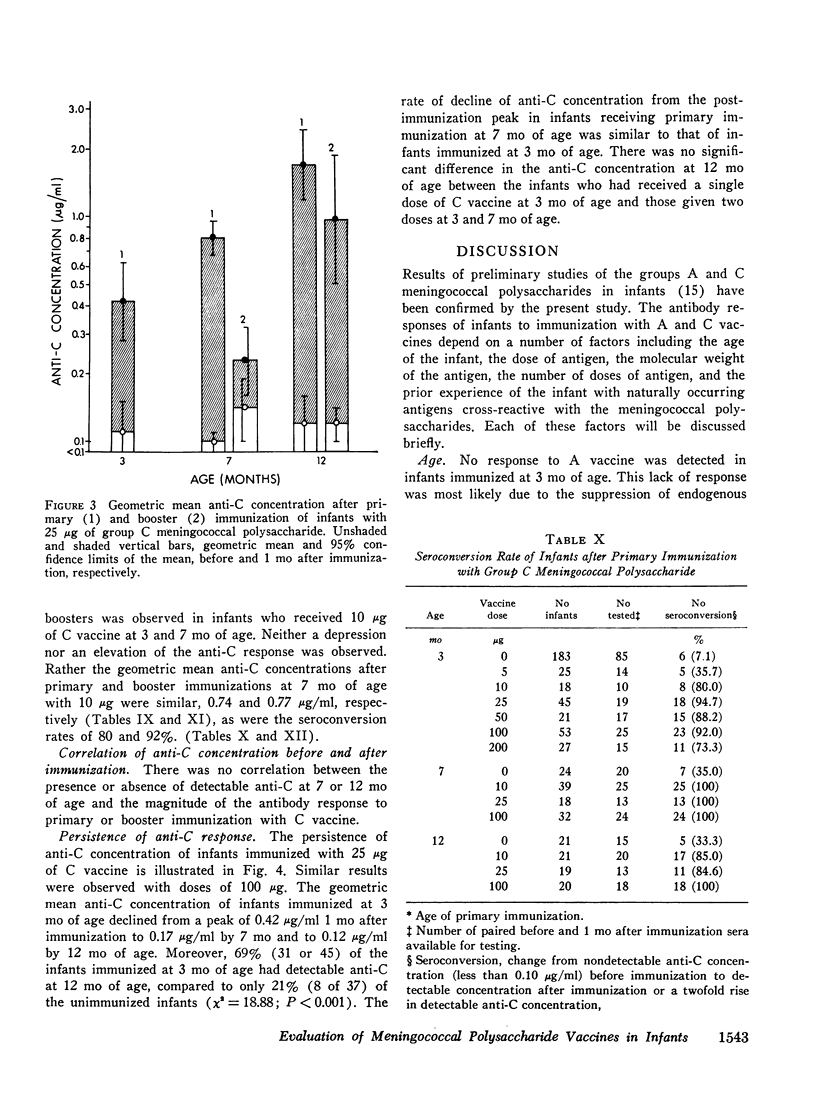
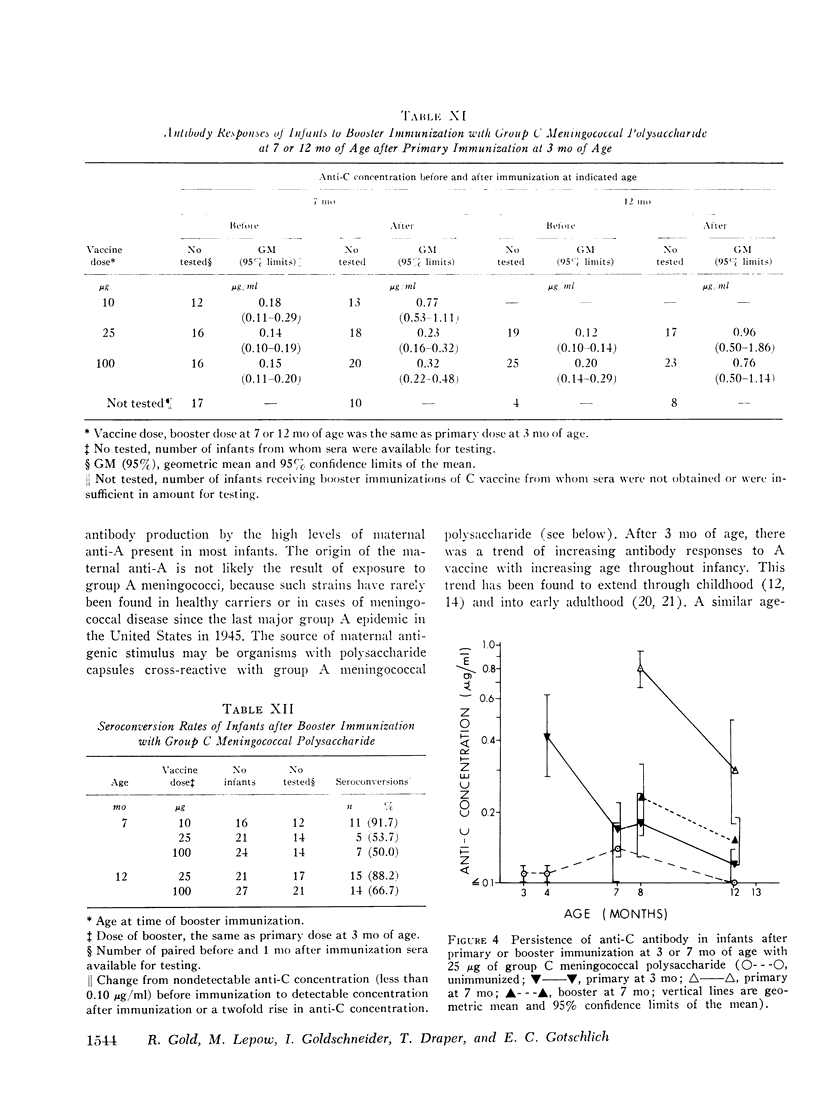
Group A and group C meningoccal polysaccharide vaccines were evaluated in infants. No significant local or systemic reactions were observed with 908 doses of vaccine given to 396 infants between 3 and 12 mo of age. The antibody response varied with the age of the infant, vaccine dose, molecular weight of vaccine, prior immunization with vaccine, and prior exposure to naturally occurring cross-reactive antigens. Only 7% of 3-mo-old infants had detectable antibody responses to primary immunization with 5-200 mug of A vaccine, presumably because of suppressive effects of high concentrations of maternal anti-A. More than 90% of 7- and 12-mo-old infants responded to A vaccine, achieving geometric mean anti-A concentrations of 0.38 and 0.98 mug/ml, respectively. The dose-response curve was flat between 10 and 200 mug of A vaccine. Geometric mean anti-A concentrations of 2.51 and 4.00 mug/ml were induced in 7- and 12-mo-old infants by booster injections of A vaccine. Approximately 90% of 3-mo-old infants had detectable antibody responses to primary immunization with C vaccine. The 100-mug dose appeared to be optimal, resulting in geometric mean anti-C concentrations of 0.49, 1.55, and 2.64 mug/ml in 3-, 7-, and 12-mo-old infants, respectively. Significant booster responses were not observed with C vaccine. Indeed, except for the 10-mug dose, booster injections of C vaccine in 7- and 12-mo-old infants resulted in lower anti-C concentrations than did primary immunizations.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amato Neto V., Finger H., Gotschlich E. C., Feldman R. A., de Avila C. A., Konichi S. R., Laus W. C. Serologic response to serogroup C meningococcal vaccine in Brazilian preschool children. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1974 May-Jun;16(3):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artenstein M. S., Gold R., Zimmerly J. G., Wyle F. A., Branche W. C., Jr, Harkins C. Cutaneous reactions and antibody response to meningococcal group C polysaccharide vaccines in man. J Infect Dis. 1970 Apr;121(4):372–377. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.4.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artenstein M. S., Gold R., Zimmerly J. G., Wyle F. A., Schneider H., Harkins C. Prevention of meningococcal disease by group C polysaccharide vaccine. N Engl J Med. 1970 Feb 19;282(8):417–420. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197002192820803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erwa H. H., Haseeb M. A., Idris A. A., Lapeyssonnie L., Sanborn W. R., Sippel J. E. A serogroup A meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine: studies in the Sudan to combat cerebrospinal meningitis caused by Neisseria meningitidis group A. Bull World Health Organ. 1973;49(3):301–305. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd R. F., Federspiel C. F., Schaffner W. Bacterial meningitis in urban and rural Tennessee. Am J Epidemiol. 1974 Jun;99(6):395–407. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Darby C. P., Koehler R. E., Jacobs C. F., Feldman R. A. Risk factors in bacterial meningitis: Charleston County, South Carolina. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):271–277. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W., Henke C. E., Feldman R. A. Changing patterns of bacterial meningitis in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1935-1970. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):300–307. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold R., Artenstein M. S. Meningococcal infections. 2. Field trial of group C meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine in 1969-70. Bull World Health Organ. 1971;45(3):279–282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. I. The role of humoral antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1307–1326. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Lepow M. L., Gotschlich E. C. Immunogenicity of the group A and group C meningococcal polysaccharides in children. J Infect Dis. 1972 May;125(5):509–519. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.5.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Lepow M. L., Gotschlich E. C., Mauck F. T., Bachl F., Randolph M. Immunogenicity of group A and group C meningococcal polysaccharides in human infants. J Infect Dis. 1973 Dec;128(6):769–776. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.6.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C. A simplification of the radioactive antigen-binding test by a double label technique. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):910–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Goldschneider I., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. IV. Immunogenicity of group A and group C meningococcal polysaccharides in human volunteers. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1367–1384. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. 3. Preparation and immunochemical properties of the group A, group B, and group C meningococcal polysaccharides. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1349–1365. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Rey M., Triau R., Sparks K. J. Quantitative determination of the human immune response to immunization with meningococcal vaccines. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):89–96. doi: 10.1172/JCI106801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Winkelhake J. L., Zollinger W. D., Brandt B. L., Artenstein M. S. Immunochemical similarity between polysaccharide antigens of Escherichia coli 07: K1(L):NM and group B Neisseria meningitidis. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):262–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Benacerraf B. The regulatory influence of activated T cells on B cell responses to antigen. Adv Immunol. 1972;15:1–94. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60683-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. B., Weaver R. E., Thornsberry C., Feldman R. A. Trends in disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis: 1972 and 1973. J Infect Dis. 1974 Aug;130(2):212–214. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.2.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monto A. S., Brandt B. L., Artenstein M. S. Response of children to Neisseria meningitidis polysaccharide vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):394–400. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Gordon R. E., Robbins J. B. Polysaccharides of the genus Bacillus cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharides of Diplococcus pneumoniae type 3, Haemophilus influenzae type b, and Neisseria meningitidis group A. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):896–900. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.896-900.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Schneerson R., Robbins J. B., Turck M. Urinary-tract escherichia coli with cross-reactive antigens to encapsulated pyogenic bacteria. Lancet. 1972 Aug 5;2(7771):250–253. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91687-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Myerowitz L., Whisnant J. K., Argaman M., Schneerson R., Handzel Z. T., Gotschlich E. C. Enteric bacteria cross-reactive with Neisseria meningitidis groups A and C and Diplococcus pneumoniae types I and 3. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):651–656. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.651-656.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza de Morais J., Munford R. S., Risi J. B., Antezana E., Feldman R. A. Epidemic disease due to serogroup C Neisseria meningitidis in Saõ Paulo, Brazil. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(5):568–571. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.5.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahdan M. H., Rizk F., el-Akkad A. M., el-Ghoroury A. A., Hablas R., Girgis N. I., Amer A., Boctar W., Sippel J. E., Gotschlich E. C. A controlled field trial of a serogroup A meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine. Bull World Health Organ. 1973 Jun;48(6):667–673. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


