Abstract
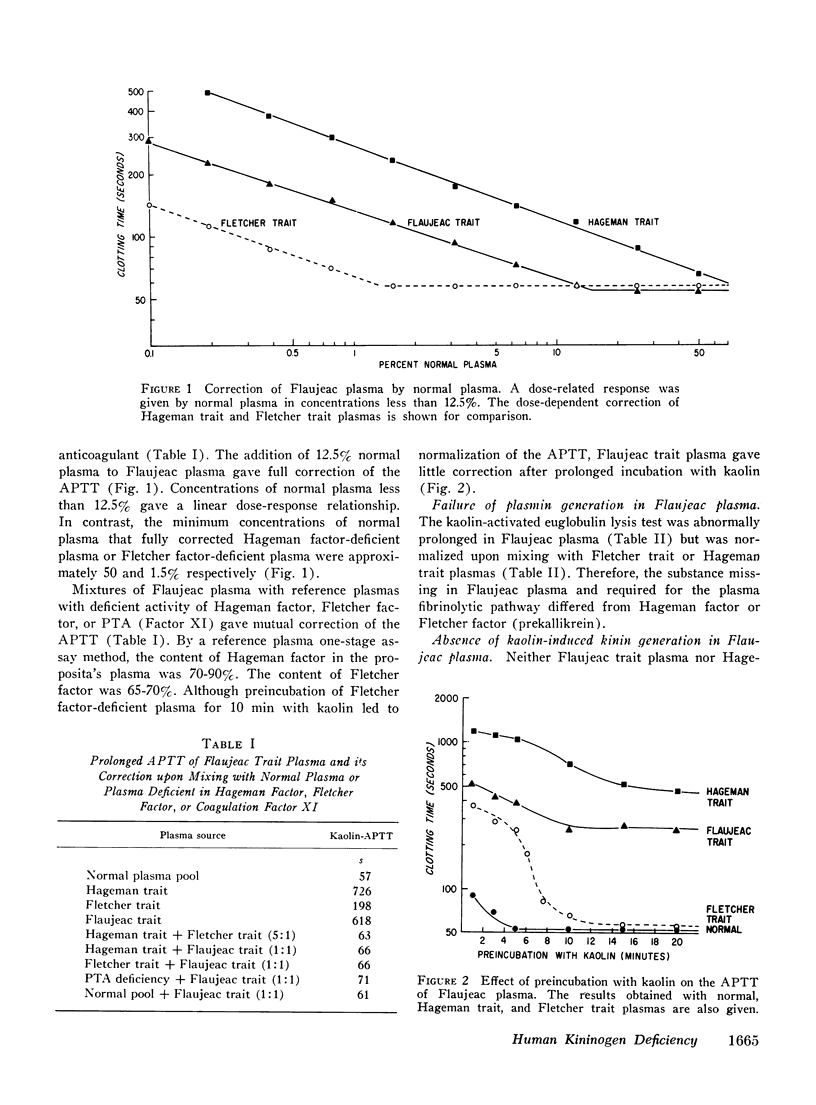
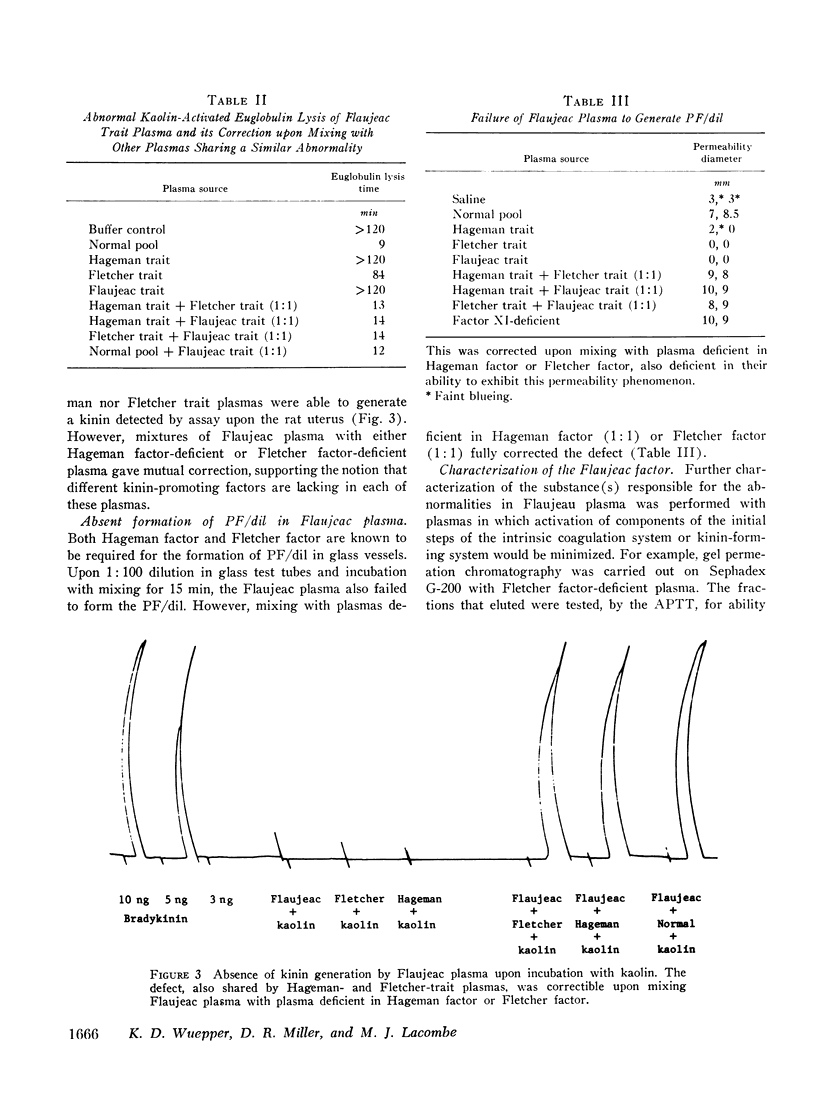
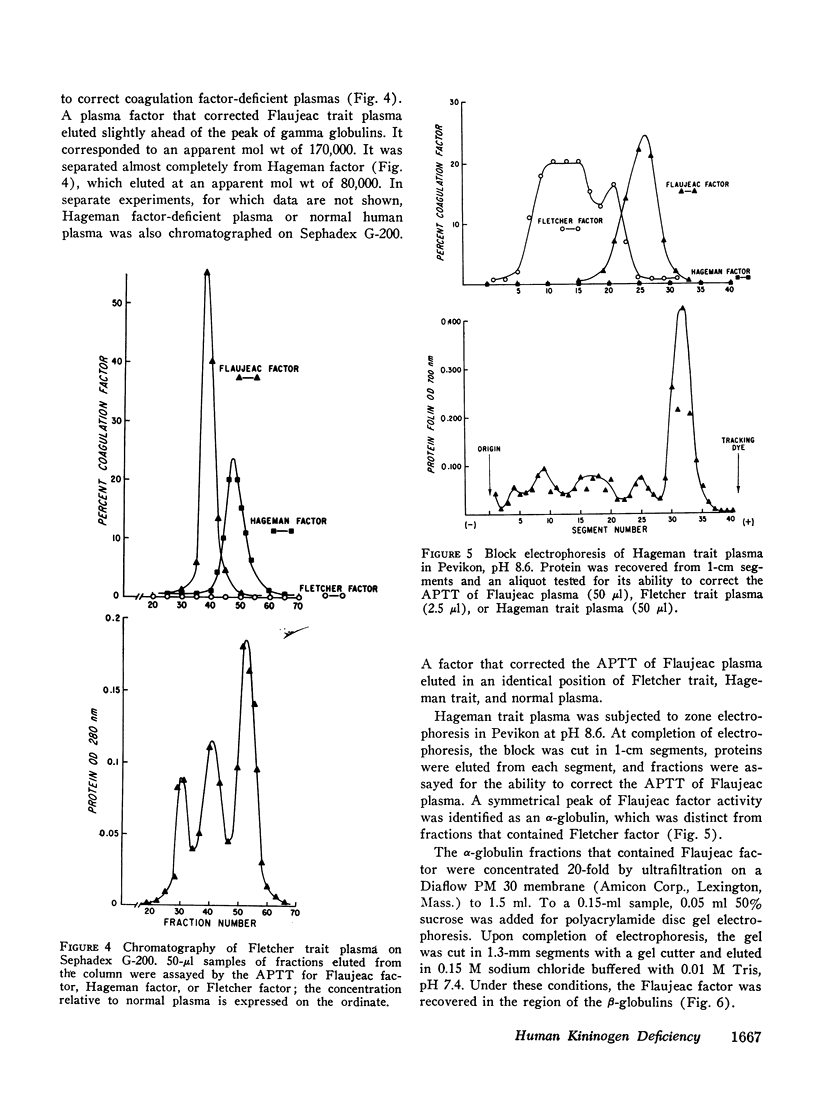
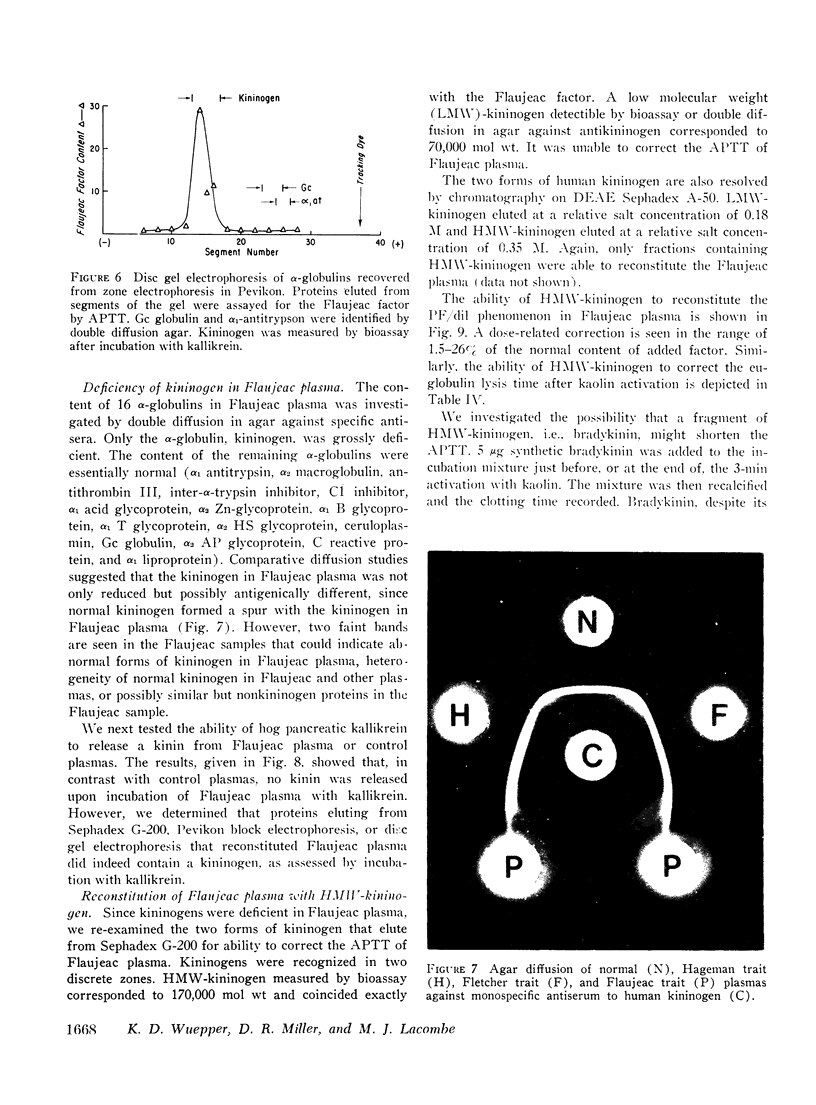
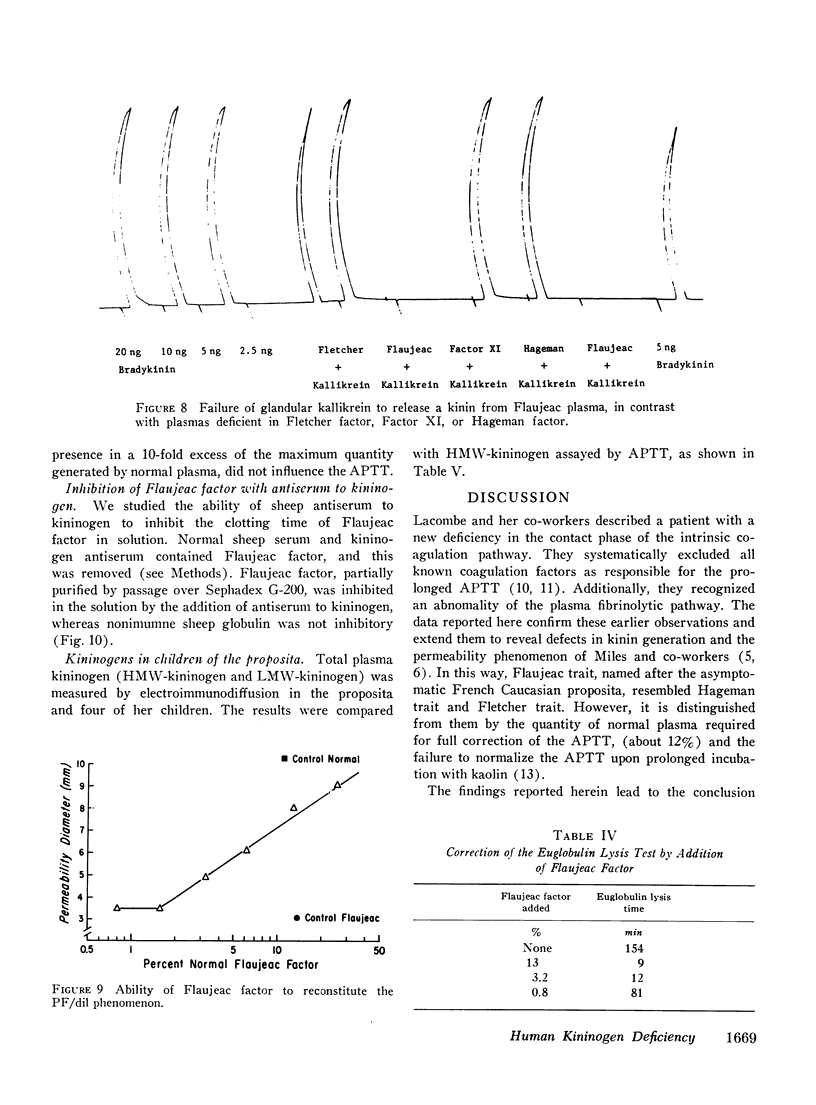
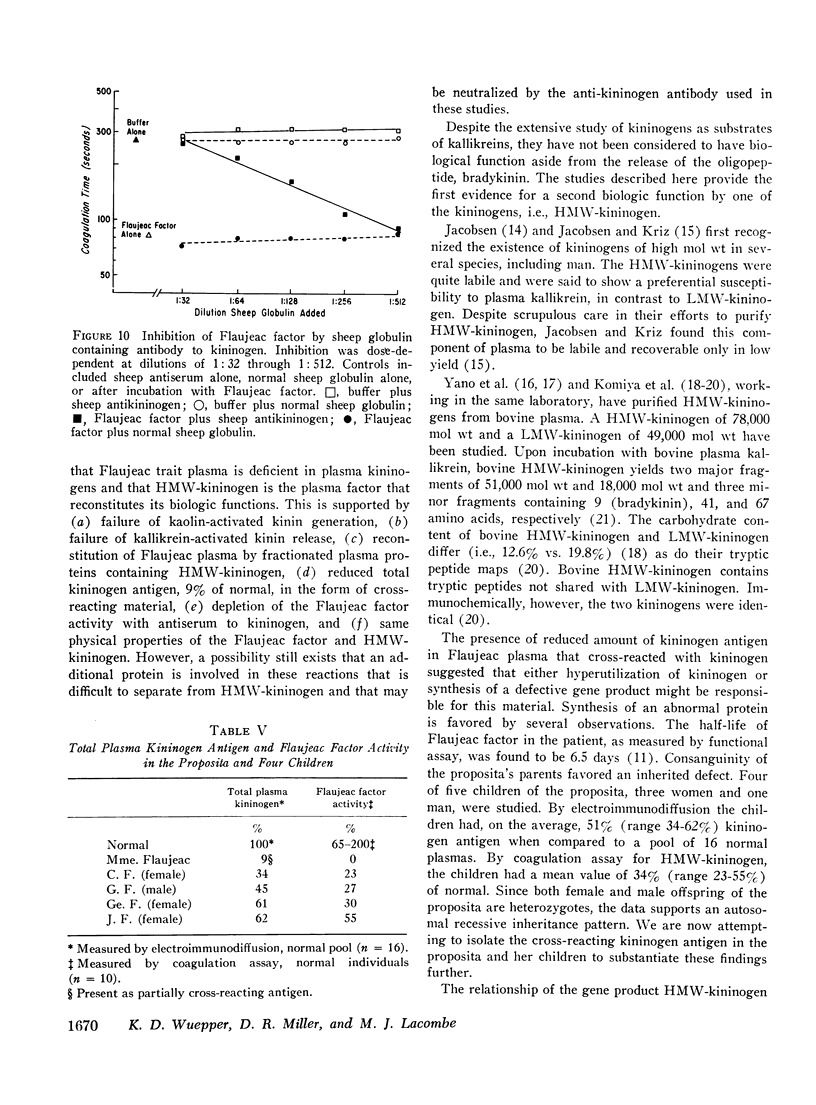
Flaujeac trait plasma resembled Hageman trait or Fletcher trait, in that the intrinsic coagulation pathway, plasma fibinolytic pathway, kinin-forming system, permeability factor of dilution (PF/dil) phenomenon were abnormal. The defect in each assay was reconstituted by afactor separable from Hageman factor or Fletcher factor. This substance was an alpha-globulin with an approximate mol wt of 170,000. Flaujeac plasma did not release a kinin upon incubation with kallikrein and was deficient in total kininogen antigen. Antiserum to kininogen inhibited the activity of the factor in solution. Flaufeac factor was identified as a kininogen of high molecular weight (HMW-kininogen). The mean total kininogen antigen in four children of the proposita was 51% (range 34-62%) of normal. A functional coagulation assay of HMW-kininogen in the children was 34% (range 23-55%). The results were consistent with autosomal recessive inheritance. The plasma pathways of intrinsic coagulation, fibrinolysis, kinin formation, and PF/dil generation are dependent upon HMW-kininogen. We believe this is the first demonstration of biological function for a kininogen apart from its role as a substrate for kallikreins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hathaway W. E., Alsever J. The relation of 'Fletcher Factor' to factors XI and XII. Br J Haematol. 1970 Feb;18(2):161–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway W. E., Belhasen L. P., Hathaway H. S. Evidence for a new plasma thromboplastin factor. I. Case report, coagulation studies and physicochemical properties. Blood. 1965 Nov;26(5):521–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IATRIDIS S. G., FERGUSON J. H. Effect of surface and Hageman factor on the endogenous or spontaneous activation of the fibrinolytic system. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1961 Dec 15;6:411–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen S. Separation of 2 different substrates for plasma kinin-forming enzymes. Nature. 1966 Apr 2;210(5031):98–99. doi: 10.1038/210098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komiya M., Kato H., Suzuki T. Bovine plasma kininogens. I. Further purification of high molecular weight kininogen and its physicochemical properties. J Biochem. 1974 Oct;76(4):811–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komiya M., Kato H., Suzuki T. Bovine plasma kininogens. II. Microheterogeneities of high molecular weight kininogens and their structural relationships. J Biochem. 1974 Oct;76(4):823–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacombe M. J. Déficit constitutionnel en un nouveau facteur de la coagulation intervenant au niveau de contact: le facteur "Flaujeac". C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1975 Feb 24;280(8):1039–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKAY M. E., MILES A. A., SCHACHTER M., WILHELM D. L. Susceptibility of the guinea pig to pharmacological factors from its own serum. Nature. 1953 Oct 17;172(4381):714–716. doi: 10.1038/172714b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIS J. Activation of plasma by contact with glass: evidence for a common reaction which releases plasma kinin and initiates coagulation. J Physiol. 1958 Nov 10;144(1):1–22. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILES A. A. LARGE MOLECULAR SUBSTANCES AS MEDIATORS OF THE INFLAMMATORY REACTION. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Aug 27;116:855–865. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb52551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEWIAROWSKI S., PROU-WARTELLE O. [Role of the contact factor (Hageman factor) in fibrinolysis]. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1959 Sep 1;3:593–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., COLOPY J. E. A familial hemorrhagic trait associated with a deficiency of a clot-promoting fraction of plasma. J Clin Invest. 1955 Apr;34(4):602–613. doi: 10.1172/JCI103109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffman S., Lee P. Preparation, characterization, and activation of a highly purified factor XI: evidence that a hitherto unrecognized plasma activity participates in the interaction of factors XI and XII. Br J Haematol. 1974 May;27(1):101–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D. Prekallikrein deficiency in man. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1345–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano M., Nagasawa S., Horiuchi K., Suzuki T. Separation of a new substrate, kininogen-I, for plasma kallikrein in bovine plasma. J Biochem. 1967 Oct;62(4):504–506. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano M., Nagasawa S., Suzuki T. Partial purification and some properties of high molecular weight kininogen, bovine kininogen-I. J Biochem. 1971 Mar;69(3):471–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]