Abstract
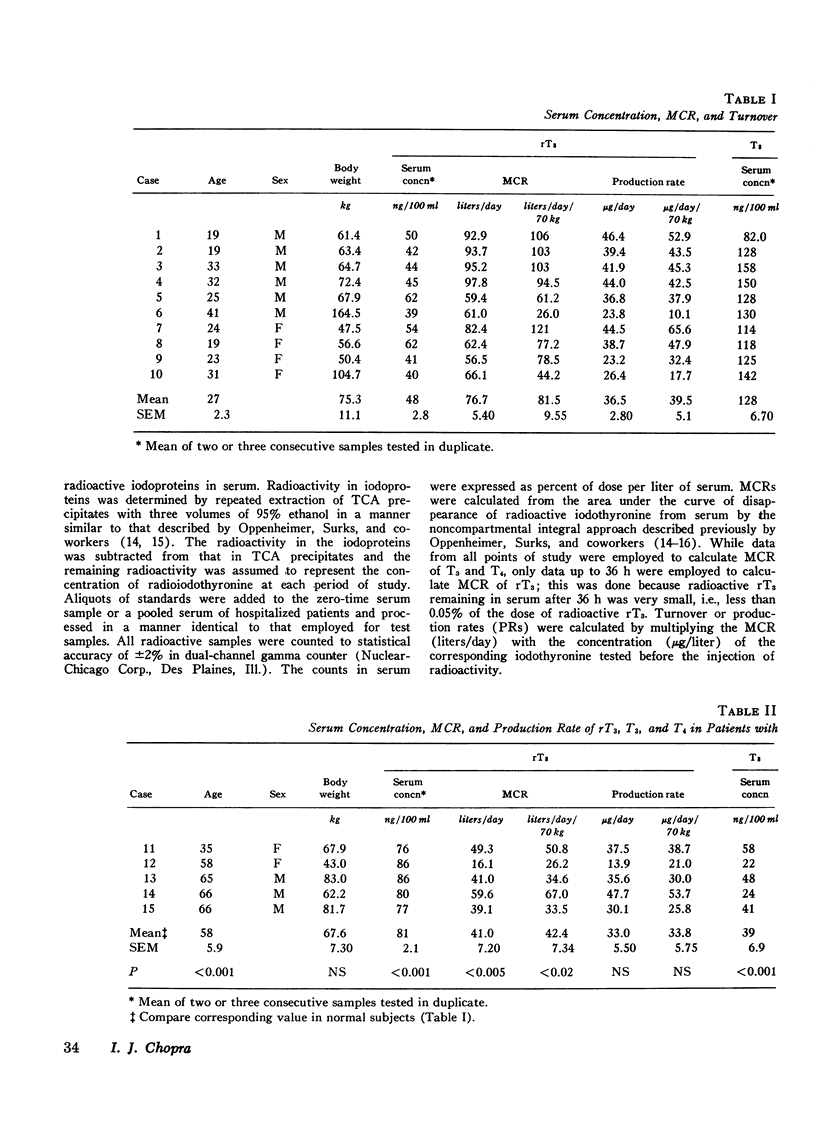
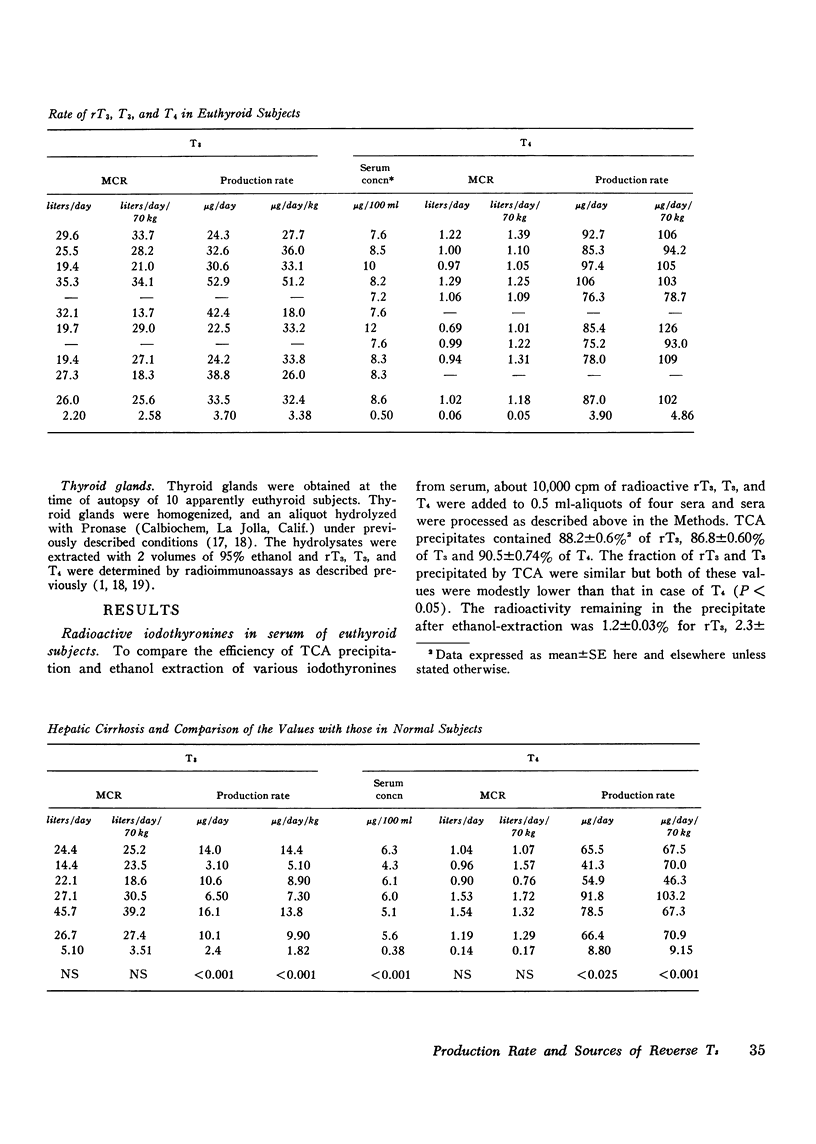
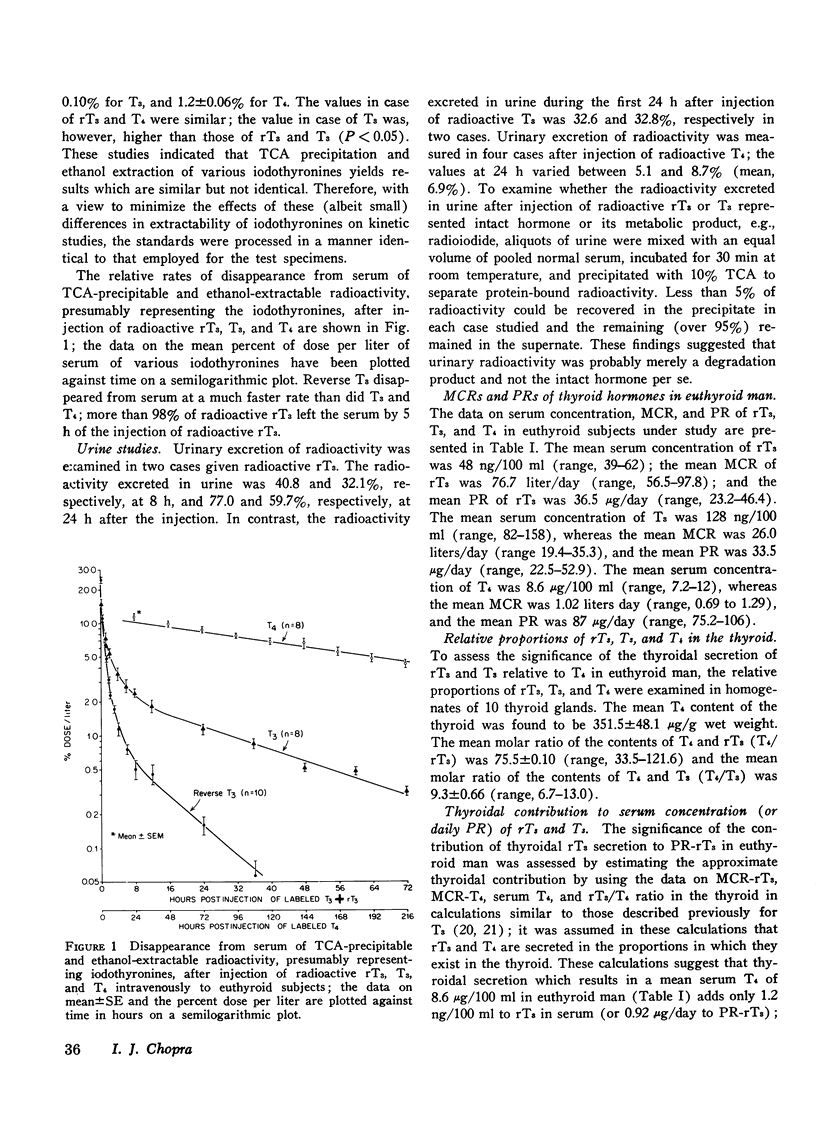
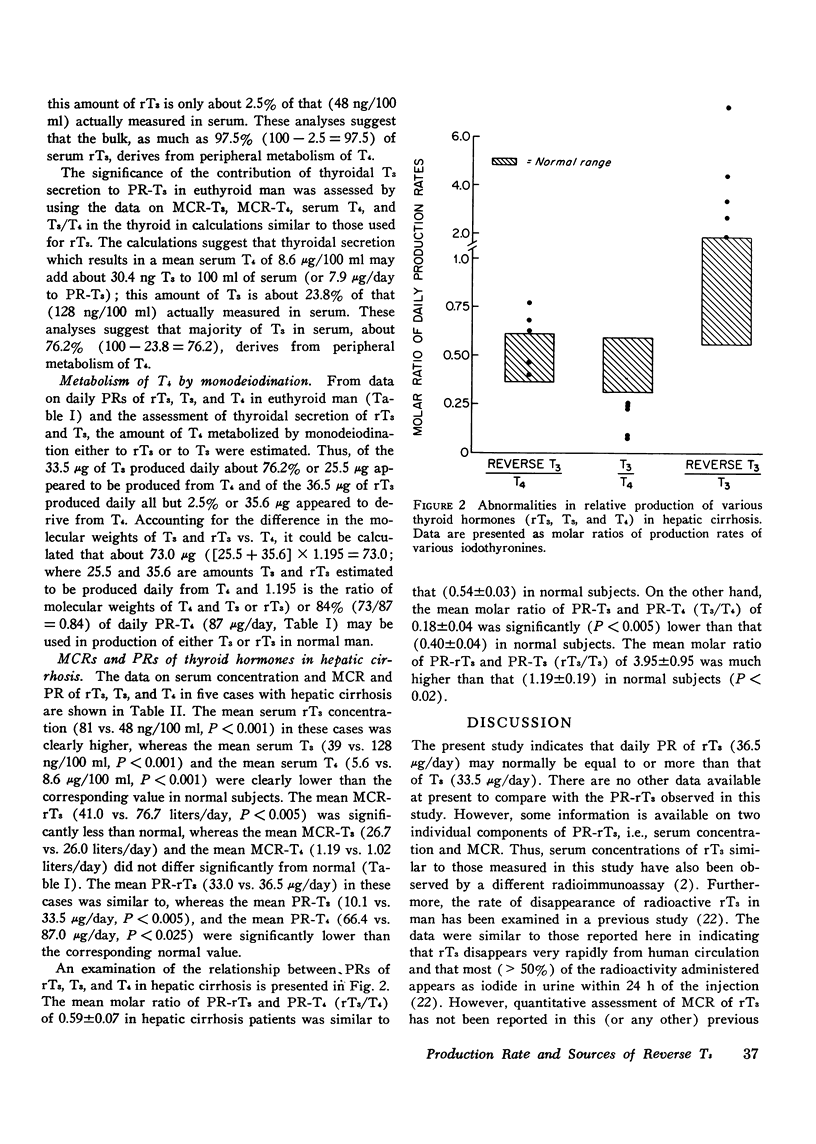
While 3, 3', 5'-triiodothyronine (reverse T3, rT3) has been detected both in human serum and in thyroglobulin, no quantitative assessment of its metabolic clearance rate (MCR), production rate (PR), or secretion by the thyroid is yet available. This study examines this information in euthyroid subjects and evaluates it in light of similar information about two other iodothyronines in the thyroid: 3, 5, 3'-triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Thus, it was noted that rT3 is cleared from human serum at a much faster rate than are T3 and T4; the mean (+/-SE) MCR of rT3 was 76.7+/-5.4 liters/day in 10 subjects, whereas MCR-T3 and MCR-T4 in 8 of them were 26.0+/-2.2 liters/day and 1.02+/-0.06 liters/day, respectively. Therefore, even though the mean serum concentration of rT3, 48+/-2.8 ng/100 ml, was much lower than that (128+/-6.7 ng/100 ml) of T3, the mean PR-rT3 (36.5+/-2.8 mug/day) and the mean PR-T3 (33.5+/-3.7 mug/day) were similar; in comparison, the mean serum concentration and PR of T4 were 8.6+/-0.5 mug/100 ml and 87.0+/-3.9 mug/day, respecitvely. These data and those on the relative proportion of rT3, T3, and T4 in 10 thyroid glands were used to assess the significance of the contribution of thyroidal secretion to PR-rT3 and PR-T3. It was estimated that whereas thyroidal secretion may account for about 23.8% of serum T3 (or PR-T3), it may account for only about 2.5% of serum rT3 (or PR-rT3). Since peripheral metabolism of T4 is the only known source of rT3 and T3 other than the thyroidal secretion, it could be calculated that as much as 73.0 mug or 84% of daily PR-T4 may normally be metabolized by monodeiodination either to T3 or to rT3. MCR and PR of various iodothyronines were also examined in five cases with hepatic cirrhosis, where, as documented previously, serum rT3 may be elevated while serum T3 is diminished. The mean MCR-rT3 in these cases (41.0 liters/day) was clearly (P is less than 0.005) less than that (76.7 liters/day) in normal subjects. This was the case at a time when the mean MCR-T3 (26.7 liters/day) and the mean MCR-T4 (1.19 liters/day) did not differ from those (vide supra) in normal subjects. Distinct from changes in MCRs, the mean PR-rT3 (33.0 mug/day) was similar to, and the mean PR-T3 (10.1 mug/day) and the mean PR-T4 (66.4 mug/day) were much less than, the corresponding value in normal subjects. Furthermore, while the ratio of PR-rT3 and PR-T4 (rT3/T4) in individual patients was either supranormal or normal, the ratio of PR-T3 and PR-T4 (T3/T4) was clearly subnormal. The various data suggest that: (a) just as in the case of T3, the thyroid gland is a relatively minor source of rT3; peripheral metabolism of T4 is apparently its major source; (b) the bulk of T4 metabolized daily is monodeiodinated to T3 or to rT3; (c) monodeiodination may be an obligatory step in metabolism of T4; (d) monodeiodination of T4 to rT3 is maintained normal or is increased in hepatic cirrhosis at a time when monodeiodination of T4 to T3 is decreased.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S. Quantitative aspects of iodine metabolism: the exchangeable organic iodine pool, and the rates of thyroidal secretion, peripheral degradation and fecal excretion, of endogenously synthesized organically bound iodine. J Clin Invest. 1954 Nov;33(11):1533–1552. doi: 10.1172/JCI103032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOMSTEDT B., PLANTIN L. O. THE EXTRATHYROIDAL DISTRIBUTION OF 131-I THYROXINE. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1965 Apr;48:536–546. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0480536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman L. E., Ingbar S. H., Sterling K. Conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3) in athyreotic human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):855–864. doi: 10.1172/JCI106304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman L. E., Vagenakis A., Downs P., Foster A. E., Sterling K., Ingbar S. H. Effects of replacement doses of sodium L-thyroxine on the peripheral metabolism of thyroxine and triiodothyronine in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1010–1017. doi: 10.1172/JCI107265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri R. R., Steinberg M., Searle G. L. Metabolic clearance rate of L-triiodothyronine in man: a comparison of results by single-injection and constant infusion methods. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Oct;33(4):624–629. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-4-624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. A radioimmunoassay for measurement of 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine (reverse T3). J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):583–592. doi: 10.1172/JCI107795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. A radioimmunoassay for measurement of thyroxine in unextracted serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jun;34(6):938–947. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-6-938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Chopra U., Smith S. R., Reza M., Solomon D. H. Reciprocal changes in serum concentrations of 3,3',5-triiodothyronine (T3) in systemic illnesses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Dec;41(06):1043–1049. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-6-1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Fisher D. A., Solomon D. H., Beall G. N. Thyroxine and triiodothyronine in the human thyroid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Feb;36(2):311–316. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-2-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Ho R. S., Lam R. An improved radioimmunoassay of triiodothyronine in serum: its application to clinical and physiological studies. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Nov;80(5):729–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Sack J., Fisher D. A. 3,3',5'-Triiodothyronine (reverse T3) and 3,3',5-triiodothyronine (T3) in fetal and adult sheep: studies of metabolic clearance rates, production rates, serum binding, and thyroidal content relative to thyroxine. Endocrinology. 1975 Nov;97(5):1080–1088. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-5-1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Sack J., Fisher D. A. Circulating 3,3', 5'-triiodothyronine (reverse T3) in the human newborn. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1137–1141. doi: 10.1172/JCI108030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Solomon D. H., Ho R. S. A radioimmunoassay of thyroxine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Nov;33(5):865–868. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-5-865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J., Williams D. E., Orgiazzi J., Solomon D. H. Opposite effects of dexamethasone on serum concentrations of 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine (reverse T3) and 3,3'5-triiodothyronine (T3). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Nov;41(5):911–920. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-5-911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNN J. T., STANBURY J. B. The metabolism of 3:3':5'-triiodothyronine in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Jul;18(7):713–720. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-7-713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A., Chopra I. J., Dussault J. H. Extrathyroidal conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in sheep. Endocrinology. 1972 Oct;91(4):1141–1144. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-4-1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLEASON G. I. Some notes on the exchange of iodine with thyroxine homologues. J Biol Chem. 1955 Apr;213(2):837–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS J., PITT-RIVERS R., TROTTER W. R. Effect of 3:5:3'-L-triiodothyronine in myxoedema. Lancet. 1952 May 24;1(6717):1044–1045. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)90695-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Simultaneous estimation of rates of thyroxine degradation and thyroid hormone synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jun;34(6):808–819. doi: 10.1172/JCI103136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inada M., Sterling K. Thyroxine Turnover and Transport in Laennec's Cirrhosis of the Liver. J Clin Invest. 1967 Aug;46(8):1275–1282. doi: 10.1172/JCI105620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingbar S. H., Braverman L. E. Active form of the thyroid hormone. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:443–449. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue K., Taurog A. Digestion of 131I-labeled thyroid tissue with maximum recovery of 131I-iodothyronines. Endocrinology. 1967 Aug;81(2):319–332. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISSITZKY S., BISMUTH J., ROLLAND M. [Separation of the iodized compounds of serum and the thyroid by filtration on dextran gel (Sephadex)]. Clin Chim Acta. 1962 Mar;7:183–189. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(62)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONEY W. L., KUMAOKA S., RAWSON R. W., KROC R. L. Comparative effects of thyroxine analogues in experimental animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Apr 23;86:512–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnon J., Row V. V., Volpé R. The influence of liver damage in man on the distribution and disposal rates of thyroxine and triiodothyronine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jan;34(1):144–151. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-1-144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoloff J. T., Low J. C., Dussault J. H., Fisher D. A. Simultaneous measurement of thyroxine and triiodothyronine peripheral turnover kinetics in man. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):473–483. doi: 10.1172/JCI106835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura S., Pittman C. S., Chambers J. B., Jr, Buck M. W., Shimizu T. Reduced peripheral conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):643–652. doi: 10.1172/JCI108134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODDIE T. H., FISHER D. A., ROGERS C. WHOLE-BODY COUNTING OF I-131-LABELED THYROXINE. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Jul;24:628–637. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-7-628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Shapiro H. C., Bernstein G., Surks M. I. Differences in primary cellular factors influencing the metabolism and distribution of 3,5,3'-L-triiodothyronine and L-thyroxine. J Clin Invest. 1970 May;49(5):1016–1024. doi: 10.1172/JCI106301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Letter: (to the editor). Erratum: revised calculations of common parameters of iodothyronine metabolism and distribution by noncompartmental analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Dec;41(06):1172–1173. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-6-1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTMAN J. A., BROWN R. W., REGISTER H. B., Jr Biological activity of 3,3',5'-triiodo-DL-thyronine. Endocrinology. 1962 Jan;70:79–83. doi: 10.1210/endo-70-1-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman C. S., Chambers J. B., Jr, Read V. H. The extrathyroidal conversion rate of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1187–1196. doi: 10.1172/JCI106596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STASILLI N. R., KROC R. L., MELTZER R. I. Antigoitrogenic and calorigenic activities of thyroxine analogues in rats. Endocrinology. 1959 Jan;64(1):62–82. doi: 10.1210/endo-64-1-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Metabolism of phenolic- and tyrosyl-ring labeled L-thyroxine in human beings and rats. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Oct;33(4):612–618. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-4-612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Schadlow A. R., Stock J. M., Oppenheimer J. H. Determination of iodothyronine absorption and conversion of L-thyroxine (T 4 ) to L-triiodothyronine (T 3 ) using turnover rate techniques. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):805–811. doi: 10.1172/JCI107244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyroid physiology in health and disease. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jul;81(1):68–81. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vagenakis A. G., Burger A., Portnary G. I., Rudolph M., O'Brian J. R., Azizi F., Arky R. A., Nicod P., Ingbar S. H., Braverman L. E. Diversion of peripheral thyroxine metabolism from activating to inactivating pathways during complete fasting. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Jul;41(1):191–194. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



