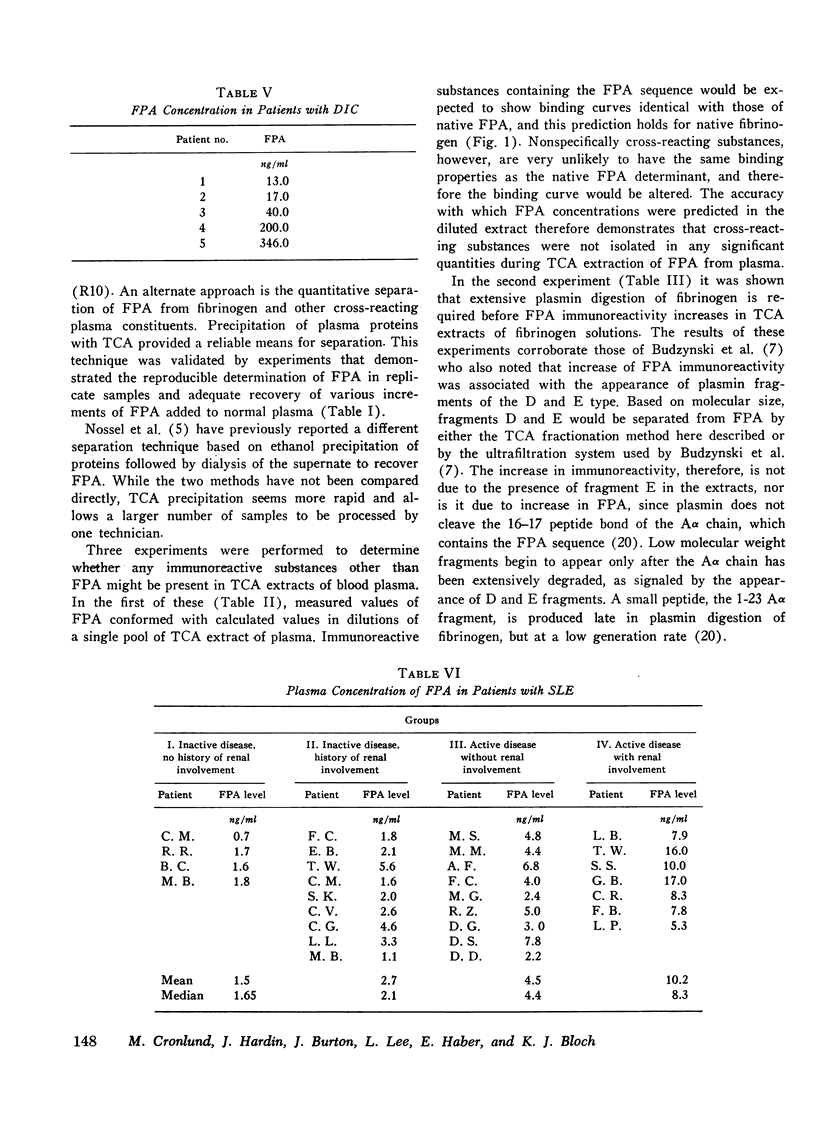
Abstract
A radioimmunoassay for fibrinopeptide A (FPA) has been developed. This assay uses rabbit antibodies induced by injection of native FPA-human serum albumin conjugates and 125I introduced into tyrosine-FPA synthesized in out laboratory. Plasma FPA is separated from fibrinogen by TCA extraction. The assay is capable of detecting as little as 50 pg/ml of FPA. In 20 normal donors this assay revealed a mean concentration of 0.9 ng/ml (0.3 SD). In five patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation, FPA concentrations ranged from 13.0 to 346 ng/ml. Two groups of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) whose disease had achieved complete remission were studied; one consisted of four patients with no history of lupus nephritis and another with a history of nephritis. Mean FPA concentrations of 1.5 ng/ml (range, 0.7-1.8 ng/ml) and 2.7 ng/ml (range, 1.1-5.6 ng/ml) were found in these two groups, respectively. Another group of nine patients with active SLE, but without evidence of lupus nephritis, had a mean FPA concentration of 4.5 ng/ml (range, 2.4-7.8 ng/ml). Finally, a group of seven patients with active SLE, including active nephritis, had a mean FPA concentration of 10.2 ng/ml (range, 5.3-17.0 ng/ml). A positive correlation was found between the concentration of plasma FPA and serum DNA-binding activity and an inverse correlation was found between plasma FPA and the concentration of serum C3. No correlation existed between plasma FPA and concentration of serum creatinine. Several possibilities for the origin of plasma FPA in patients with SLE were considered; at present it seems most likely that FPA arises through the action of thrombin on fibrinogen.
Full text
PDF

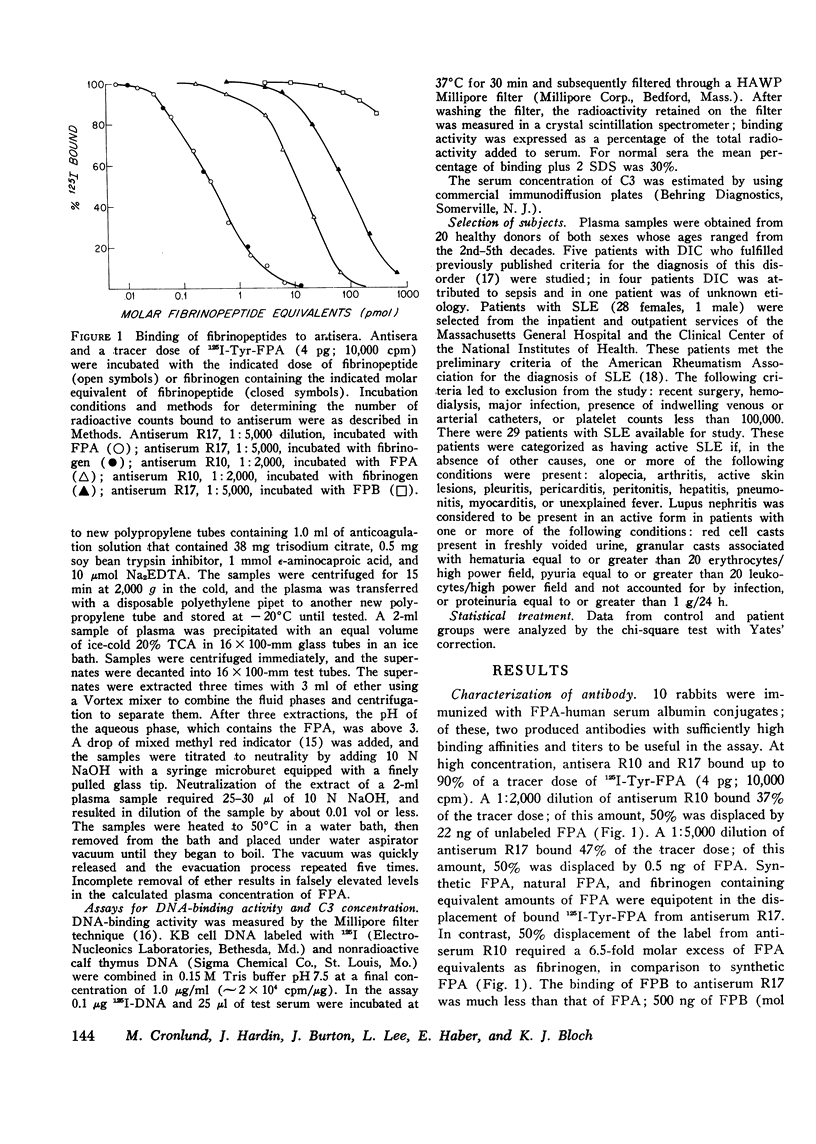
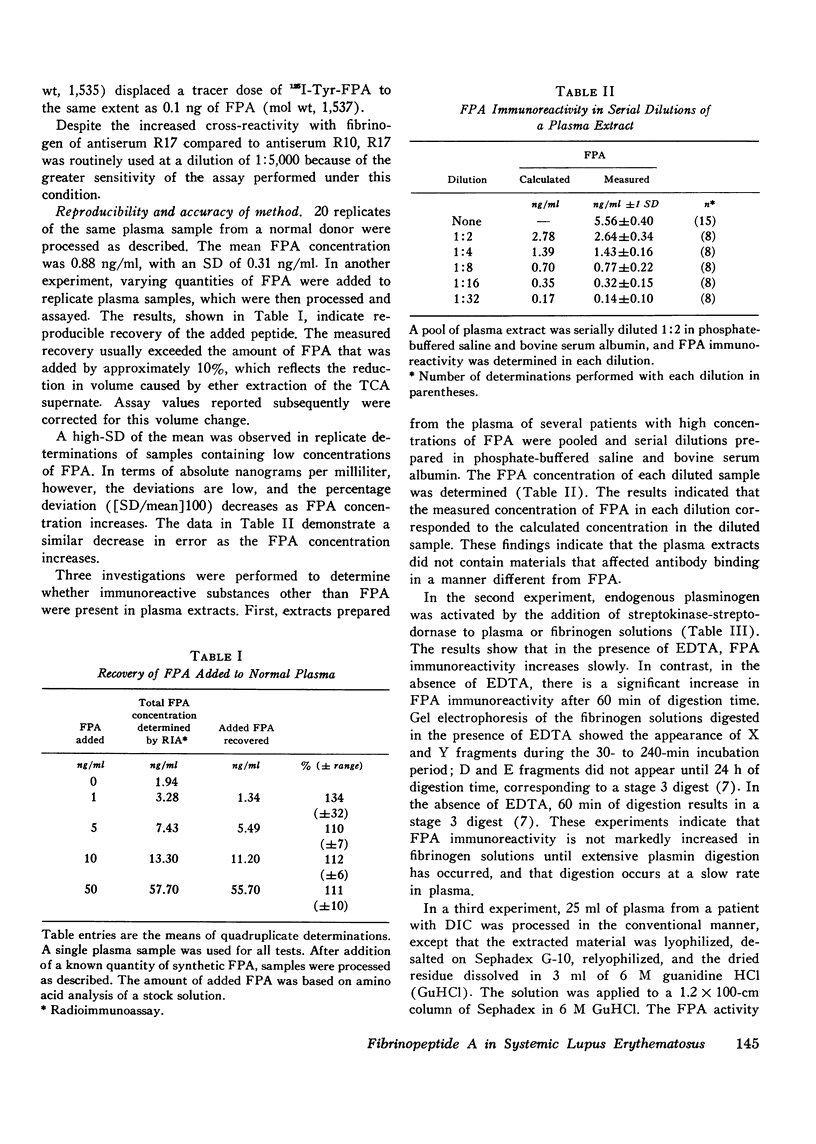
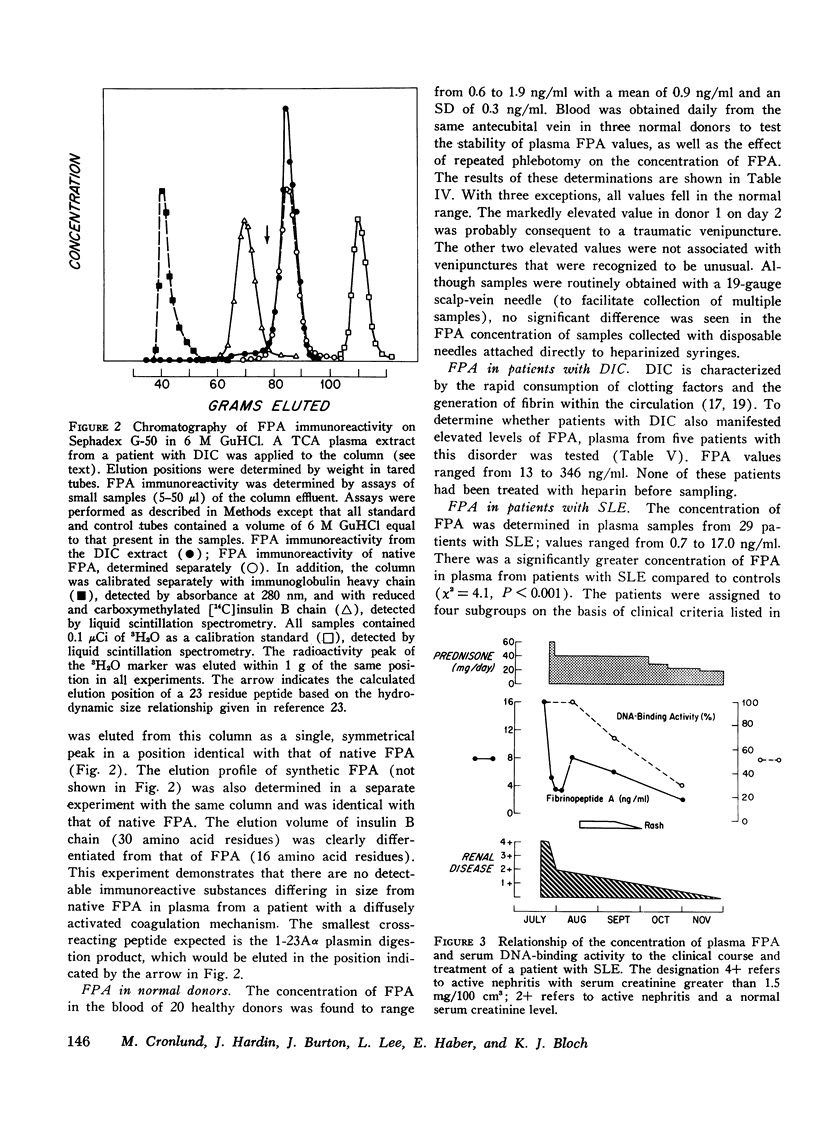
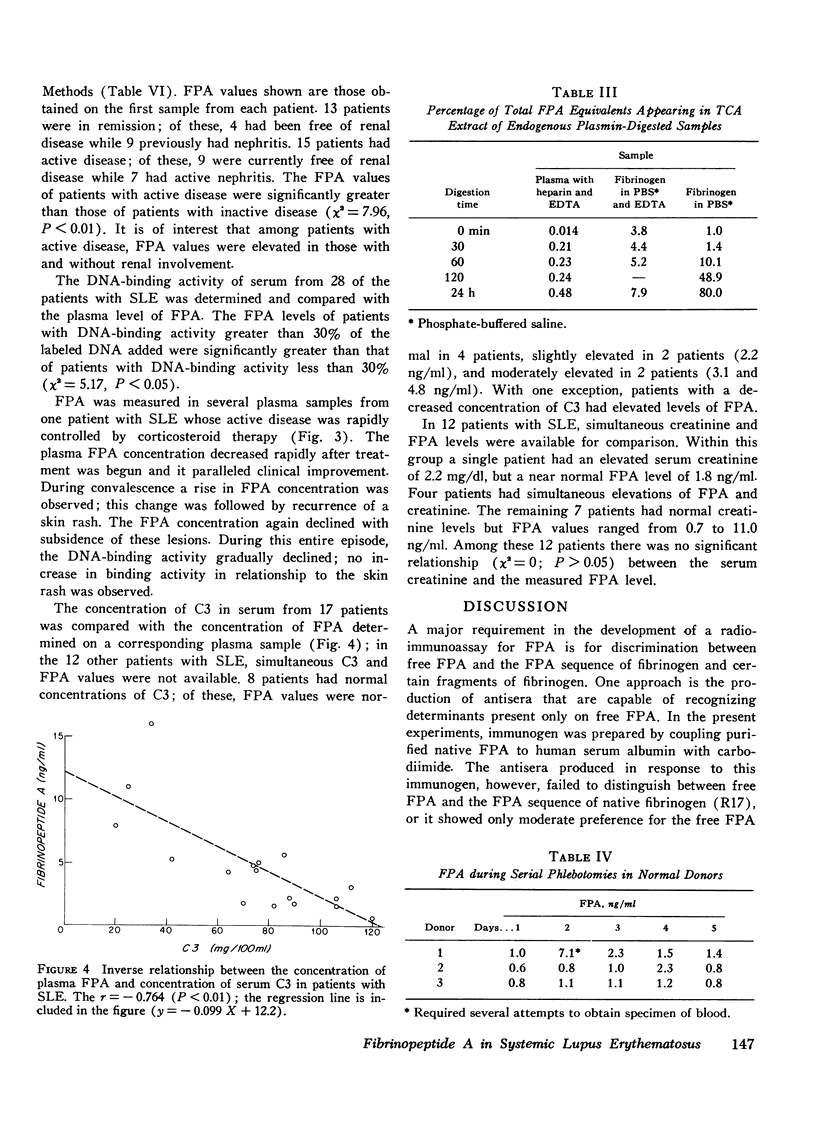



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bond R. E., Donadio J. V., Jr, Holley K. E., Bowie E. J. Fibrinolytic split products. A clinicopathological correlative study in adults with lupus glomerulonephritis and various renal diseases. Arch Intern Med. 1973 Aug;132(2):182–187. doi: 10.1001/archinte.132.2.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzynski A. Z., Marder V. J., Sherry S. Reaction of plasmic degradation products of fibrinogen in the radioimmunoassay of human fibrinopeptide A. Blood. 1975 Jun;45(6):757–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Robboy S. J., Minna J. D. Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC): an approach. Am J Med. 1972 May;52(5):679–689. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrits W. B., Flier O. T., van der Meer J. Fibrinopeptide A immunoreactivity in human plasma. Thromb Res. 1974 Aug;5(2):197–212. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzig R. H., Ratnoff O. D., Shainoff J. R. Studies on a procoagulant fraction of southern copperhead snake venom: the preferential release of fibrinopeptide B. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Sep;76(3):451–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker L. G., Ruddy S., Carpenter C. B., Schur P. H., Merrill J. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Austen K. F. Metabolism of third complement component (C3) in nephritis. Involvement of the classic and alternate (properdin) pathways for complement activation. N Engl J Med. 1972 Oct 26;287(17):835–840. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197210262871701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga S., Wallén P., Gröndahl N. J., Henschen A., Blombäck B. On the primary structure of human fibrinogen. Isolation and characterization of N-terminal fragments from plasmic digests. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Mar;8(2):189–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanyerezi B. R., Lwanga S. K., Block K. J. Fibrinogen degradation products in serum and urine of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Relation to renal disease and pathogenetic mechanism. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Mar-Apr;14(2):267–275. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiser H. Preparation of 125I-labeled native DNA for use in radioimmunoassays for anti-native-DNA antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Jul-Aug;16(4):468–470. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisker C. T., Rush R. Detection of intravascular coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2235–2241. doi: 10.1172/JCI106720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKI K. The polymerization of proteins; the action of thrombin on fibrinogen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Jul;32(2):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi S. L., Aptekar R. G., Steinberg A. D., Gralnick H. R., Decker J. L. Urinary fibrin split products in lupus nephritis. Correlation with other parameters of renal disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Mar-Apr;17(2):158–164. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. B. Solid-phase peptide synthesis. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:221–296. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Younger L. R., Wilner G. D., Procupez T., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr Radioimmunoassay of human fibrinopeptide A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2350–2353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Yudelman I., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr, Spanondis K., Wilner G. D., Qureshi G. D. Measurement of fibrinopeptide A in human blood. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):43–53. doi: 10.1172/JCI107749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Edgington T. S. An alternative pathway for fibrinolysis. I. The cleavage of fibrinogen by leukocyte proteases at physiologic pH. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul;56(1):30–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI108076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen K., Burton J., Haber E. Competitive inhibitors of renin. Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 25;12(20):3877–3882. doi: 10.1021/bi00744a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan M. G., Lackner H., Karpatkin S. Platelet function and coagulation profile in lupus erythematosus. Studies in 50 patients. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Oct;81(4):462–468. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-4-462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Bridson W., Rayford P. L. Rapid calculation of radioimmunoassay results. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Nov;74(5):770–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemblatt M. S., Margolies M. N., Cannon L. E., Haber E. Peptides: an analytical method for their resolution by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis applicable to a wide range of sizes and solubilities. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90516-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salo O. P., Tallberg T., Mustakallio K. K. Demonstration of fibrin in skin diseases. I. Lichen ruber planus and lupus erythematosus. Acta Derm Venereol. 1972;52(4):291–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Sandson J. Immunologic factors and clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1968 Mar 7;278(10):533–538. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196803072781004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehm E. R., Trygstad C. W. Split products of fibrin in human renal disease. Am J Med. 1969 May;46(5):774–786. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y. Studies of the metabolism and distribution of fibrinogen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Apr;69(4):624–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle E. N. Fibrinogen catabolism studies in patients with renal disease. Q J Med. 1973 Jan;42(165):205–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle E. N., Taylor G. Fibrin breakdown products and fibrinolysis in renal disease. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Mar;21(2):140–146. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.2.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



