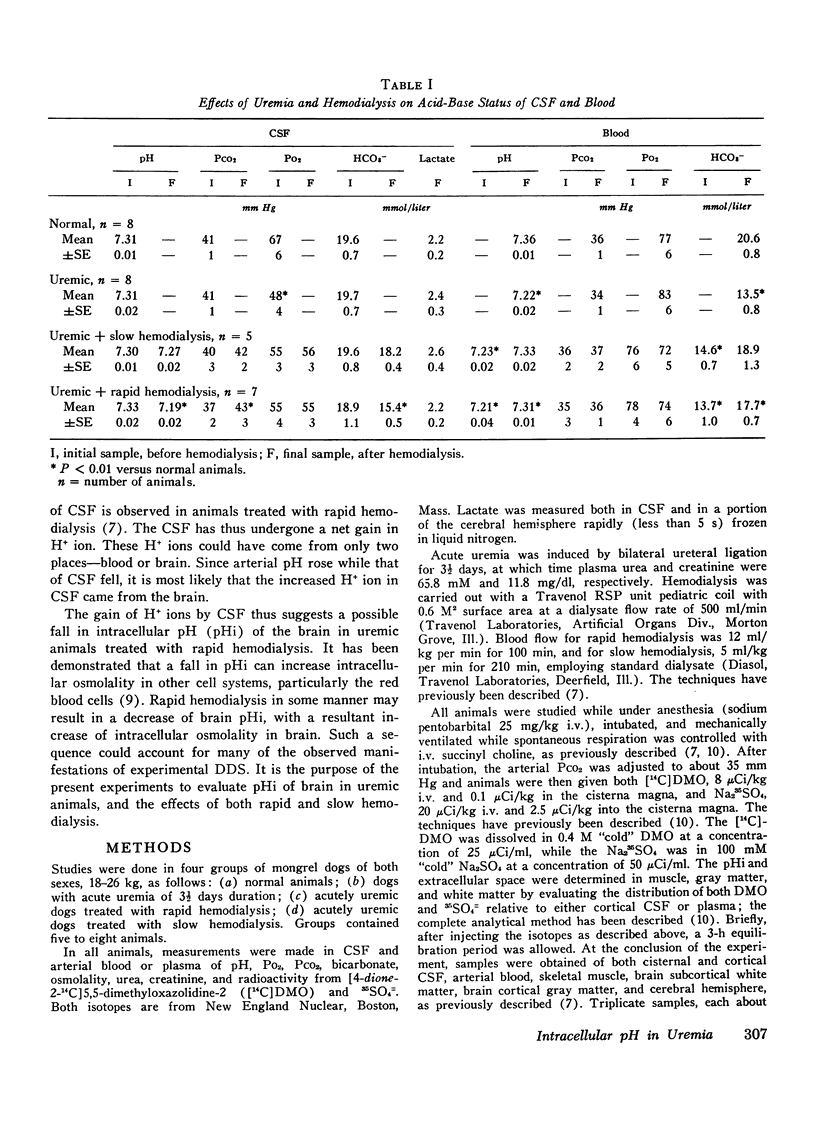
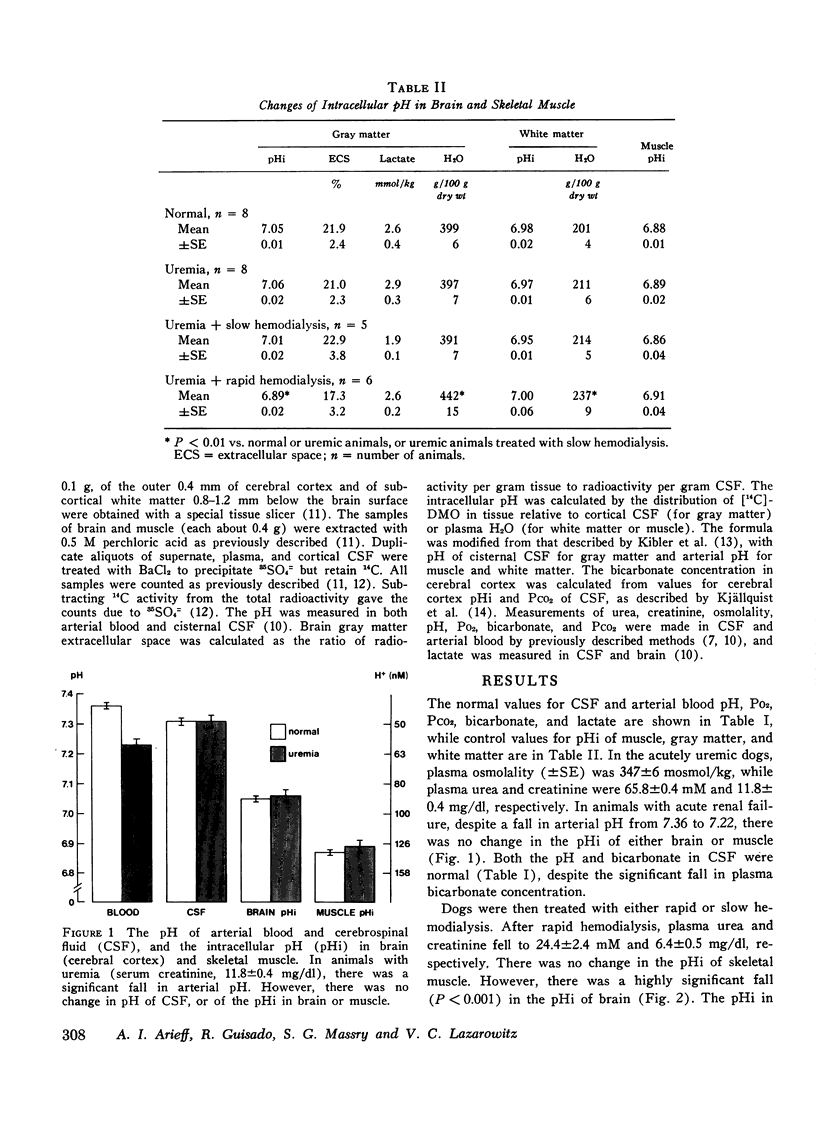
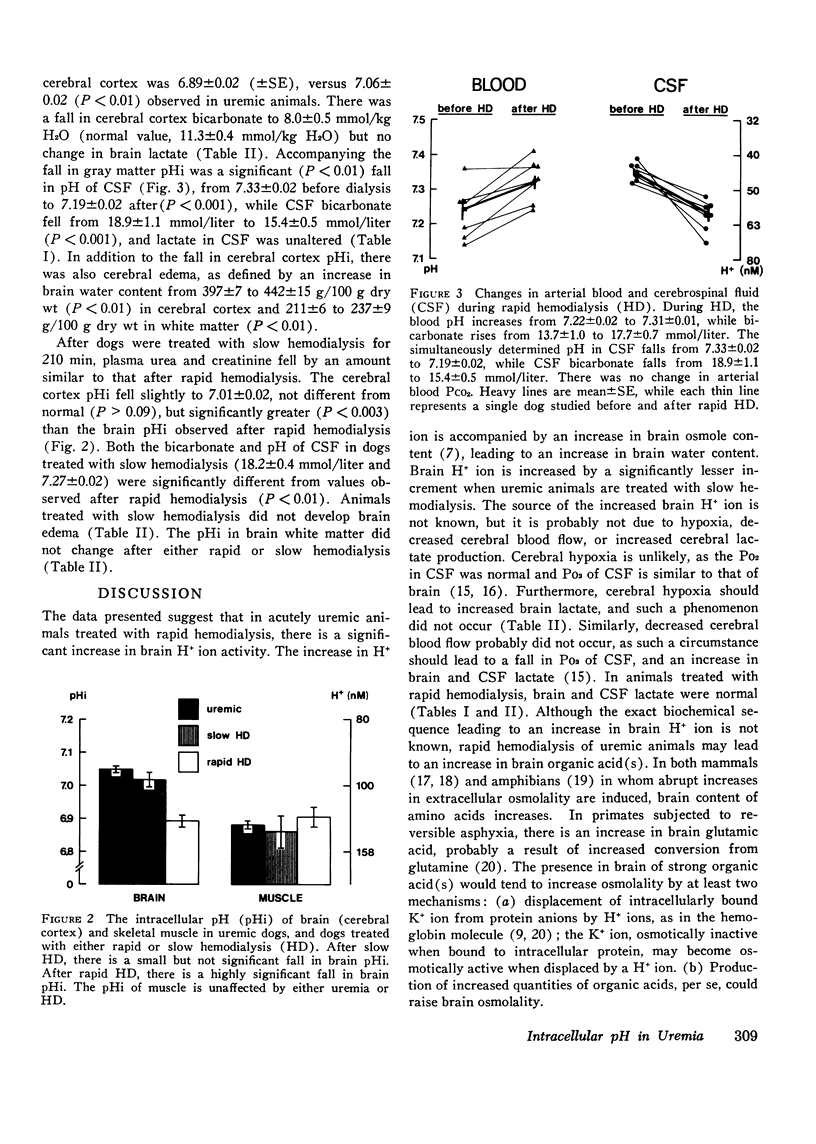
Abstract
Rapid hemodialysis of uremic animals may induce a syndrome characterized by increased cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure, grand mal seizures, and electroencephalographic abnormalities. There is a fall in pH and bicarbonate concentration in CSF, and brain osmolality exceeds that of plasma, resulting in a net movement of water into the brain. This syndrome has been called experimental dialysis disequilibrium syndrome. The fall in pH of CSF may be secondary to a fall of intracellular pH (pHi) in brain. Since changes in pHi can alter intracellular osmolality in other tissues, it was decided to investigate brain pHi in uremia, and the effects of hemodialysis. Brain pHi was measured by evaluating the distribution of 14C-labeled dimethadione in brain relative to CSF, while extracellular space was calculated as the 35504=/4 space relative to CSF. In animals with acute renal failure, brain (cerebral cortex) pHi was 7.06+/-0.02 (+/-SE) while that in CSF was 7.31+/-0.02, both values not different from normal. After rapid hemodialysis (100 min) of uremic animals, plasma creatinine fell from 11.8 to 5.9 mg/dl. Brain pHi was 6.89+/-0.02 and CSF pH and 7.19+/-0.02, both values significantly lower than in uremic animals (P less than 0.01), and there was a 12% increase in brain water content. After slow hemodialysis (210 min), brain pHi (7.01+/-0.02) and pH in CSF (7.27+/-0.02) were both significantly greater than values observed after rapid hemodialysis (P less than 0.01), and brain water content was normal. None of the above maneuvers had any effect on pHi of skeletal muscle or subcortical white matter. The data show that rapid hemodialysis of uremic dogs is accompanied by a significant fall in pH of CSF and pHi in cerebral cortex. Accompanying the fall in brain pHi is cerebral edema.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arieff A. I., Kerian A., Massry S. G., DeLima J. Intracellular pH of brain: alterations in acute respiratory acidosis and alkalosis. Am J Physiol. 1976 Mar;230(3):804–812. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.3.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arieff A. I., Massry S. G., Barrientos A., Kleeman C. R. Brain water and electrolyte metabolism in uremia: effects of slow and rapid hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 1973 Sep;4(3):177–187. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arieff A. I., Massry S. G. Calcium metabolism of brain in acute renal failure. Effects of uremia, hemodialysis, and parathyroid hormone. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):387–392. doi: 10.1172/JCI107571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assal J. P., Aoki T. T., Manzano F. M., Kozak G. P. Metabolic effects of sodium bicarbonate in management of diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes. 1974 May;23(5):405–411. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.5.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz E. Cerebral blood flow: its measurement and regulation. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jul;52(3):595–630. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.3.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bito L. Z., Myers R. E. On the physiological response of the cerebral cortex to acute stress (reversible asphyxia). J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(2):349–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W., Villamil M., Kleeman C. R. Extracellular fluid, ionic distribution and exchange in isolated frog brain. Am J Physiol. 1968 Mar;214(3):643–651. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.3.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWIE J., LAMBIE A. T., ROBSON J. S. The influence of extracorporeal dialysis on the acid-base composition of blood and cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Sci. 1962 Dec;23:397–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grushkin C. M., Korsch B., Fine R. N. Hemodialysis in small children. JAMA. 1972 Aug 21;221(8):869–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY A. C., LINTON A. L., LUKE R. G., RENFREW S. Electroencephalographic changes during haemodialysis. Lancet. 1963 Feb 23;1(7278):408–411. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92302-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIBLER R. F., O'NEILL R. P., ROBIN E. D. INTRACELLULAR ACID-BASE RELATIONS OF DOG BRAIN WITH REFERENCE TO THE BRAIN EXTRACELLULAR VOLUME. J Clin Invest. 1964 Mar;43:431–443. doi: 10.1172/JCI104928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjällquist A., Nardini M., Siesjö B. K. The regulation of extra- and intracellular acid-base parameters in the rat brain during hyper- and hypocapnia. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Aug;76(4):485–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin E., Arieff A., Kleeman C. R. Evidence of different compartments in the brain for extracellular markers. Am J Physiol. 1971 Nov;221(5):1319–1325. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.5.1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood A. H. Acute and chronic hyperosmolality. Effects on cerebral amino acids and energy metabolism. Arch Neurol. 1975 Jan;32(1):62–64. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490430084018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. A., Singer M. M. Respiration and cerebrospinal fluid pH in metabolic acidosis and alkalosis. J Appl Physiol. 1965 Sep;20(5):905–911. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1965.20.5.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohman J. L., Jr, Marliss E. B., Aoki T. T., Munichoodappa C. S., Khanna V. V., Kozak G. P. The cerebrospinal fluid in diabetic ketoacidosis. N Engl J Med. 1971 Feb 11;284(6):283–290. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197102112840601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULI H. G., VORBURGER C., REUBI F. Chronic derangements of cerebrospinal fluid acid-base components in man. J Appl Physiol. 1962 Nov;17:993–998. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1962.17.6.993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Fedson D. S., Brigham K. L., Permutt S., Mondal A. Relation of ventilation during base deficit to acid-base values in blood and spinal fluid. J Appl Physiol. 1971 May;30(5):677–683. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.30.5.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontén U., Siesjö B. K. Gradients of CO2 tension in the brain. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 Jun;67(2):129–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner J. B., Plum F. Spinal-fluid pH and neurologic symptoms in systemic acidosis. N Engl J Med. 1967 Sep 21;277(12):605–613. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196709212771201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum B. J., Coburn J. W., Shinaberger J. H., Massry S. G. Acid-base status during the interdialytic period in patients maintained with chronic hemodialysis. Ann Intern Med. 1969 Dec;71(6):1105–1111. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-71-6-1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank R. P., Baxter C. F. Metabolism of glucose, amino acids, and some related metabolites in the brain of toads (Bufo boreas) adapted to fresh water or hyperosmotic environments. J Neurochem. 1973 Aug;21(2):301–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb04251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurston J. H., Hauhart R. E., Jones E. M., Ater J. L. Effects of salt and water loading on carbohydrate and energy metabolism and levels of selected amino acids in the brains of young mice. J Neurochem. 1975 May;24(5):953–957. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb03661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakim K. G. The pathophysiology of the dialysis disequilibrium syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 1969 Jun;44(6):406–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


