Abstract
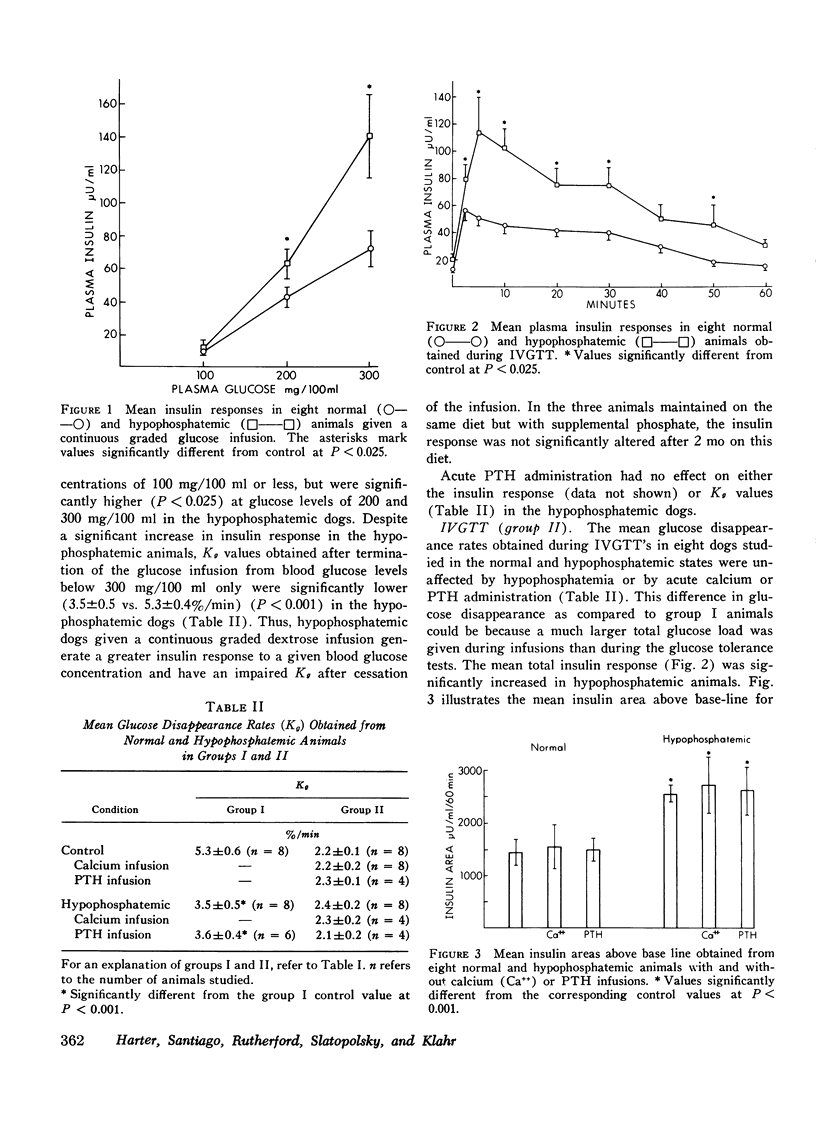
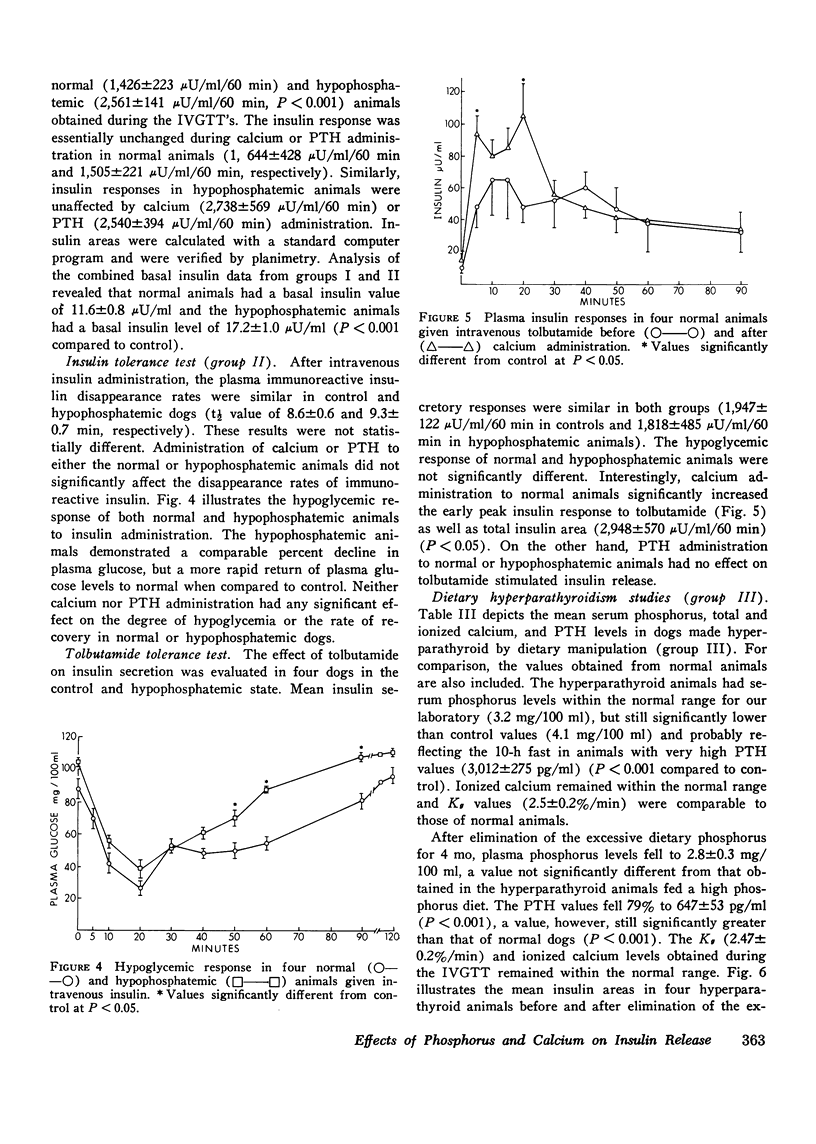
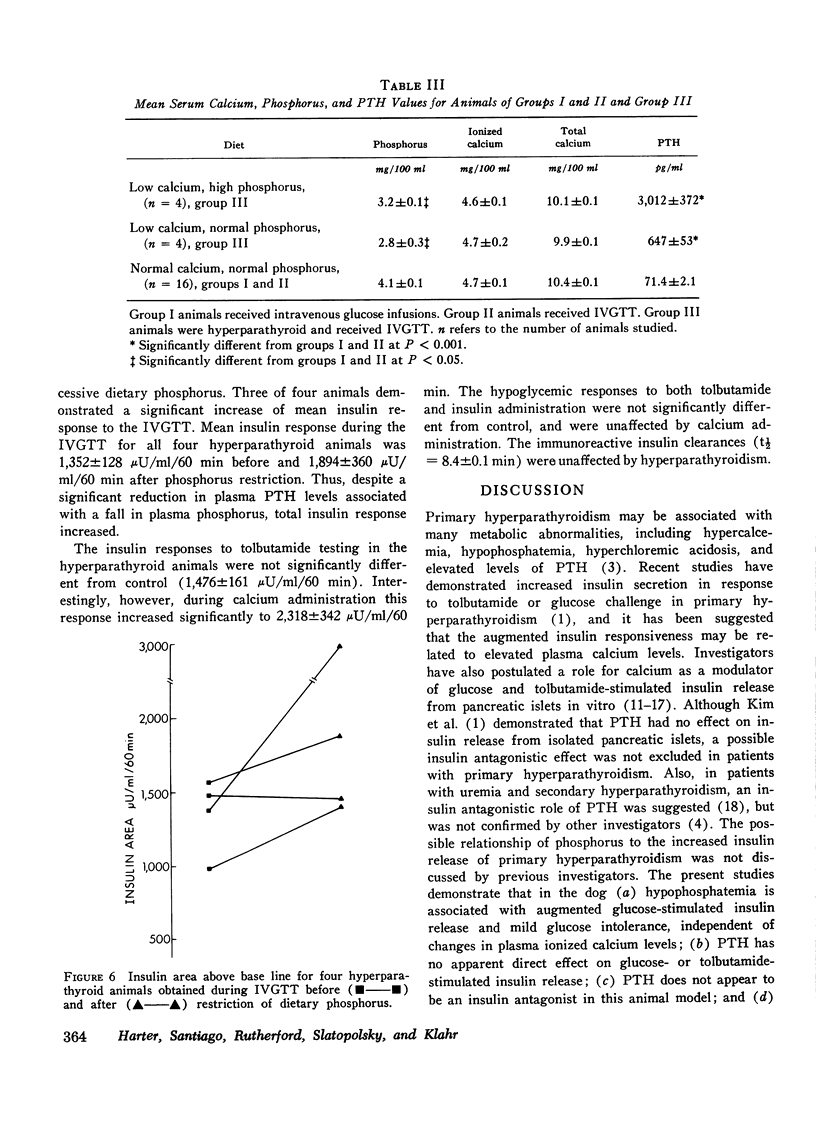
The relative contributions of Ca++, phosphorus, and parathyroid hormone (PTH) on insulin secretion were evaluated in three groups of dogs. Dogs were studied with glucose infusions (group I) or standard intravenous glucose tolerance tests (IVGTT) (group II) before and after the development of diet-induced hypophosphatemia. Mean serum phosphorus levels for both groups fell from 4.1 to 1.1 mg/100 ml. Animals in group I demonstrated a fall in glucose disappearance rates (Kg) from 5.3+/-0.6% min to 3.5+/-0.5% after induction of hypophosphatemia (P less than 0.001). Mean insulin response was significantly greater in the hypophosphatemic animals than in controls in this group. In group II animals, mean insulin areas obtained during the IVGTT increased from 1,426+/-223 to 2,561+/-141 muU/ml/60 min after induction of hypophosphatemia, and were unaffected by Ca++ or PTH administration. Ca++ administration, but not hypophosphatemia or PTH infusion, increased significantly the mean insulin response to tolbutamide. Secondary hyperparathyroidism was induced by dietary manipulation in four dogs (group III). Mean PTH values increased from 71.4+/-2.1 to 3,012+/-372 pg/ml (P less than 0.001). Mean insulin response to an IVGTT was similar to group III animals, but increased from 1,352+/-128 to 1,894+/-360 muU/ml/60 min after the excessive dietary phosphorus was reduced for 3 mo, and plasma phosphorus fell from 3.2+/-0.1 to 2.8+/-0.3 mg/100 ml. PTH values decreased to 647+/-53 pg/ml. The insulin response to tolbutamide was comparable to that in group II animals, but increased significantly after calcium administration. Immunoreactive insulin disappearance rates were unaffected by hypophosphatemia or diet-induced secondary hyperparathyroidism. These data demonstrate that hypophosphatemia is associated with an augmented glucose-stimulated insulin release, without any effect on tolbutamide-stimulated insulin release. Hypercalcemia produces an augmented tolbutamide-stimulated insulin release with no apparent effect on glucose-stimulated insulin release. Finally, PTH does not appear to be an insulin antagonist and has no apparent effect on either glucose- or tolbutamide-stimulated insulin release in animals with dietary-induced secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amend W. J., Jr, Steinberg S. M., Lowrie E. G., Lazarus J. M., Soeldner J. S., Hampers C. L., Merrill J. P. The influence of serum calcium and parathyroid hormone upon glucose metabolism in uremia. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Sep;86(3):435–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudry I. H., Gould M. K. Kinetics of glucose uptake in isolated soleus muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 6;177(3):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry D. L., Bennett L. L., Grodsky G. M. Requirement for calcium ion in insulin secretion by the perfused rat pancreas. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jan;214(1):174–178. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.1.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg J. M. Effect of glucose and free fatty acid on phosphate transport in dog kidney. Am J Physiol. 1972 May;222(5):1153–1160. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.5.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. W., Massry S. G., Arieff A. I., Coburn J. W. Renal bicarbonate wasting during phosphate depletion. A possible cause of altered acid-base homeostasis in hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2556–2561. doi: 10.1172/JCI107447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould M. K., Chaudry I. H. The action of insulin on glucose uptake by isolated rat soleus muscle. I. Effects of cations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 14;215(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M. A threshold distribution hypothesis for packet storage of insulin. II. Effect of calcium. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):584–593. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M., Bennett L. L. Cation requirements for insulin secretion in the isolated perfused pancreas. Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):910–913. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUFFMAN E. R., HLAD C. J., Jr, WHIPPLE N. E., ELRICK H. The influence of blood glucose on the renal clearance of phosphate. J Clin Invest. 1958 Mar;37(3):369–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI103616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halver B. The effect of parathyroid hormone on the tubular reabsorption of glucose. Acta Med Scand. 1966 Apr;179(4):427–432. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb05479.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter H. R., Mercado A., Rutherford W. E., Rodriguez H., Slatopolsky E., Klahr S. Effects of phosphate depletion and parathyroid hormone on renal glucose reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1974 Dec;227(6):1422–1427. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.6.1422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruska K. A., Kopelman R., Rutherford W. E., Klahr S., Slatopolsky E., Greenwalt A., Bascom T., Markham J. Metabolism in immunoreactive parathyroid hormone in the dog. The role of the kidney and the effects of chronic renal disease. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul;56(1):39–48. doi: 10.1172/JCI108077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Kalkhoff R. K., Costrini N. V., Cerletty J. M., Jacobson M. Plasma insulin disturbances in primary hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2596–2605. doi: 10.1172/JCI106760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn P. G., Clausen T. The relationship between the transport of glucose and cations across cell membranes in isolated tissues. VII. The effects of extracellular Na + and K + on the transport of 3-O-methylglucose and glucose in rat soleus muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 17;255(3):798–814. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEFEVRE P. G., HABICH K. I., HESS H. S., HUDSON M. R. PHOSPHOLIPID-SUGAR COMPLEXES IN RELATION TO CELL MEMBRANE MONOSACCHARIDE TRANSPORT. Science. 1964 Feb 28;143(3609):955–957. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3609.955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laflamme G. H., Jowsey J. Bone and soft tissue changes with oral phosphate supplements. J Clin Invest. 1972 Nov;51(11):2834–2840. doi: 10.1172/JCI107106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laron Z., Rosenberg T. Inhibition of insulin release and stimulation of growth hormone release by hypocalcemia in a boy. Horm Metab Res. 1970 Mar;2(2):121–122. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1096804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindall A., Carmena R., Cohen S., Comty C. Insulin hypersecretion in patients on chronic hemodialysis. Role of parathyroids. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 May;32(5):653–658. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-5-653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littledike E. T., Witzel D. A., Whipp S. C. Insulin: evidence for inhibition of release in spontaneous hypocalcemia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Oct;129(1):135–139. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotz M., Zisman E., Bartter F. C. Evidence for a phosphorus-depletion syndrome in man. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 22;278(8):409–415. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802222780802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Brisson G., Malaisse-Lagae F. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. I. Interaction of epinephrine and alkaline earth cations. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Dec;76(6):895–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallette L. E., Bilezikian J. P., Heath D. A., Aurbach G. D. Primary hyperparathyroidism: clinical and biochemical features. Medicine (Baltimore) 1974 Mar;53(2):127–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini P. F., Piancino G., Modica A. Changes in phosphorus clearance determined by the administration of glucose in diseases of the parathyroids and in other pathological conditions. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1967 Apr;54(4):629–636. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0540629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J., Batchelder T., Farquhar J. W., Reaven G. M. Disassociation of the plasma insulin response from the blood glucose concentration during glucose infusions in normal dogs. Metabolism. 1973 Oct;22(10):1277–1286. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDLE P. J., SMITH G. H. Regulation of glucose uptake by muscle. 2. The effects of insulin, anaerobiosis and cell poisons on the penetration of isolated rat diaphragm by sugars. Biochem J. 1958 Nov;70(3):501–508. doi: 10.1042/bj0700501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas O., Walaas E., Wick A. N. The stimulatory effect by insulin on the incorporation of 32P radioactive inorganic phosphate into intracellular inorganic phosphate, adenine nucleotides and guanine nucleotides of the intact isolated rat diaphragm. Diabetologia. 1969 Apr;5(2):79–87. doi: 10.1007/BF01212001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda K., Hurukawa Y., Okuyama M., Kikuchi M., Yoshinaga K. Glucose tolerance and insulin secretion in patients with parathyroid disorders. Effect of serum calcium on insulin release. N Engl J Med. 1975 Mar 6;292(10):501–504. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197503062921003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



