Abstract
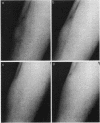
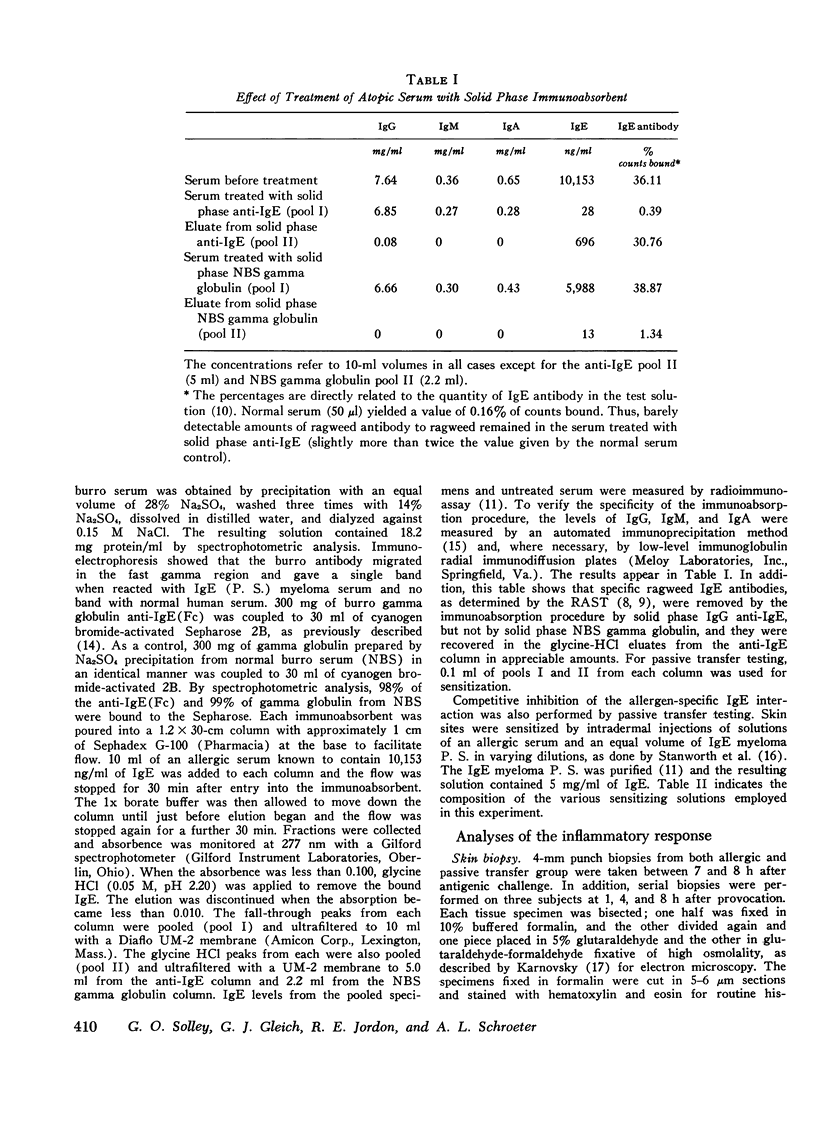
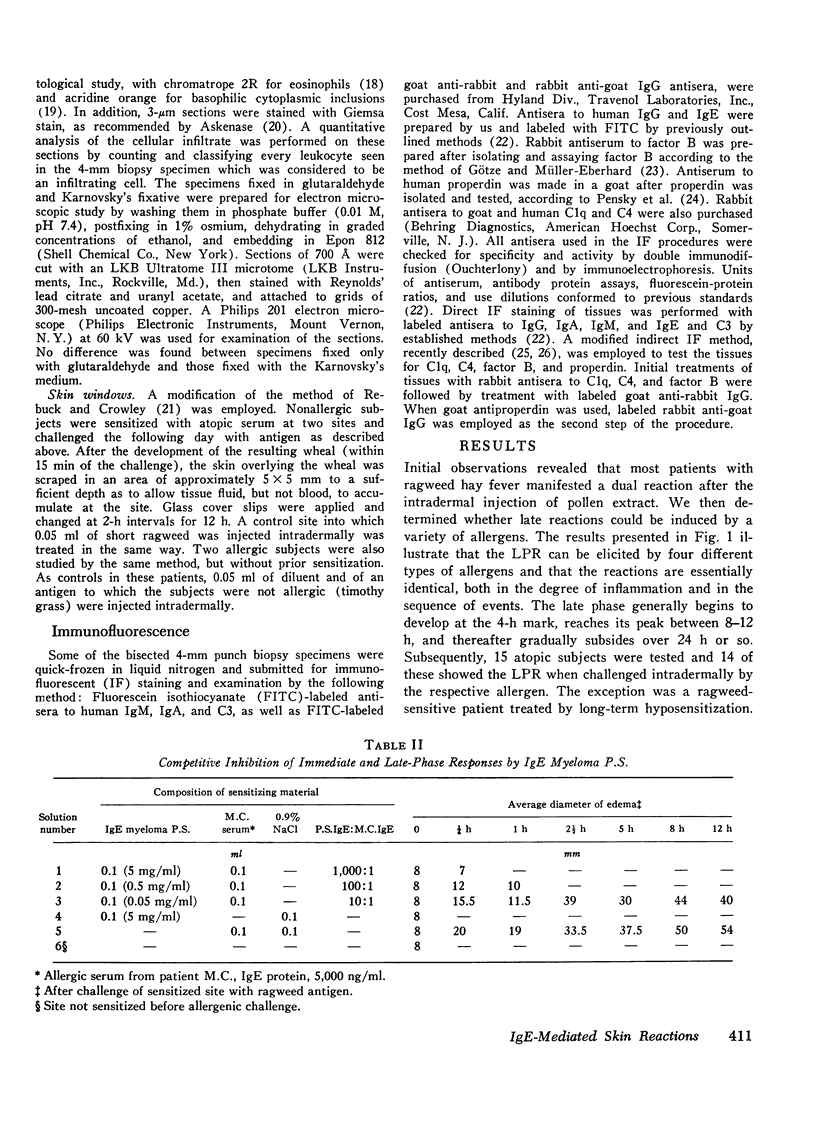
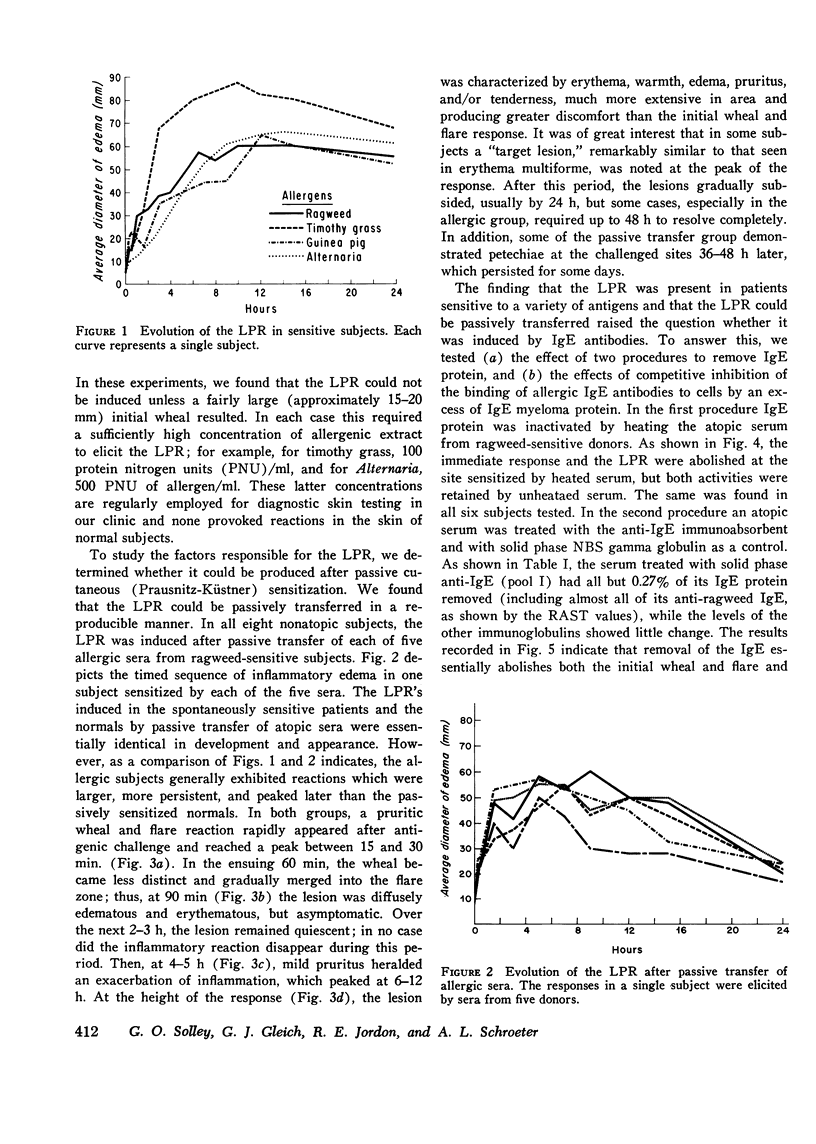
IgE antibodies are usually thought to induce only immediate skin reactions. We have shown that the intradermal injection of a number of different allergens can produce a prolonged inflammatory reaction after the immediate wheal and flare in most sensitive subjects. This late inflammatory response occurs 6-12 h after challenge and is characterized by diffuse edema, erythema, pruritus, and heat. Both immediate and late responses can also be seen after passive sensitization of skin sites in nonatopic subjects. That IgE is involved in inducing the reaction was shown by the abolition of both immediate and late responses by passive transfer tests in the following experiments: (a) heating atopic serum at 56degreesC for 4 h, (b) removing IgE from the atopic serum by a solid phase anti-IgE immunoabsorbent, and (c) competitively inhibiting the binding of IgE antibodies to cells by an IgE myeloma protein. In addition, both responses were induced by affinity chromatography-purified IgE antibody, followed by antigenic challenge. Very similar lesions could also be induced by intradermal injection of Compound 48/80, thus suggesting a central role in the reaction for the mast cell or basophil. Histologically, the late phase is characterized by edema and a mixed cellular infiltration, predominantly lymphocytic but also containing eosinophils, neutrophils and basophils. Direct immunofluorescent staining did not show deposition of immunoglobulins or complement components, except IgM in 2 of 15 and C3 in 1 of 15 patients. This finding indicates that the late phase does not depend on the deposition of immune complexes. The results of the study suggest that IgE-allergen interaction on the surfaces of mast cells or on infiltrating basophils causes both immediate and late cutaneous responses.
Full text
PDF

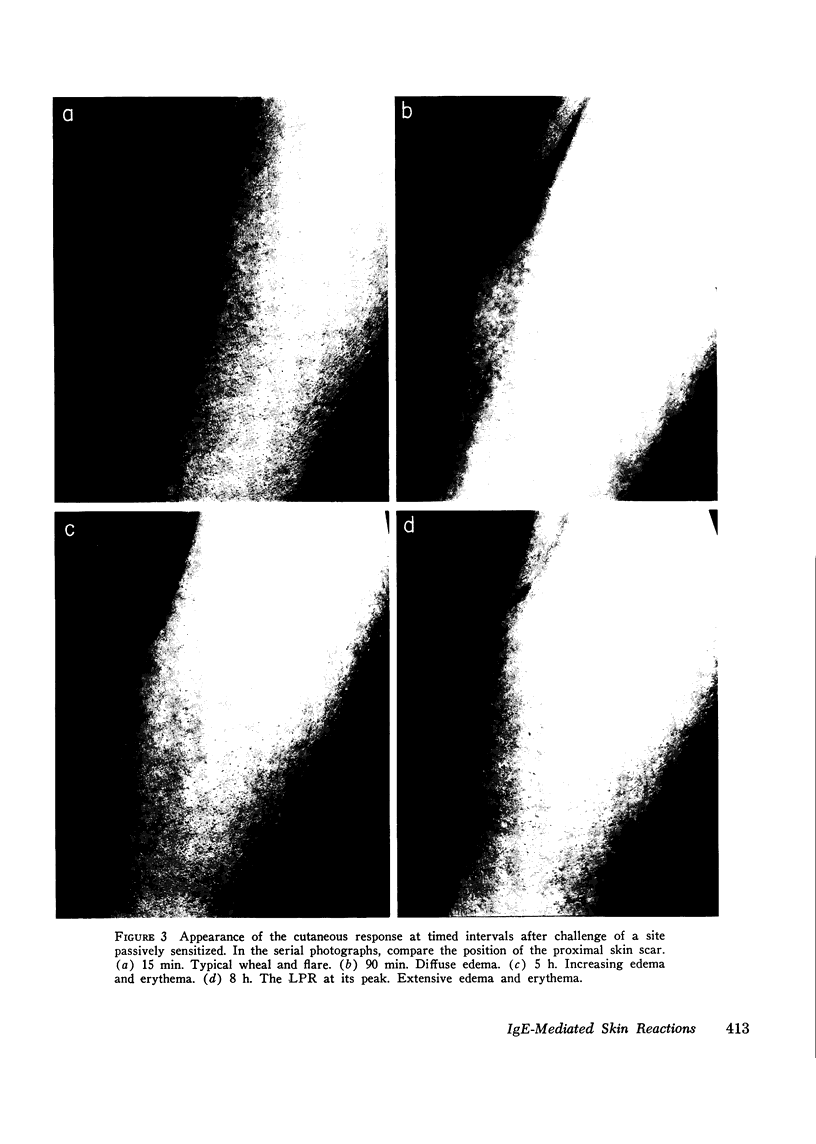
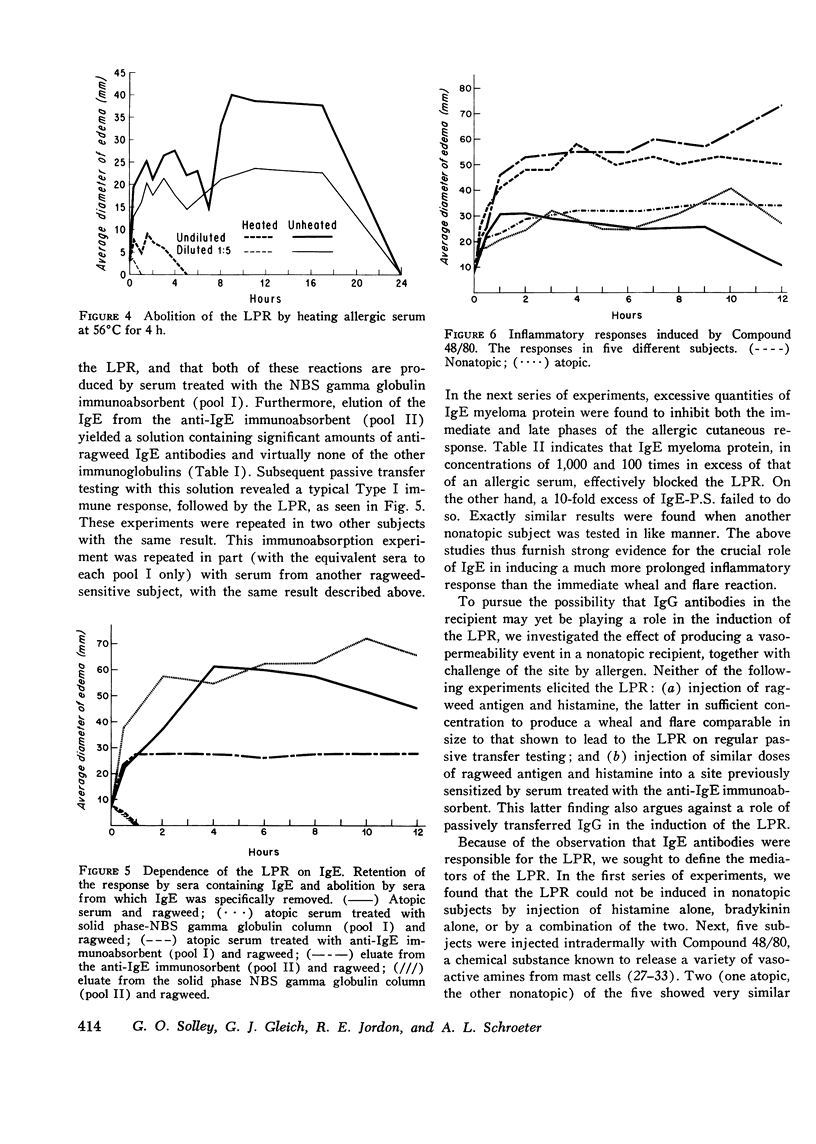
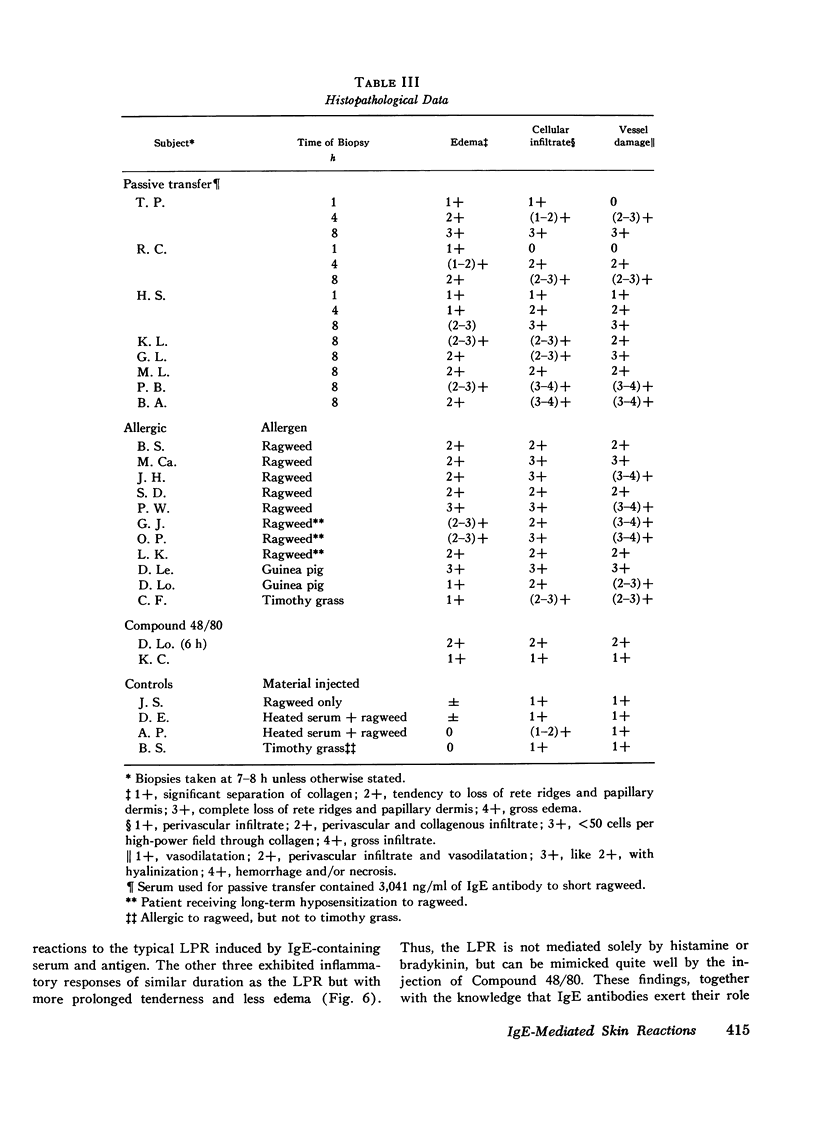
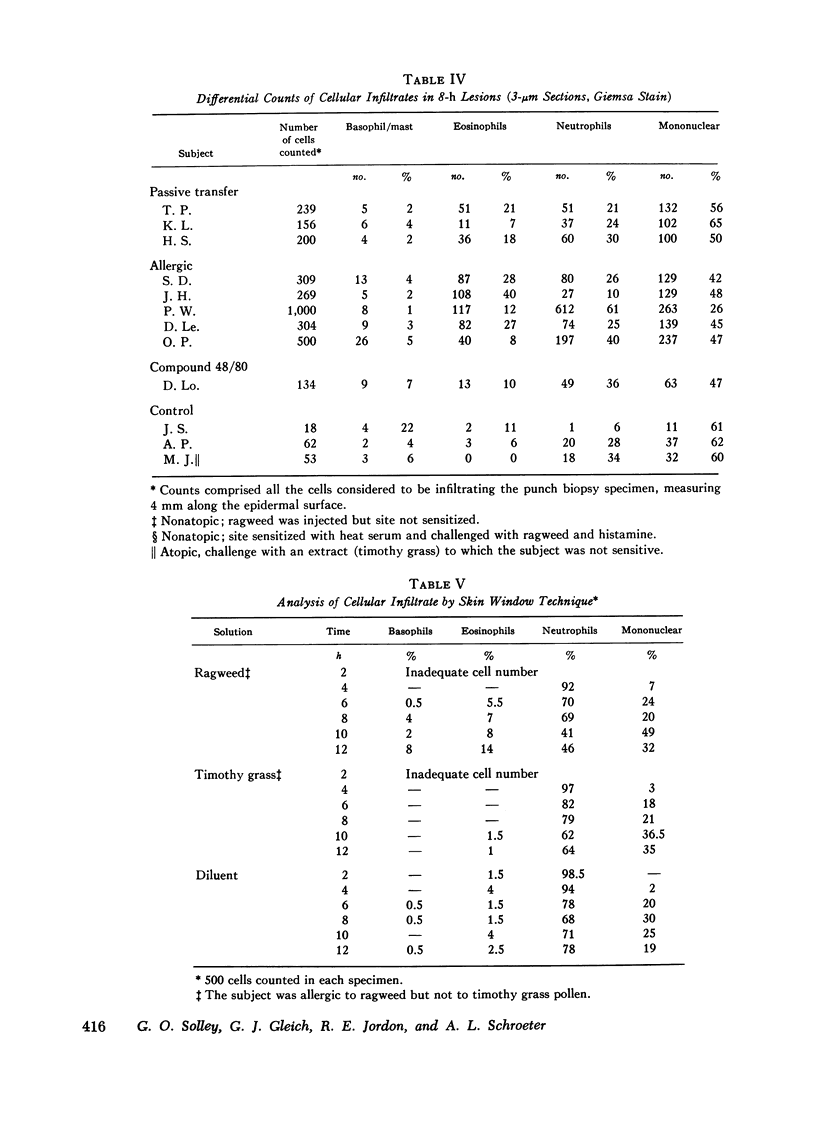




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGGARD ERIK, BERGQVIST U., HOEGBERG B., JOHANSSON K., THON I. L., UVNAES B. BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE PRINCIPLES OCCURRING ON HISTAMINE RELEASE FROM CAT PAW, GUINEA PIG LUNG AND ISOLATED RAT MAST CELLS. Acta Physiol Scand. 1963 Sep-Oct;59:97–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1963.tb02727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anggård E., Strandberg K. Efflux of prostaglandin E 2 from cat paws perfused with compound 48-80. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Jul;82(3):333–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askenase P. W. Cutaneous basophil hypersensitivity in contact-sensitized guinea pigs. I. Transfer with immune serum. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1144–1155. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BHATTACHARYA B. K., LEWIS G. P. The effects of reserpine and compound 48/80 on the release of amines from the mast cells of rats. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1956 Dec;11(4):411–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1956.tb00008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BICKIS I., VON BERTALANFFY L. Identification of cytoplasmic basophilia (ribonucleic acid) by fluorescence microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1956 Sep;4(5):481–493. doi: 10.1177/4.5.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booij-Noord H., Orie N. G., De Vries K. Immediate and late bronchial obstructive reactions to inhalation of house dust and protective effects of disodium cromoglycate and prednisolone. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1971 Dec;48(6):344–354. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(71)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolovich J., Hargreave F. E., Chalmers R., Shier K. J., Gauldie J., Bienenstock J. Late cutaneous allergic responses in isolated IgE-dependent reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1973 Jul;52(1):38–46. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(73)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolovich J., Little D. C. Correlates of skin test reactions to Bacillus subtilis enzyme preparations. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1972 Jan;49(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(72)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrington K. J., Bennich H. Thermally induced structural changes in immunoglobulin E. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 25;248(24):8378–8384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensky J., Hinz C. F., Jr, Todd E. W., Wedgwood R. J., Boyer J. T., Lepow I. H. Properties of highly purified human properdin. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):142–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felarca A. B., Lowell F. C. The accumulation of eosinophils and basophils at skin sites as related to intensity of skin reactivity and symptoms in atopic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1971 Sep;48(3):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(71)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Kaplan A. P. Mononuclear cell chemotactic activity of kallikrein and plasminogen activator and its inhibition by C1 inhibitor and alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1928–1934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Averbeck A. K., Swedlund H. A. Measurement of IgE in normal and allergic serum by radioimmunoassay. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Apr;77(4):690–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Shuster S. Responses of skin blood vessels to bradykinin, histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):255–267. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T., Lee E. H. Biologic function of the Fc fragments of E myeloma protein. Immunochemistry. 1970 Aug;7(8):687–702. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka T., Ishizaka K., Tomioka H. Release of histamine and slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) by IgE-anti-IgE reactions on monkey mast cells. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):513–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordon R. E., Schroeter A. L., Good R. A., Day N. K. The complement system in bullous pemphigoid. II. Immunofluorescent evidence for both classical and alternate-pathway activation. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Jan;3(3):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhlin L., Michaëlsson G. Cutaneous reactions to kallikrein, bradykinin and histamine in healthy subjects and in patients with urticaria. Acta Derm Venereol. 1969;49(1):26–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Kay A. B., Austen K. F. A prealbumin activator of prekallikrein. 3. Appearance of chemotactic activity for human neutrophils by the conversion of human prekallikrein to kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):81–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Austen K. F. Chemotaxis of human basophil leucocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Aug;11(4):557–563. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER A. R. Delayed allergic reactions in otolaryngology. Northwest Med. 1961 Dec;60:1190–1198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz H., Tschida A. R. Automated quantitative immunochemical analysis of human immunoglobulins. Clin Chem. 1972 Nov;18(11):1364–1367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllen M. K., Assem E. S., Maunsell K. House-dust mite asthma. Results of challenge tests on five criteria with Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. Br Med J. 1970 May 30;2(5708):501–504. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5708.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. S., Pepys J. Allergic broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis. Clinical immunology. 2. Skin, nasal and bronchial tests. Clin Allergy. 1971 Dec;1(4):415–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1971.tb00793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newball H. H., Talamo R. C., Lichtenstein L. M. Release of leukocyte kallikrein mediated by IgE. Nature. 1975 Apr 17;254(5501):635–636. doi: 10.1038/254635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. M. Compound 48/80: a potent histamine liberator. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1951 Sep;6(3):499–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1951.tb00661.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost T. T., Tomasi T. B., Jr Evidence for complement activation via the alternate pathway in skin diseases, I. Herpes gestationis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and bullous pemphigoid. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jul;52(7):1779–1787. doi: 10.1172/JCI107359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REBUCK J. W., CROWLEY J. H. A method of studying leukocytic functions in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1955 Mar 24;59(5):757–805. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1955.tb45983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. G., Kerigan A. T., Hargreave F. E., Chalmers R., Dolovich J. Late asthmatic responses induced by ragweed pollen allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1974 Oct;54(4):244–254. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(74)90067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLAVIN R. G., FINK J. N., BECKER R. J., TENNEBAUM J. I., FEINBERG S. M. DELAYED RESPONSE TO ANTIGEN CHALLENGE IN INDUCED DELAYED REACTIVITY. A CLINICAL AND CYTOLOGIC STUDY IN MAN. J Allergy. 1964 Nov-Dec;35:499–505. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(64)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slorach S. A. Histamine and heparin release from isolated rat mast cells exposed to compound 48-80. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 May;82(1):91–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanworth D. R., Humphrey J. H., Bennich H., Johansson S. G. Specific inhibition of the Prausnitz-Küstner reaction by an atypical human myeloma protein. Lancet. 1967 Aug 12;2(7511):330–332. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan A. L., Grimley P. M., Metzger H. Electron microscopic localization of immunoglobulin E on the surface membrane of human basophils. J Exp Med. 1971 Dec 1;134(6):1403–1416. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.6.1403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G., Shivalkar P. R. 'Arthus-type' reactivity in the nasal airways and skin in pollen sensitive subjects. Clin Allergy. 1971 Dec;1(4):407–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1971.tb00792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka H., Ishizaka K. Mechanisms of passive sensitization. II. Presence of receptors for IgE on monkey mast cells. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):971–978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. I., Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Preformed eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis (ECF-A). J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):351–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wide L., Bennich H., Johansson S. G. Diagnosis of allergy by an in-vitro test for allergen antibodies. Lancet. 1967 Nov 25;2(7526):1105–1107. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90615-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunginger J. W., Gleich G. J. Comparison of the protein-binding capacities of cyanogen bromide-activated polysaccharides. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1972 Aug;50(2):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(72)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunginger J. W., Gleich G. J. Seasonal changes in IgE antibodies and their relationship to IgG antibodies during immunotherapy for ragweed hay fever. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1268–1275. doi: 10.1172/JCI107294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachariae H., Malmquist J., Oates J. A., Pettinger W. Studies on the mechanism of kinin formation in inflammation. J Physiol. 1967 May;190(1):81–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]