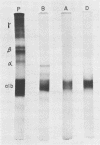
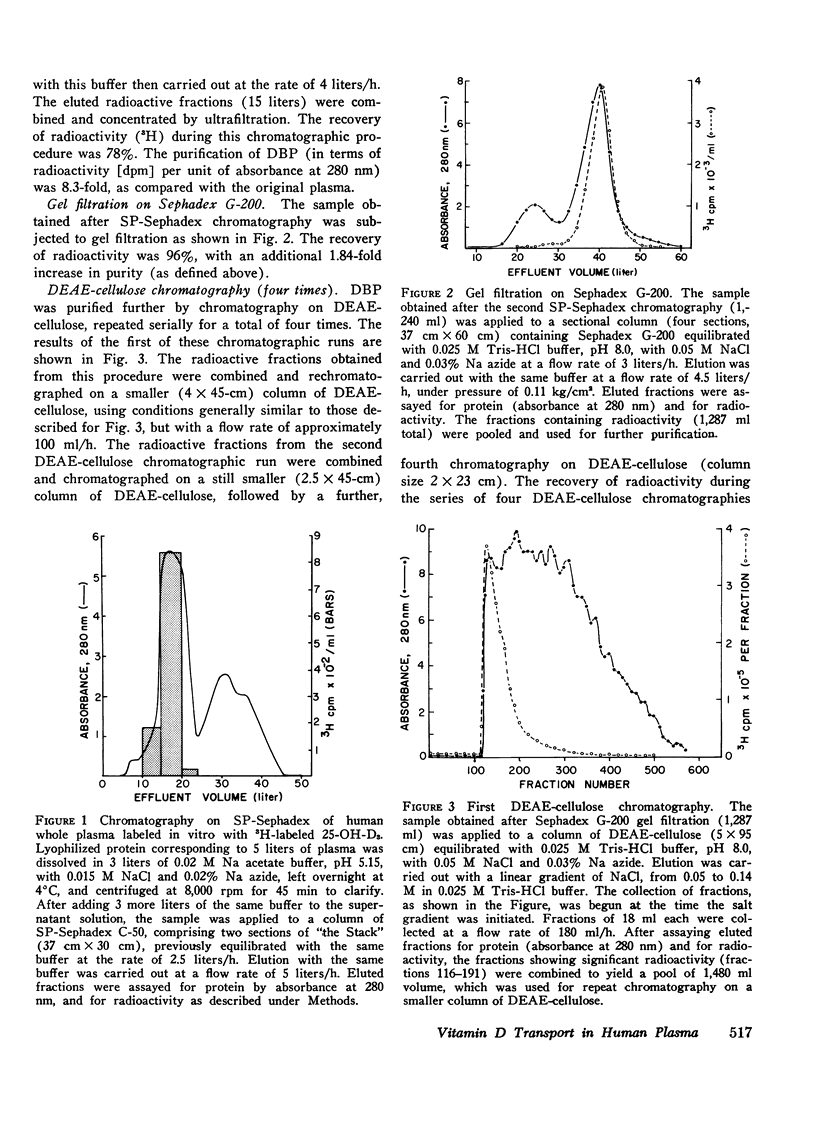
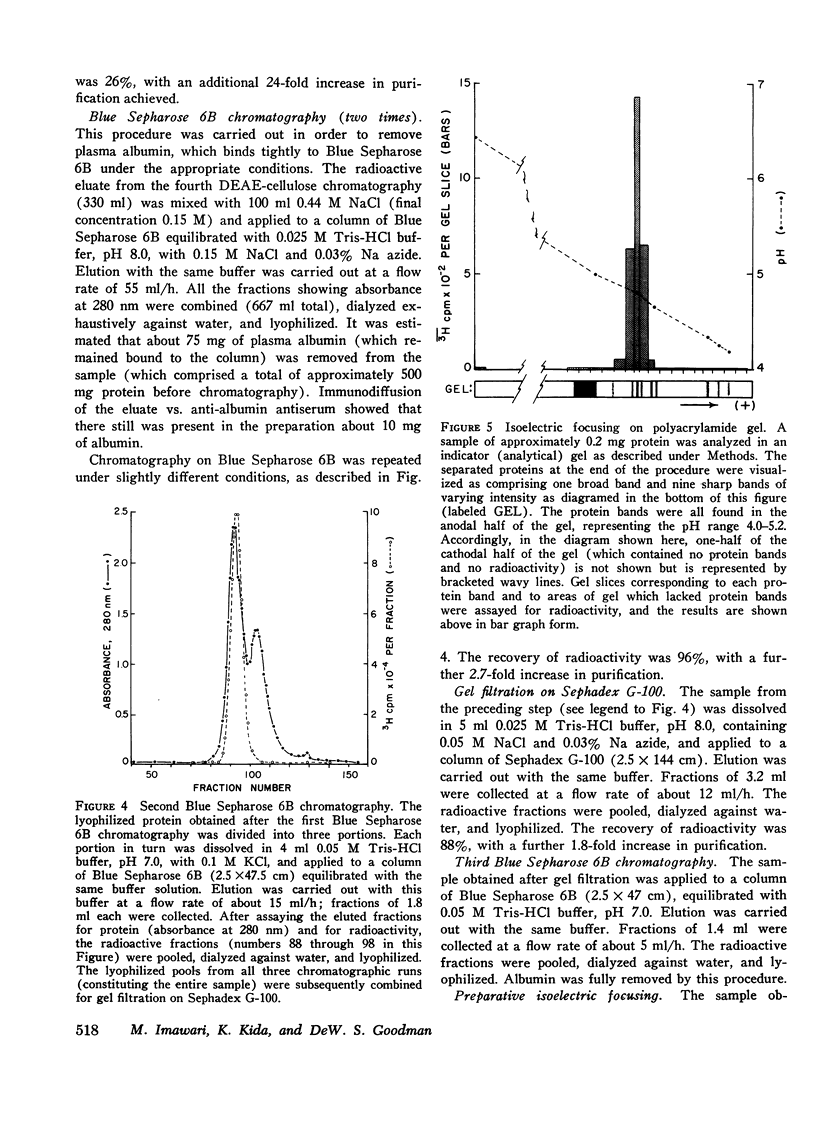
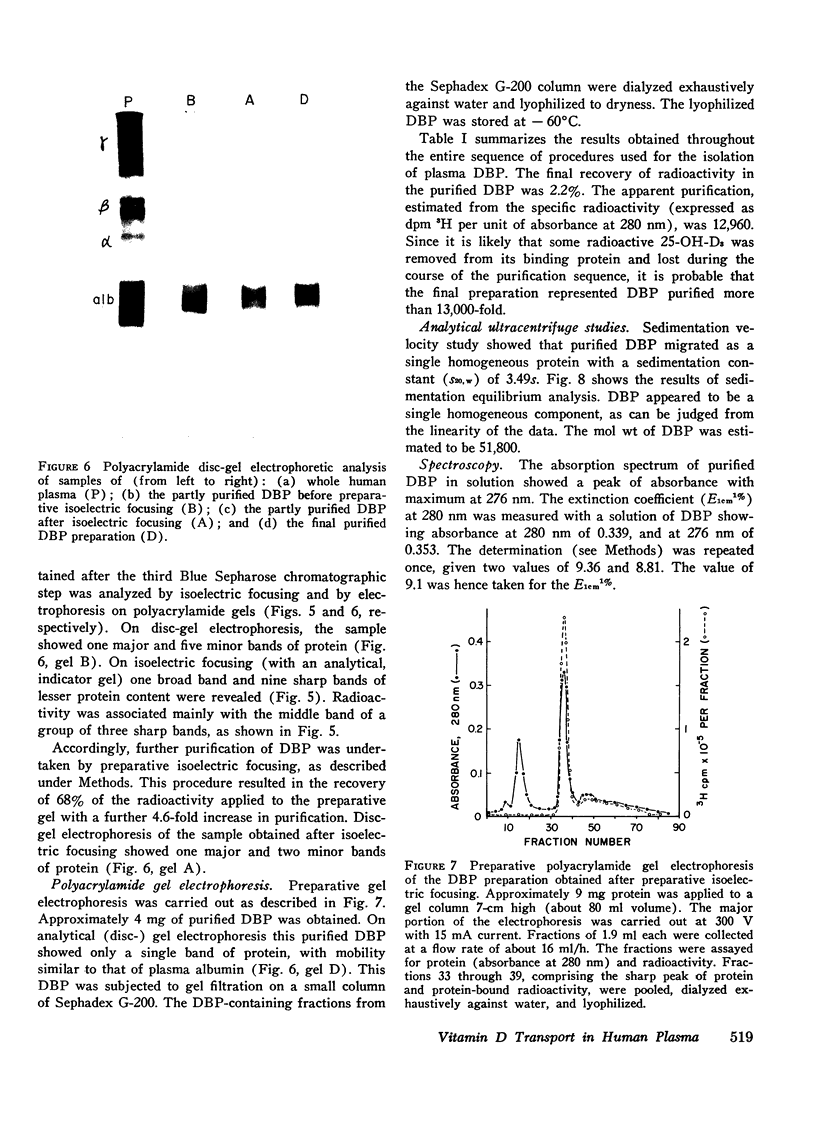
Abstract
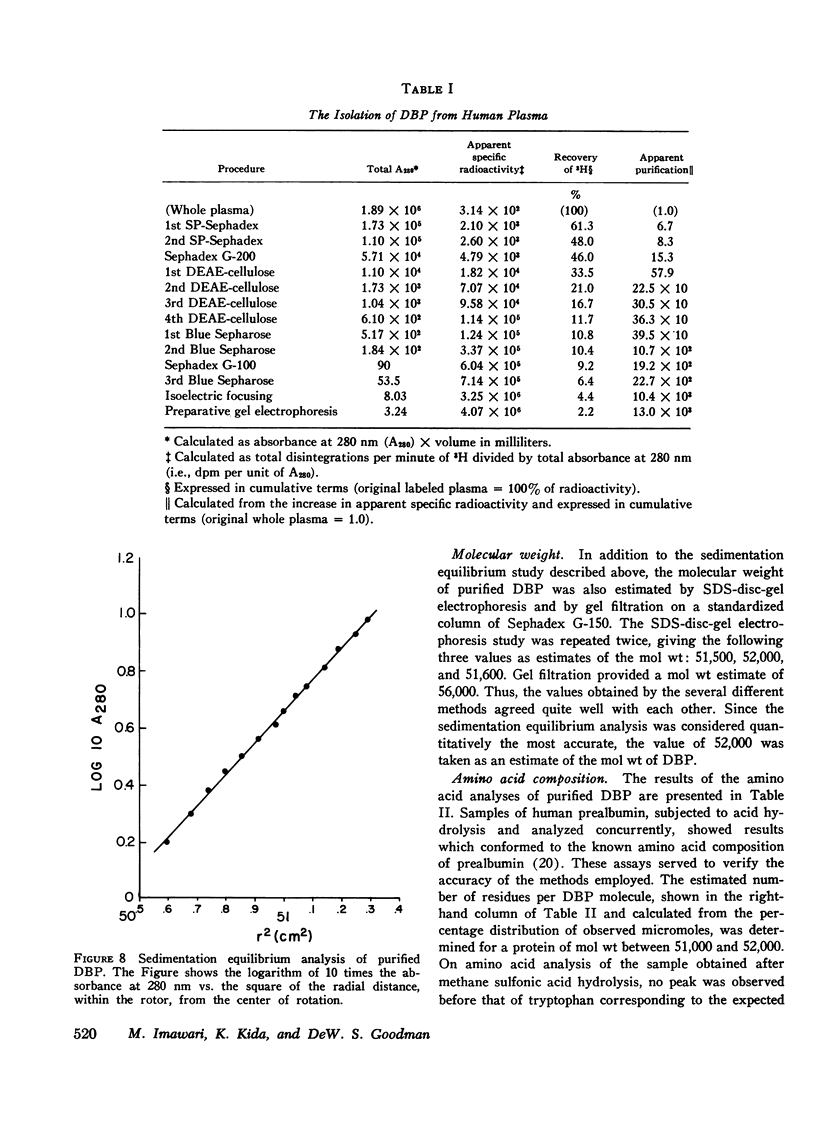
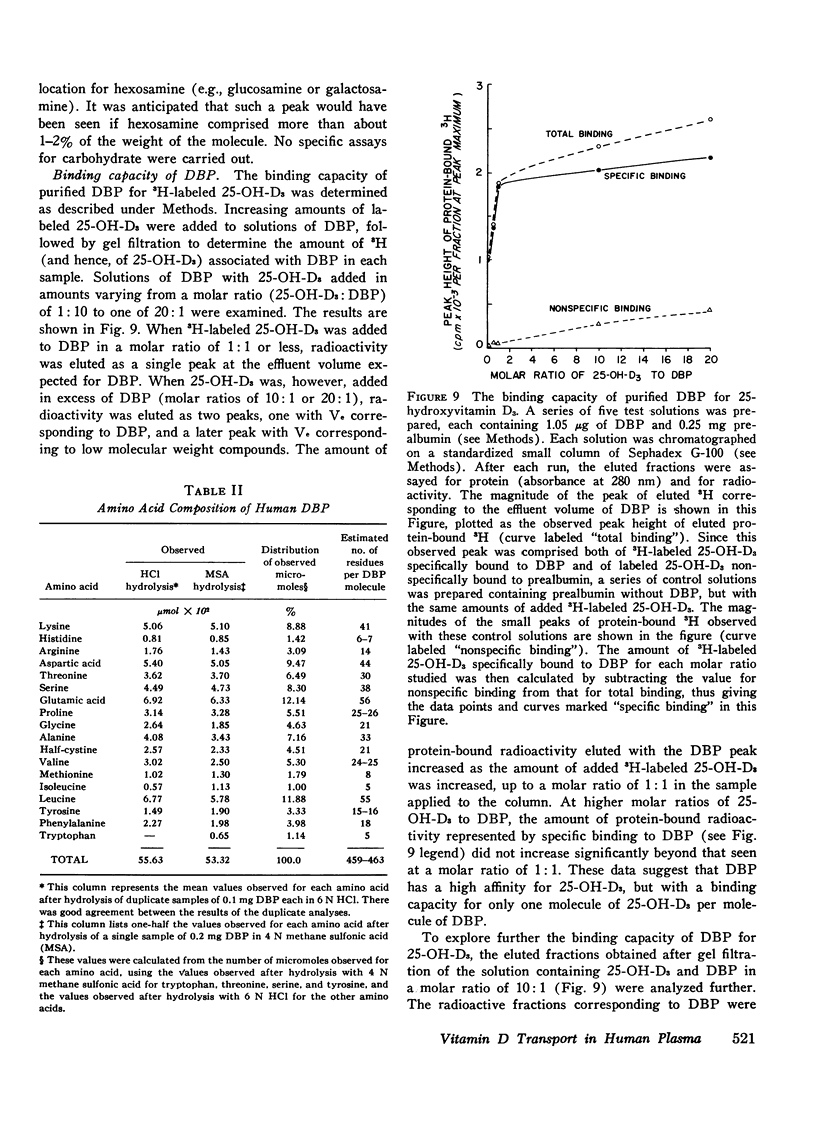
This study reports the isolation and partial characterization of vitamin D and 25-hydroxyvitamin D binding protein (DBP), the specific transport protein for vitamin D and its 25-hydroxy metabolite in human plasma. DBP was labeled by the addition of a tracer amount of 3H-labeled 25-OH-D3 to the original plasma used for protein fractionation. Previous experiments have shown that such 25-OH-D3 added in vitro binds to the same protein normally responsible for the transport of endogenous 25-OH-D and of vitamin D. The isolation of human DBP was achieved by an extensive sequence of procedures which resulted in a final yield of only approximately 4 mg of purified DBP from a starting volume of 34 liters of plasma. Purified DBP was homogeneous in the analytical ultracentrifuge and showed a single band of protein on analytical polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. DBP had a sedimentation constant of 3.49s and a mol wt of approximately 52,000. The molecular weight was assessed by sedimentation equilibrium analysis and also by sodium dodecyl sulfate-disc-gel electrophoresis and by gel filtration on a standardized column of Sephadex G-150. The amino acid composition of DBP was determined and was generally consistent with the estimated extinction coefficient (E1cm1% at 280 nm) of about 9.1. The isoelectric point of DBP was estimated as 4.8 from isoelectric focusing experiments. Direct study of the binding capacity of the purified DBP for added 25-OH-D3 showed that the isolated DBP had a high affinity for 25-OH-D3, with an apparent maximum binding capacity of one molecule of 25-OH-D3 per molecule of protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belsey R., Clark M. B., Bernat M., Glowacki J., Holick M. F., DeLuca H. F., Potts J. T., Jr The physiologic significance of plasma transport of vitamin D and metabolites. Am J Med. 1974 Jul;57(1):50–56. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90767-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F. Vitamin D: the vitamin and the hormone. Fed Proc. 1974 Nov;33(11):2211–2219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein S., Lawson D. E., Kodicek E. The transporting proteins of cholecalciferol and 25-hydroxycholecalciferol in serum of chicks and other species. Partial purification and characterization of the chick proteins. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;135(3):417–426. doi: 10.1042/bj1350417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S. Vitamin A transport and retinol-binding protein metabolism. Vitam Horm. 1974;32:167–180. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad J. G., Birge S. J. Widespread, specific binding of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):299–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai M., Raz A., Goodman D. S. Retinol-binding protein: the transport protein for vitamin A in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2025–2044. doi: 10.1172/JCI105889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda Y., Goodman D. S., Canfield R. E., Morgan F. J. The amino acid sequence of human plasma prealbumin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6796–6805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyachi Y., Vaitukaitis J. L., Nieschlag E., Lipsett M. B. Enzymatic radioiodination of gonadotropins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Jan;34(1):23–28. doi: 10.1210/jcem-34-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto Y., Goodman D. S. Vitamin A transport in rat plasma. Isolation and characterization or retinol-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2533–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. W. The hormone-like action of 1,25-(OH)2-cholecalciferol (a metabolite of the fat-soluble vitamin D) in the intestine. Vitam Horm. 1974;32:325–384. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omdahl J. L., DeLuca H. F. Regulation of vitamin D metabolism and function. Physiol Rev. 1973 Apr;53(2):327–372. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.2.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A. Isolation and partial characterization of a human vitamin D-binding plasma protein. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7748–7754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz A., Goodman D. S. The interaction of thyroxine with human plasma prealbumin and with the prealbumin-retinol-binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3230–3237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikkers H., DeLuca H. F. An in vivo study of the carrier proteins of 3H-vitamins D3 and D4 in rat serum. Am J Physiol. 1967 Aug;213(2):380–386. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.2.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. R., Raz A., Goodman D. S. Radioimmunoassay of human plasma retinol-binding protein. J Clin Invest. 1970 Sep;49(9):1754–1761. doi: 10.1172/JCI106393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. E., Goodman D. S. The turnover and transport of vitamin D and of a polar metabolite with the properties of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2159–2167. doi: 10.1172/JCI106710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Benesch R. E., Yung S., Benesch R. Preparative isoelectric focusing of CO hemoglobins on polyacrylamide gels and conversion to their oxy forms. Anal Biochem. 1973 Sep;55(1):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90310-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]