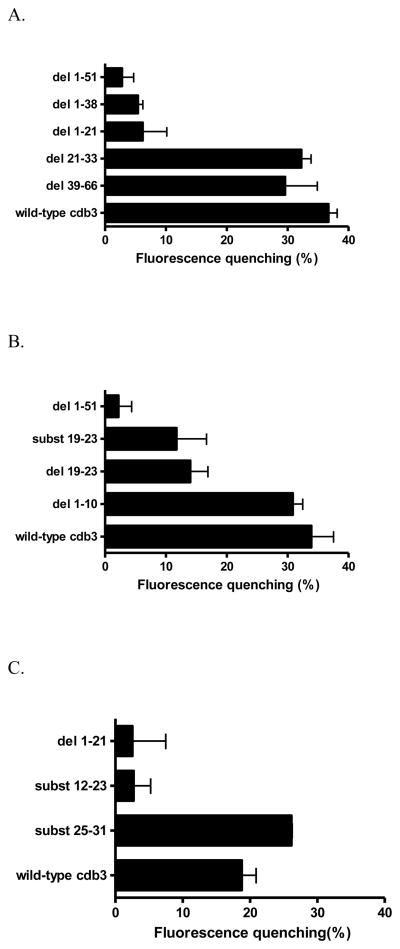
Figure 3.
A) Comparison of the relative affinities of different murine cdb3 mutants for murine deoxyHb. For analysis of deoxyHb binding affinity, the COOH-terminus of each cdb3 was fused to GFPuv and the binding of deoxyHb was assayed by quantitating the quenching of GFPuv fluorescence upon deoxyHb binding. In all cases, the inner filter effect due to Hb absorption of GFPuv fluorescence was subtracted (see Methods). As seen, mutant proteins that lack the first 21 amino acids do not bind deoxyHb (i.e. GFP fluorescence is high for del 1-51, del 1-38, an del 1-21), but when these first 21 residues are present (wild-type, del 21-33, del 39-66), binding affinity is high. A 1-51 deletion mutant was used as a negative control, since it exhibits no affinity for deoxyHb. See Fig. 1 for description of the mutations. B) Localization of the deoxyHb binding site on murine cdb3 to residues 12-23. C) Examination of substitution mutations within the binding region comprising residues 12-23 of cdb3.