Abstract
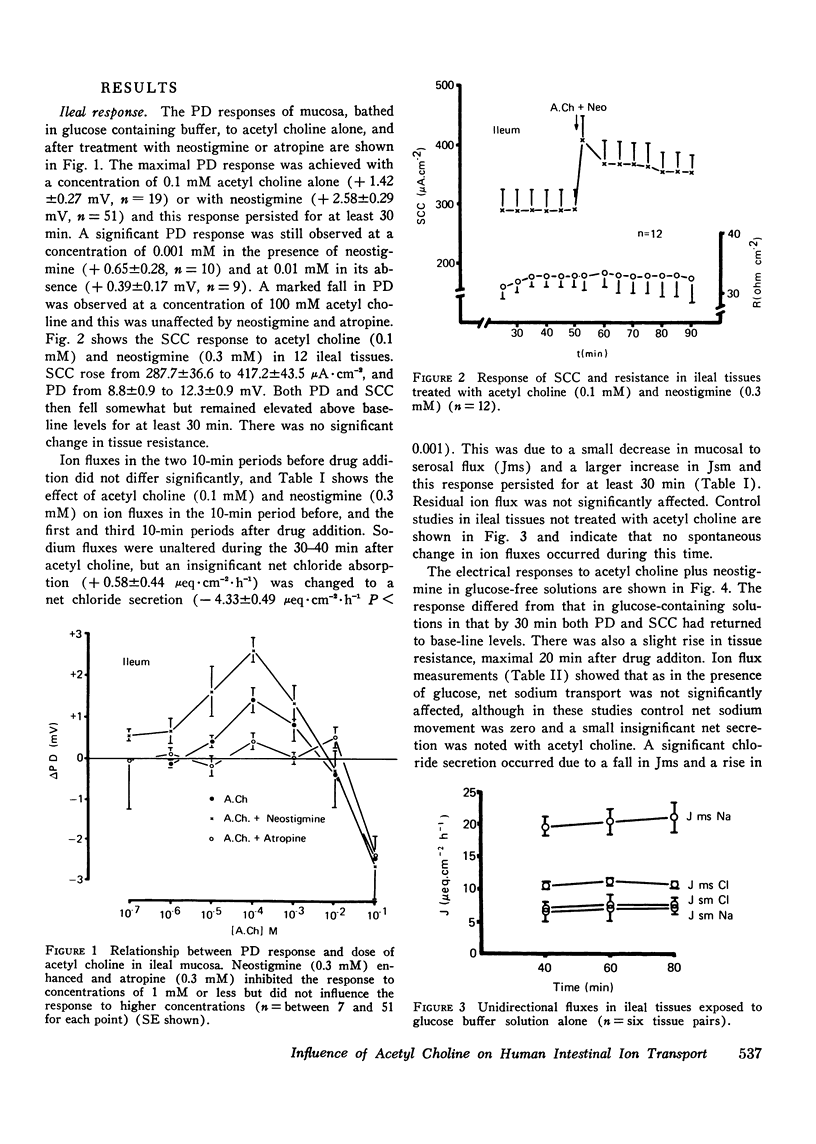
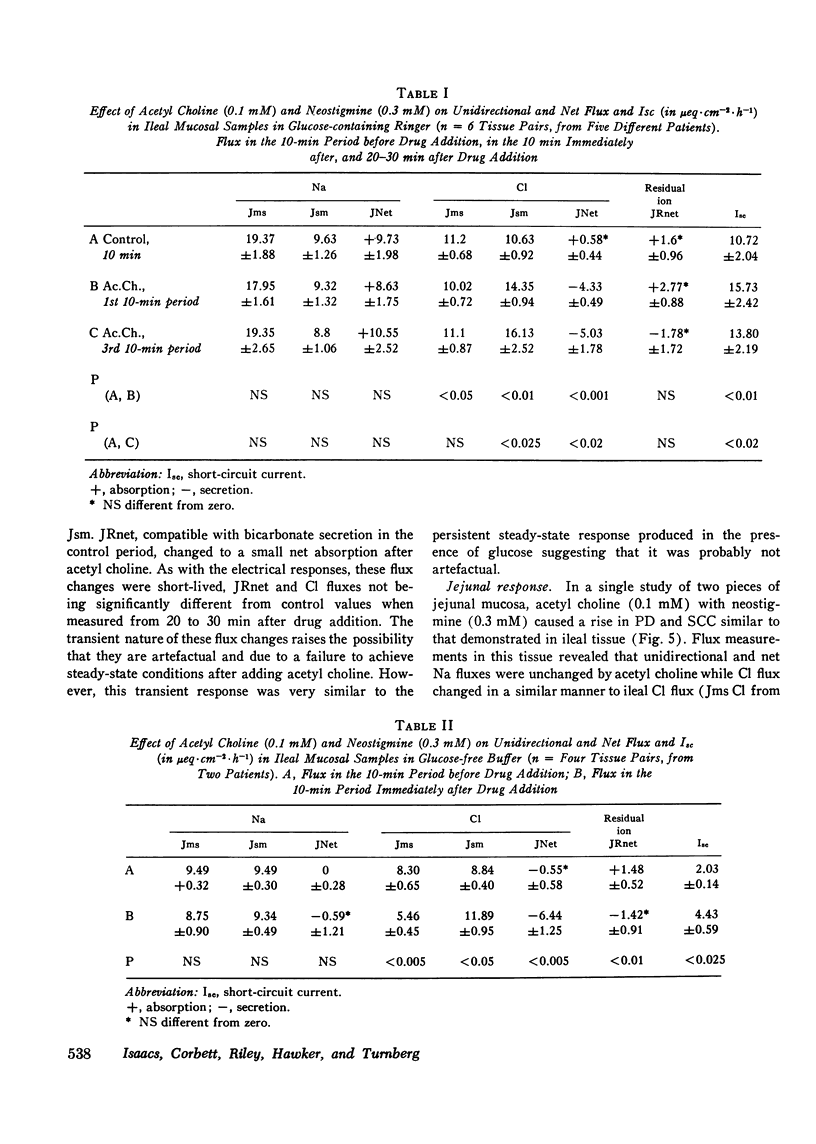
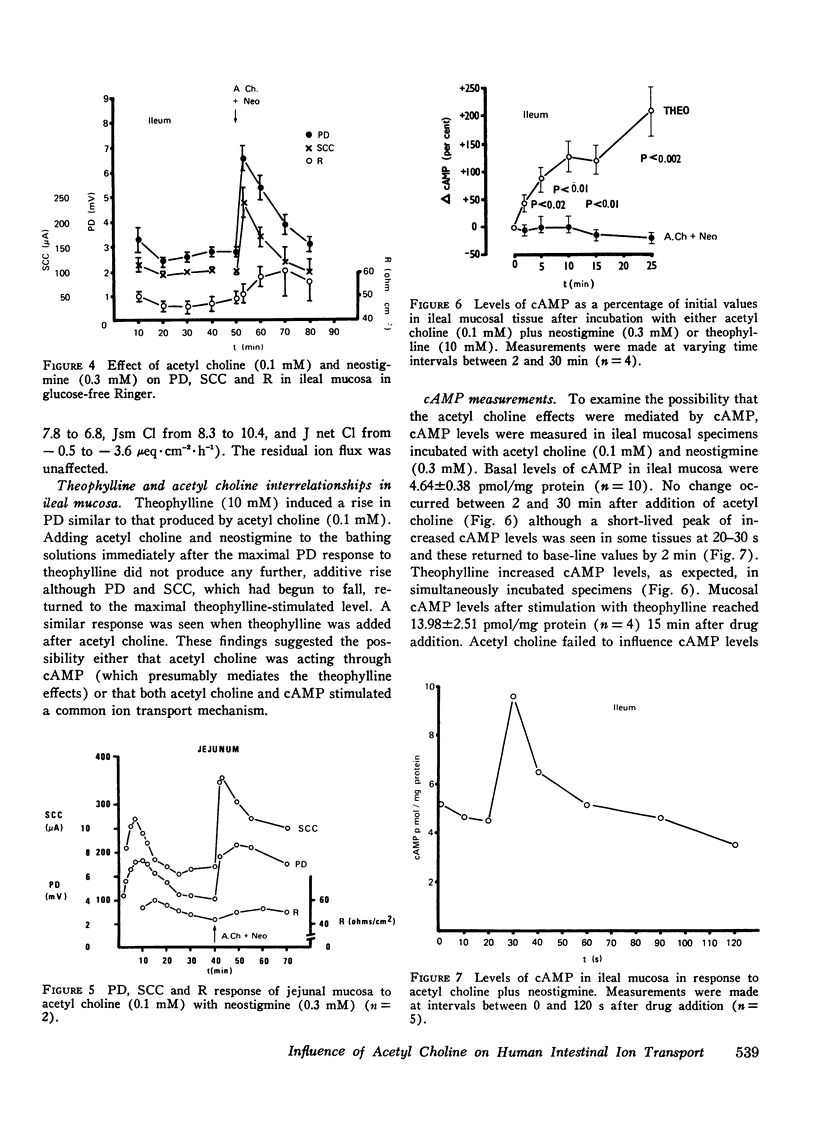
The possibility that the autonomic nervous system may influence the function of intestinal mucosa was investigated by assessing the effect of acetyl choline on ion transport in human intestine. Isolated pieces of stripped ileal mucosa were mounted in Perspex flux-chambers and bathed in isotonic glucose Ringer's solution. Acetyl choline caused a rise in mean potential difference (8.8-12.3 mV, P less than 0.002) and short circuit current (287.7-417.2 muA-cm-2, P less than 0.01) (n = 12), observable at a concentration of 0.01 mM and maximal at 0.1 mM. This effect was enhanced by neostigmine and blocked by atropine. Isotopic flux determinations revealed a change from a small mean net Cl absorption (58) to a net Cl secretion (-4.3mueq-cm-2-h-1P less than 0.001) due predominantly to an increase in the serosal to mucosal unidirectional flux of Cl (10.63-14.35 mueq-cm-2-h-1P less than 0.05) and a smaller reduction in the mucosal to serosal flux (11.22 to 10.02 mueq-cm-2-h-1P less than 0.05). Unidirectional and net Na transport was unaffected. A similar electrical and ion transport response was observed in a single study of two pieces of jejunal mucosa. In the absence of glucose net chloride secretion was produced and again an insignificant effect on net sodium transport was noted. Acetyl choline did not provoke a sustained effect on mucosal cyclic adenine nucleotide levels although a short-lived cyclic adenine nucleotide response was seen in some tissues 20-30 s after drug addition. These studies demonstrate that acetyl choline does influence human intestinal ion transport by stimulating chloride secretion and suggest a possible mechanism by which the parasympathetic nervous system could be concerned in the control of ion transport.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown B. L., Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Sgherzi A. M. A simple and sensitive saturation assay method for the measurement of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(3):561–562. doi: 10.1042/bj1210561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caren J. F., Meyer J. H., Grossman M. I. Canine intestinal secretion during and after rapid distention of the small bowel. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jul;227(1):183–188. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichhorn J. H., Salzman E. W., Silen W. Cyclic GMP response in vivo to cholinergic stimulation of gastric mucosa. Nature. 1974 Mar 15;248(445):238–239. doi: 10.1038/248238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., McColl I. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. I. Na and Cl fluxes and short-circuit current. Am J Physiol. 1971 May;220(5):1388–1396. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.5.1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. II. Effects of cyclic 3', 5'-AMP. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):992–997. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Sheerin H. E., Henderson A., Smith P. L. Catecholamine effects on cyclic AMP levels and ion secretion in rabbit ileal mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jul;229(1):86–92. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Witkum P. A., Beckman B., Sharp G. W. Stimulation of osmotic water flow in toad bladder by prostaglandin E1. Evidence for different compartments of cyclic AMP. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):256–262. doi: 10.1172/JCI108088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George W. J., Polson J. B., O'Toole A. G., Goldberg N. D. Elevation of guanosine 3',5'-cyclic phosphate in rat heart after perfusion with acetylcholine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):398–403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardcastle P. T., Eggenton J. The effect of acetylcholine on the electrical activity of intestinal epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 27;298(1):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. P., Kuo J. F., Greengard P. Role of muscarinic cholinergic receptors in regulation of guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate content in mammalian brain, heart muscle, and intestinal smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3287–3291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellans H. N., Frizzell R. A., Schultz S. G. Brush-border processes and transepithelial Na and Cl transport by rabbit ileum. Am J Physiol. 1974 May;226(5):1131–1141. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.5.1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. W. Intestinal conductance and permselectivity changes with theophylline and choleragen. Am J Physiol. 1974 Dec;227(6):1436–1443. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.6.1436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
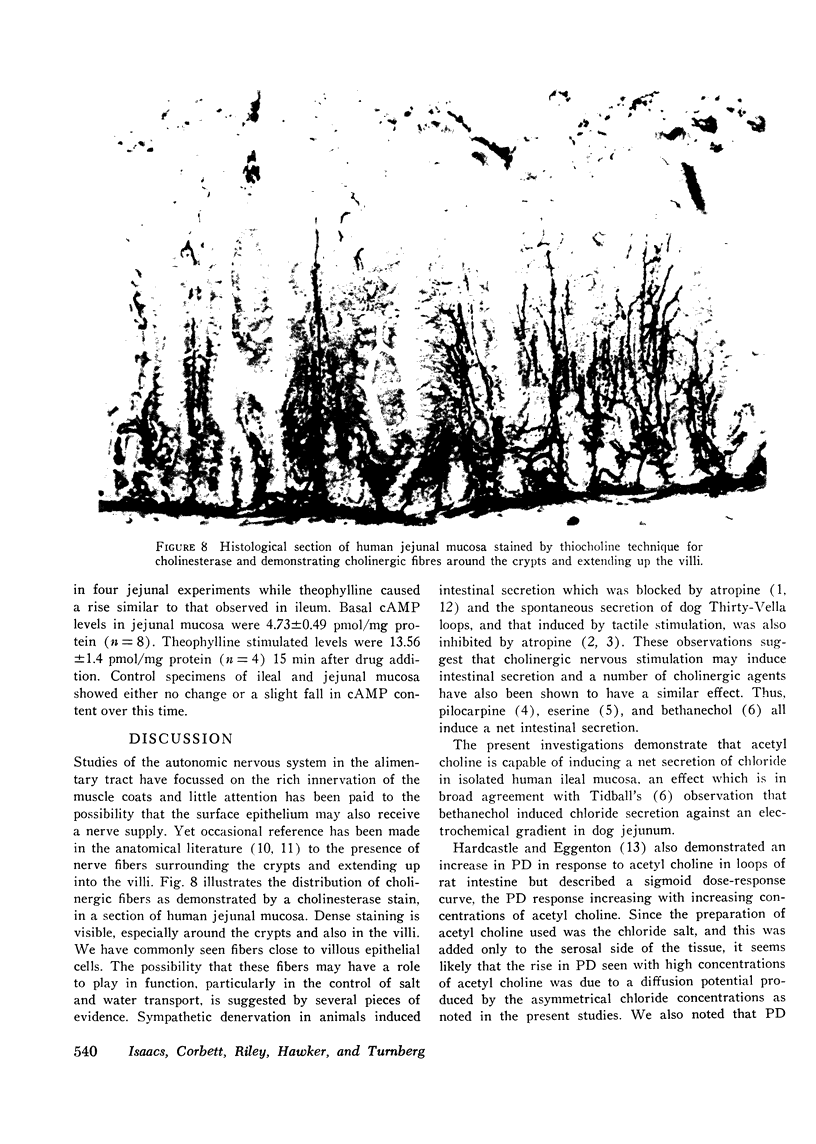
- SCHOFIELD G. C. Experimental studies on the innervation of the mucous membrane of the gut. Brain. 1960 Sep;83:490–514. doi: 10.1093/brain/83.3.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. J., Kimberg D. V., Sheerin H. E., Field M., Said S. I. Vasoactive intestinal peptide stimulation of adenylate cyclase and active electrolyte secretion in intestinal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):536–544. doi: 10.1172/JCI107790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stach W. Uber die Nervengeflechte der Duodenalzotten. Licht- und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen. Acta Anat (Basel) 1973;85(2):216–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIDBALL C. S. Active chloride transport during intestinal secretion. Am J Physiol. 1961 Feb;200:309–312. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.2.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIDBALL C. S., TIDBALL M. E. Changes in intestinal net absorption of a sodium chloride solution produced by atropine in normal and vagotomized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1958 Apr;193(1):25–28. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.193.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRIER J. S. STUDIES ON SMALL INTESTINAL CRYPT EPITHELIUM. II. EVIDENCE FOR THE MECHANISMS OF SECRETORY ACTIVITY BY UNDIFFERENTIATED CRYPT CELLS OF THE HUMAN SMALL INTESTINE. Gastroenterology. 1964 Nov;47:480–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



