Abstract
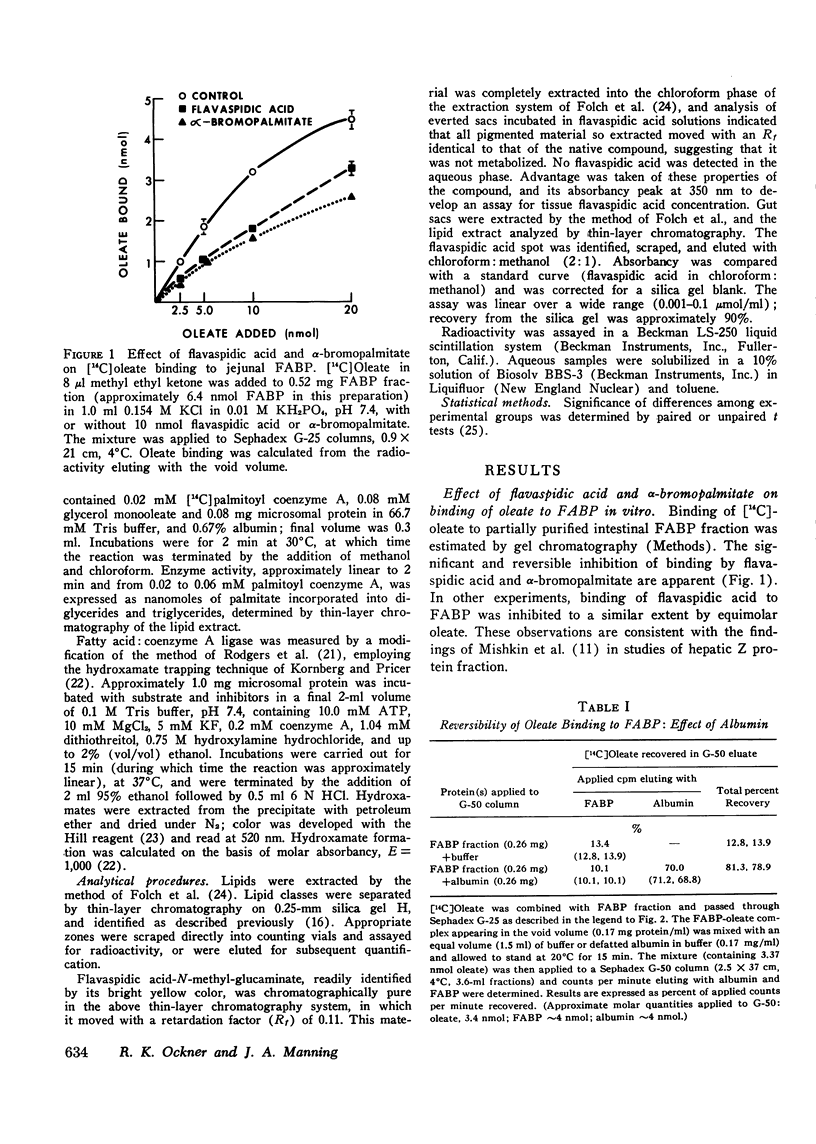
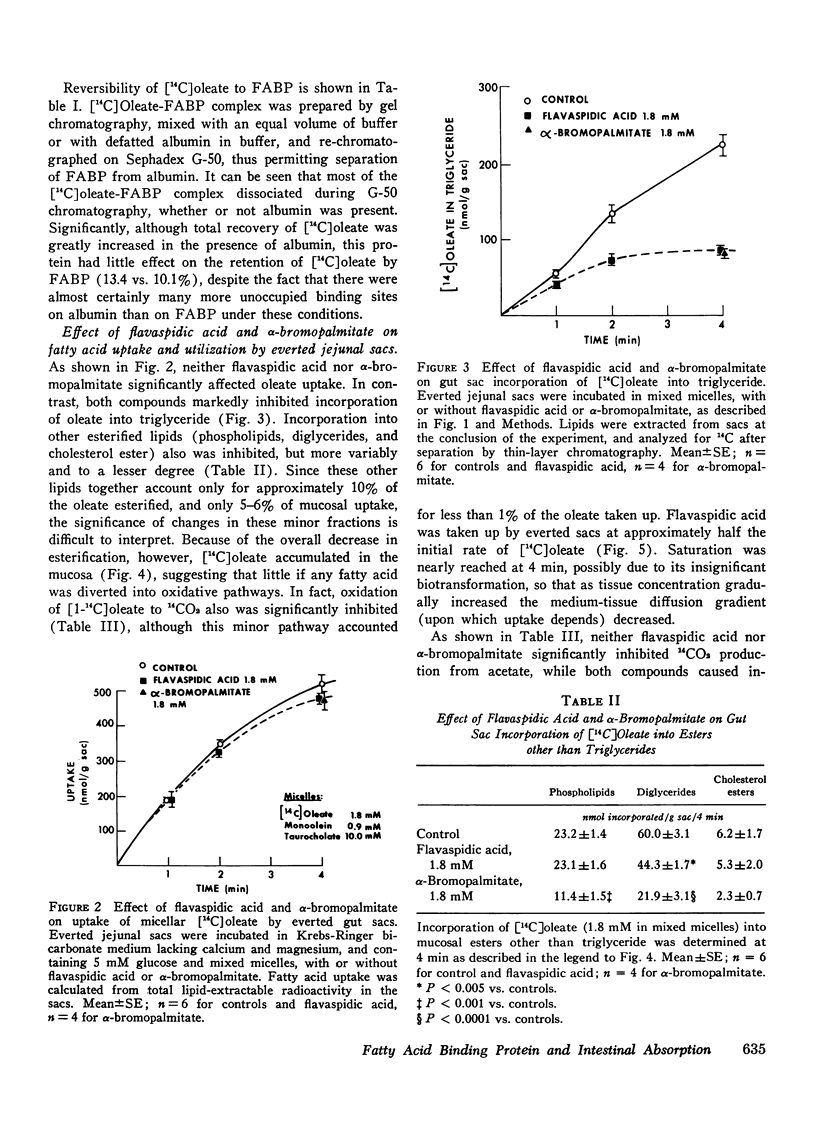
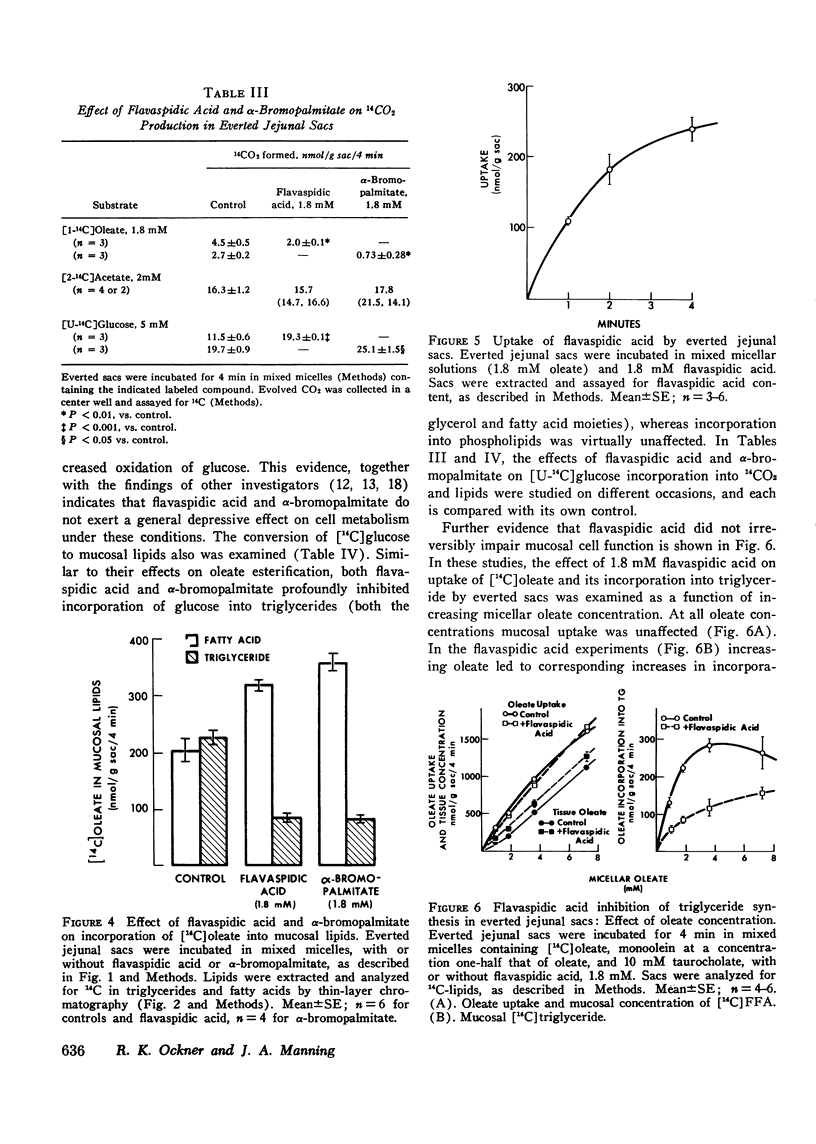
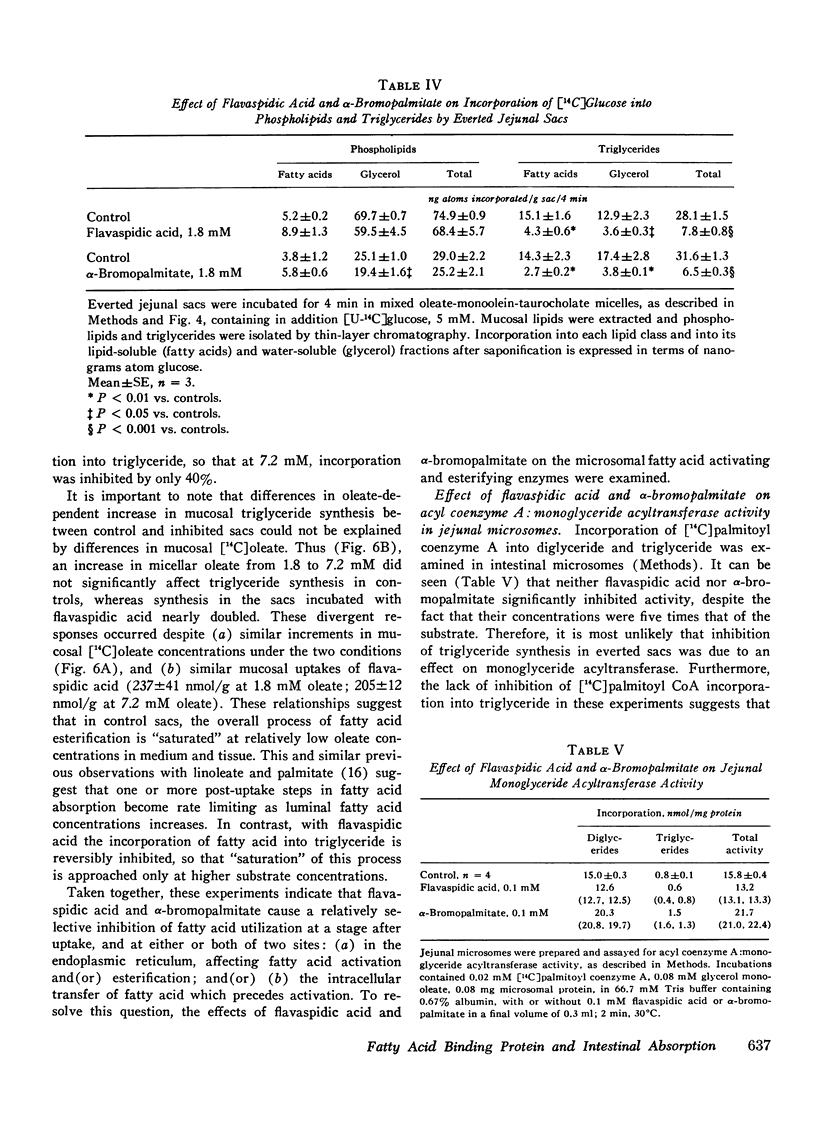
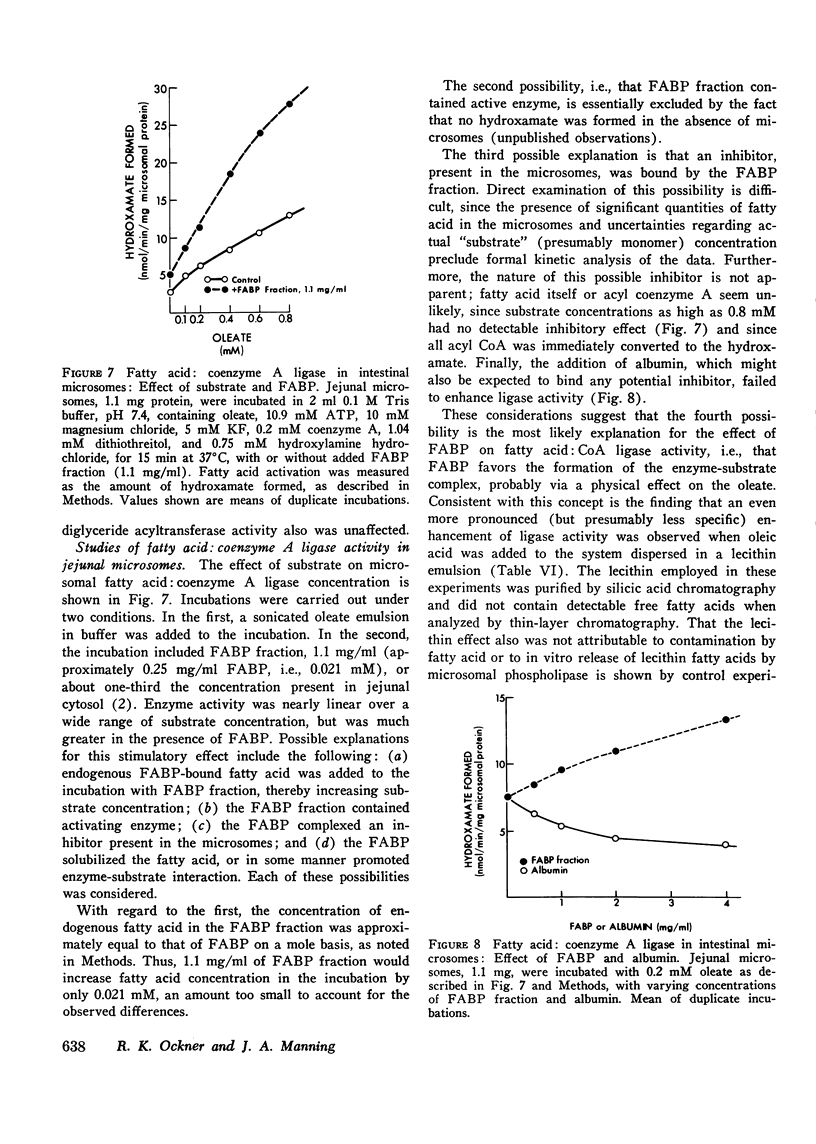
Fatty acid binding protein (FABP) is a protein of 12,000 mol wt found in cytosol of intestinal mucosa and other tissues, which exhibits high affinity for long chain fatty acids. It has been suggested that FABP (which may comprise a group of closely related proteins of 12,000 mol wt) participates in cellular fatty acid transport and metabolism. Although earlier findings were consistent with this concept, the present studies were designed to examine its physiological function more directly. Everted jejunal sacs were incubated in mixed fatty acid-monoglyceride-bile acid micelles, in the presence or absence of equimolar concentrations of either of two compounds which inhibit oleate binding to FABP:flavaspidic acid-N-methyl-glucaminate and alpha-bromopalmitate. Oleate uptake, mucosal morphology, and oxidation of [14C]acetate remained unaffected by these agents, but oleate incorporation into triglyceride was inhibited by 62-64% after 4 min. The inhibition by flavaspidic acid was reversible with higher oleate concentrations. The effect of these compounds on enzymes of triglyceride biosynthesis was examined in intestinal microsomes. Neither flavaspidic acid nor alpha-bromopalmitate inhibited acyl CoA:monoglyceride acyl-transferase. Fatty acid:coenzyme A ligase activity was significantly enhanced in the presence of partially purified FABP, probably reflecting a physical effect on the fatty acid substrate or on the formation of the enzyme-substrate complex. Activity of the enzyme in the presence of 0.1 mM oleate was only modestly inhibited by equimolar flavaspidic acid and alpha-bromopalmitate, and this effect was blunted or prevented by FABP. We conclude that in everted gut sacs, inhibition of triglyceride synthesis by flavaspidic acid and alpha-bromopalmitate could not be explained as an effect on fatty acid uptake or on esterifying enzymes in the endoplasmic reticulum but rather can be interpreted as reflecting inhibition of fatty acid binding to FABP. These findings lend further support to the concept that FABP participates in cellular fatty acid transport and metabolism. It is also possible that FABP, by effecting an intracellular compartmentalization of fatty acids and acyl CoA, may play a broader role in cellular lipid metabolism.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burges R. A., Butt W. D., Baggaley A. Some effects of alpha-bromopalmitate, an inhibitor of fatty acid oxidation, on carbohydrate metabolism in the rat. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):38P–39P. doi: 10.1042/bj1090038pb. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M., Wright E. M. Biological membranes: the physical basis of ion and nonelectrolyte selectivity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1969;31:581–646. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.31.030169.003053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. S. The interaction of human erythrocytes with sodium palmitate. J Clin Invest. 1958 Dec;37(12):1729–1735. doi: 10.1172/JCI103765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangl A., Ockner R. K. Intestinal metabolism of plasma free fatty acids. Intracellular compartmentation and mechanisms of control. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):803–813. doi: 10.1172/JCI107991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J., AHRENS E. H., Jr The separation of complex lipide mixtures by the use of silicic acid chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):311–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halestrap A. P., Denton R. M. Hormonal regulation of adipose-tissue acetyl-Coenzyme A carboxylase by changes in the polymeric state of the enzyme. The role of long-chain fatty acyl-Coenzyme A thioesters and citrate. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;142(2):365–377. doi: 10.1042/bj1420365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSTON J. M., BORGSTROEM B. THE INTESTINAL ABSORPTION AND METABOLISM OF MICELLAR SOLUTIONS OF LIPIDS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 5;84:412–423. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs R. A., Majerus P. W. The regulation of fatty acid synthesis in human skin fibroblasts. Inhibition of fatty acid synthesis by free fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 25;248(24):8392–8401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG A., PRICER W. E., Jr Enzymatic synthesis of the coenzyme A derivatives of long chain fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1953 Sep;204(1):329–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl W. E., Spector A. A. Uptake of long-chain fatty acid methyl esters by mammalian cells. J Lipid Res. 1970 Sep;11(5):458–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A. J., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Two hepatic cytoplasmic protein fractions, Y and Z, and their possible role in the hepatic uptake of bilirubin, sulfobromophthalein, and other anions. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2156–2167. doi: 10.1172/JCI106182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan S., Sauer F. Effect of -bromo-palmitate on the oxidation of palmitic acid by rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):5862–5867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishkin S., Stein L., Fleischner G., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. Z protein in hepatic uptake and esterification of long-chain fatty acids. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1634–1640. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishkin S., Stein L., Gatmaitan Z., Arias I. M. The binding of fatty acids to cytoplasmic proteins: binding to Z protein in liver and other tissues of the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 9;47(5):997–1003. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90931-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishkin S., Turcotte R. The binding of long chain fatty acid CoA to Z, a cytoplasmic protein present in liver and other tissues of the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 8;57(3):918–926. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90633-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishkin S., Yalovsky M., Kessler J. I. Stages of uptake and incorporation of micellar palmitic acid by hamster proximal intestinal mucosa. J Lipid Res. 1972 Mar;13(2):155–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Manning J. A. Fatty acid-binding protein in small intestine. Identification, isolation, and evidence for its role in cellular fatty acid transport. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):326–338. doi: 10.1172/JCI107768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Manning J. A., Poppenhausen R. B., Ho W. K. A binding protein for fatty acids in cytosol of intestinal mucosa, liver, myocardium, and other tissues. Science. 1972 Jul 7;177(4043):56–58. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4043.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Pittman J. P., Yager J. L. Differences in the intestinal absorption of saturated and unsaturated long chain fatty acids. Gastroenterology. 1972 May;62(5):981–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ontko J. A. Metabolism of free fatty acids in isolated liver cells. Factors affecting the partition between esterification and oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1788–1800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pande S. V., Siddiqui A. W., Gattereau A. Inhibition of long-chain fatty acid activation by -bromopalmitate and phytanate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 5;248(2):156–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUNEBERG L. Uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation in rat liver mitochondria with desaspidin and related phlorobutyrophenone derivative. Biochem Pharmacol. 1962 Mar;11:237–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(62)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers J. B., Jr Assay of acyl-CoA:monoglyceride acyltransferase from rat small intestine using continuous recording spectrophotometry. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jul;10(4):427–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers J. B., Riley E. M., Drummey G. D., Isselbacher K. J. Lipid absorption in adrenalectomized rats: the role of altered enzyme activity in the intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1967 Oct;53(4):547–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers J. B., Tandon R., Fromm H. Acyl-CoA synthetase for long-chain fatty acids in rat small bowel and the influence of diets containing different compositions of fatty acids on intestinal lipid reesterifying enzyme activities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 11;270(4):453–462. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPECTOR A. A., STEINBERG D., TANAKA A. UPTAKE OF FREE FATTY ACIDS BY EHRLICH ASCITES TUMOR CELLS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1032–1041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallee V. L., Wilson F. A., Dietschy J. M. Determination of unidirectional uptake rates for lipids across the intestinal brush border. J Lipid Res. 1972 Mar;13(2):184–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHAN M., STEINBERG D., PITTMAN R. ON THE INTERPRETATION OF STUDIES MEASURING UPTAKE AND ESTERIFICATION OF (1-14-C)PALMITIC ACID BY RAT ADIPOSE TISSUE IN VITRO. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Apr 20;84:154–166. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


