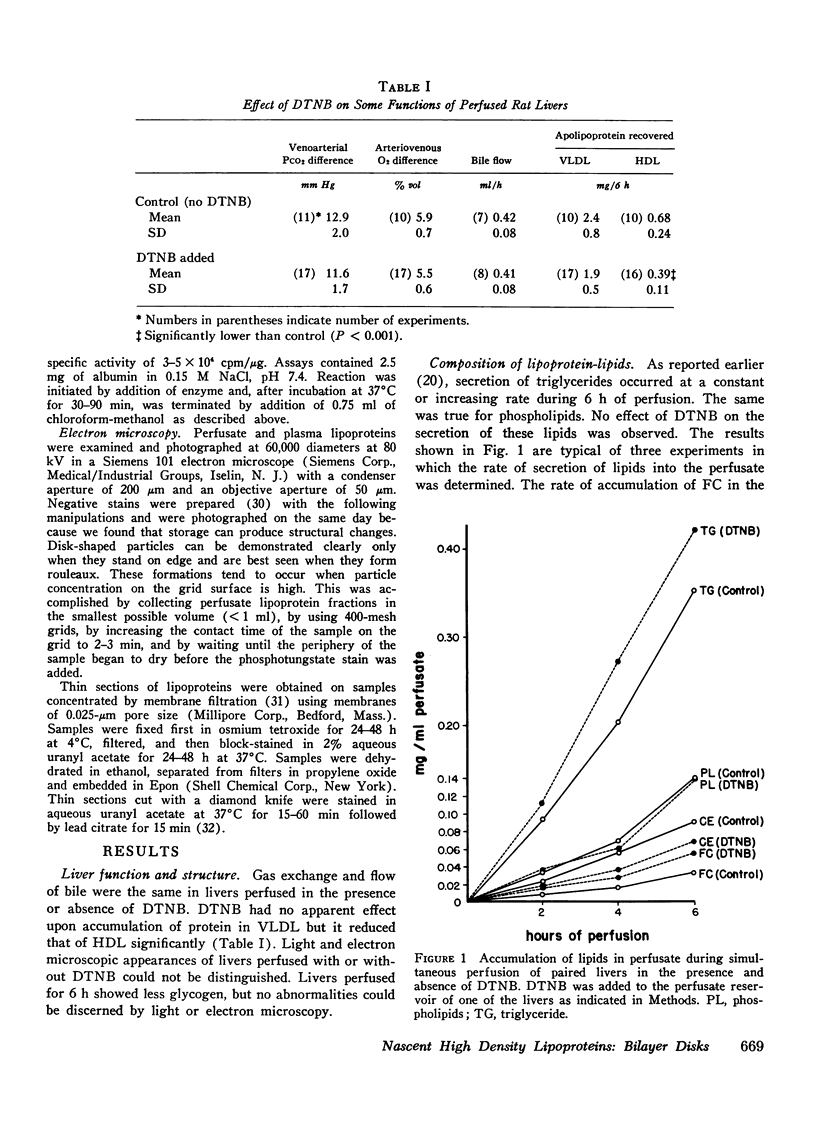
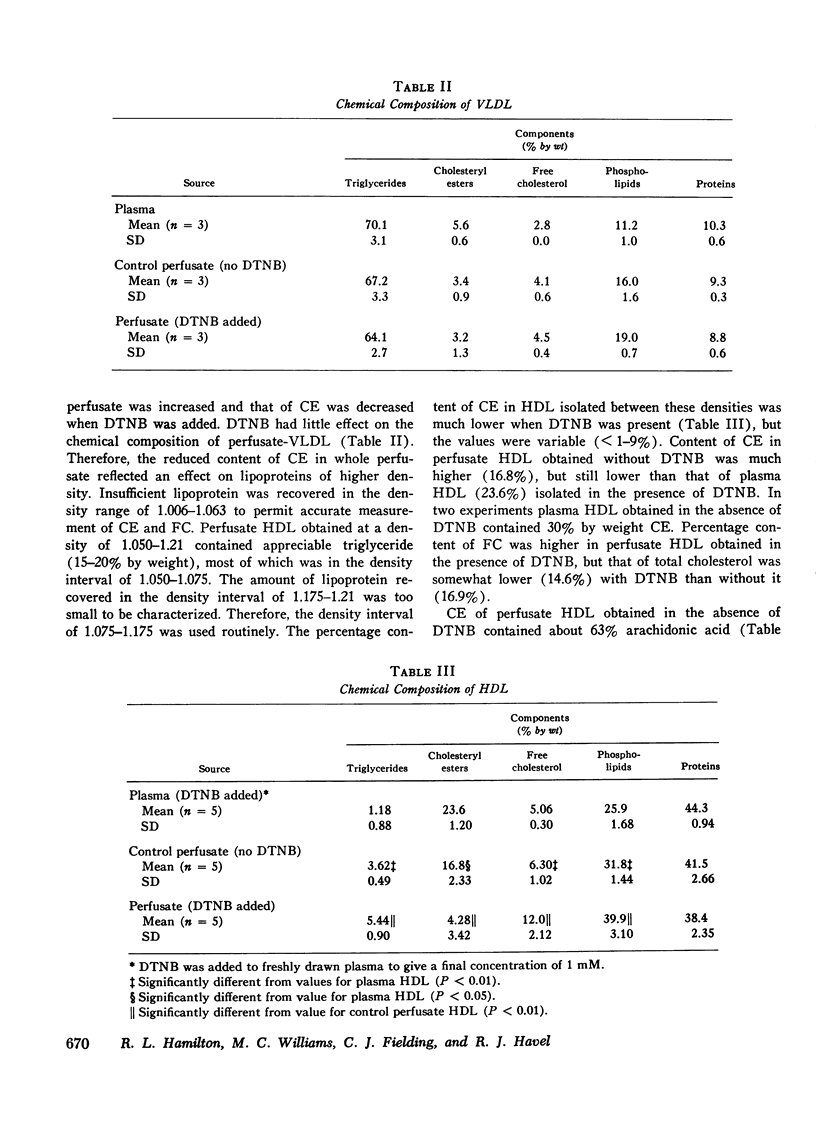
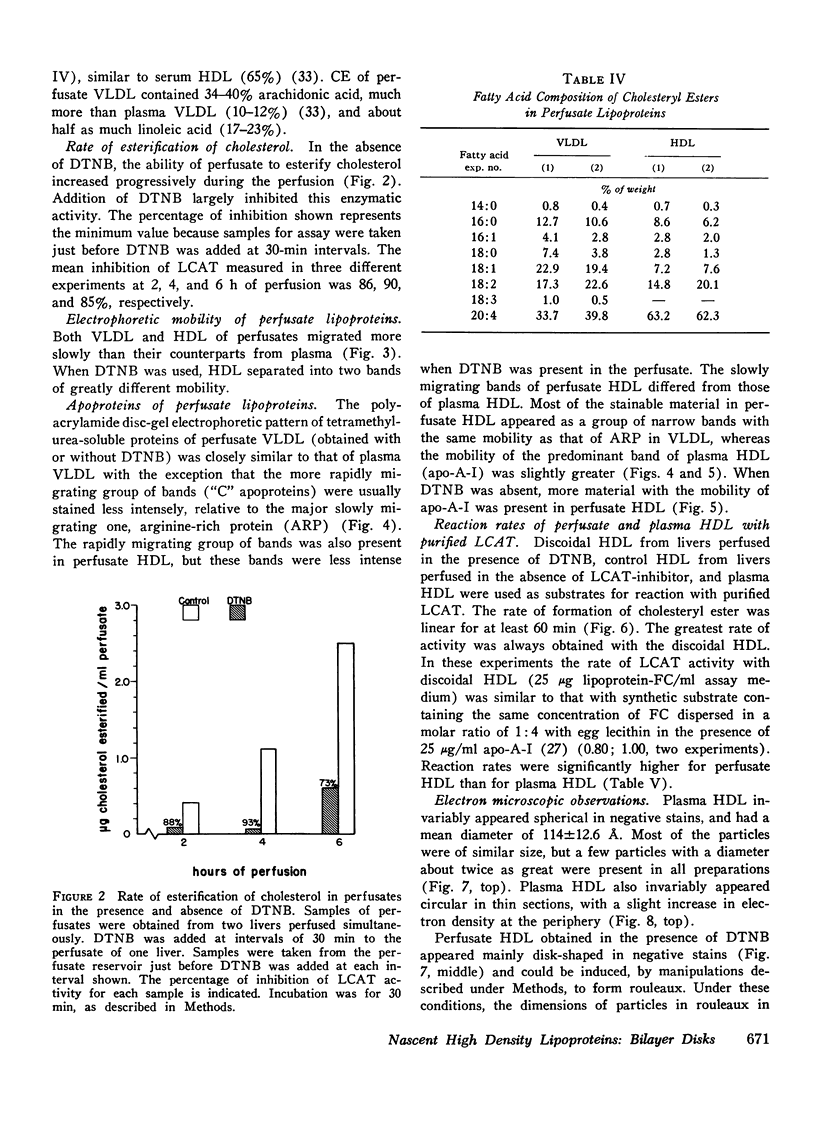
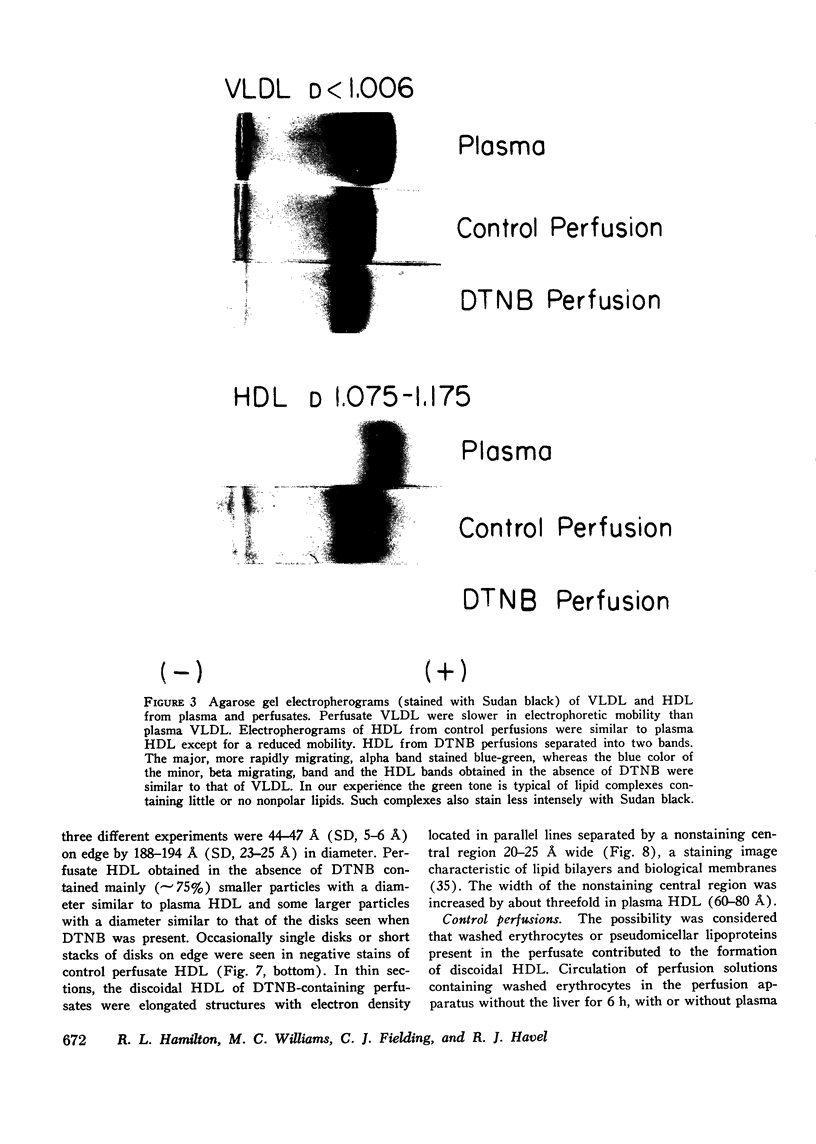
Abstract
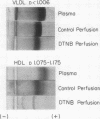
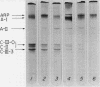
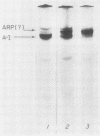
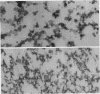
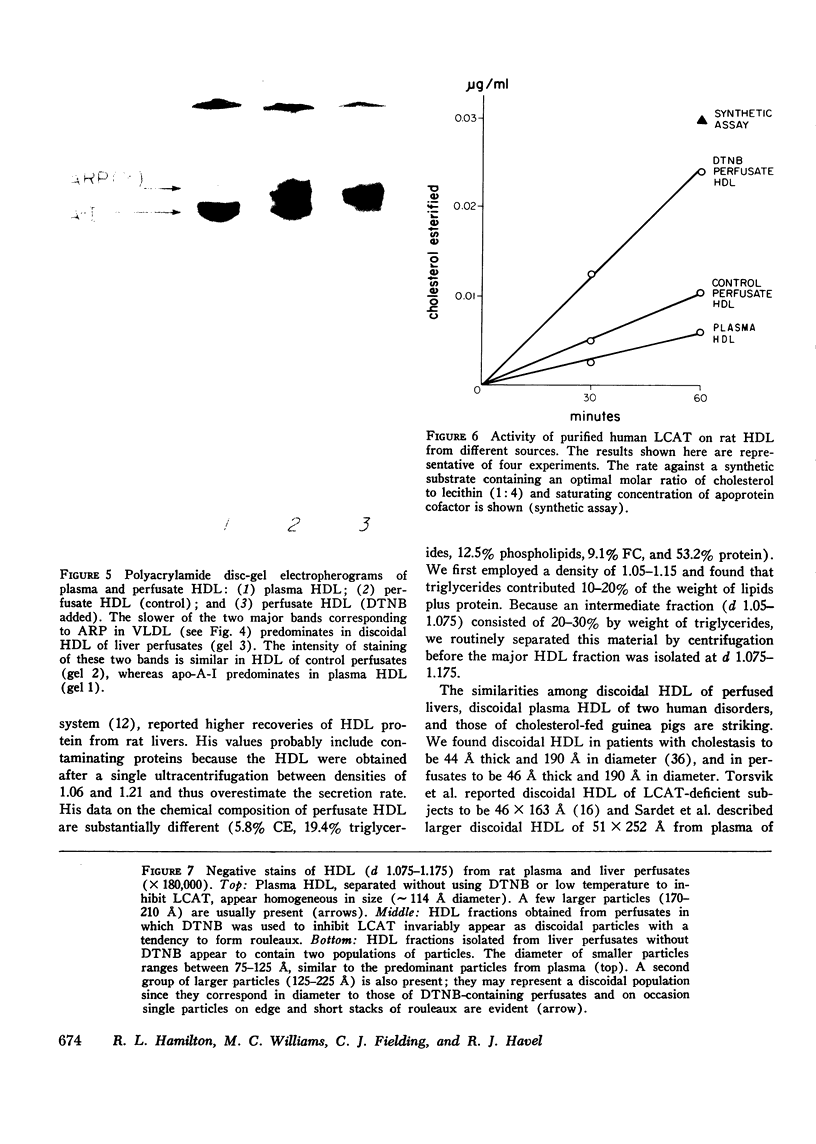
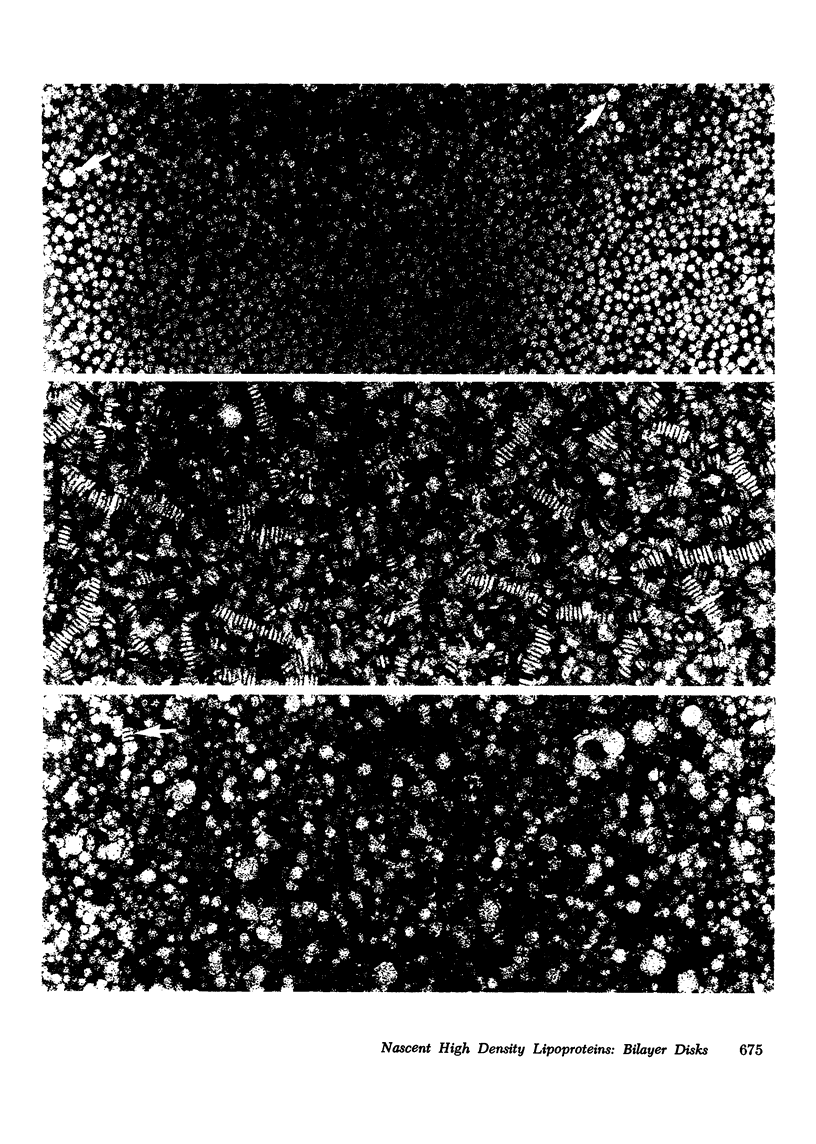
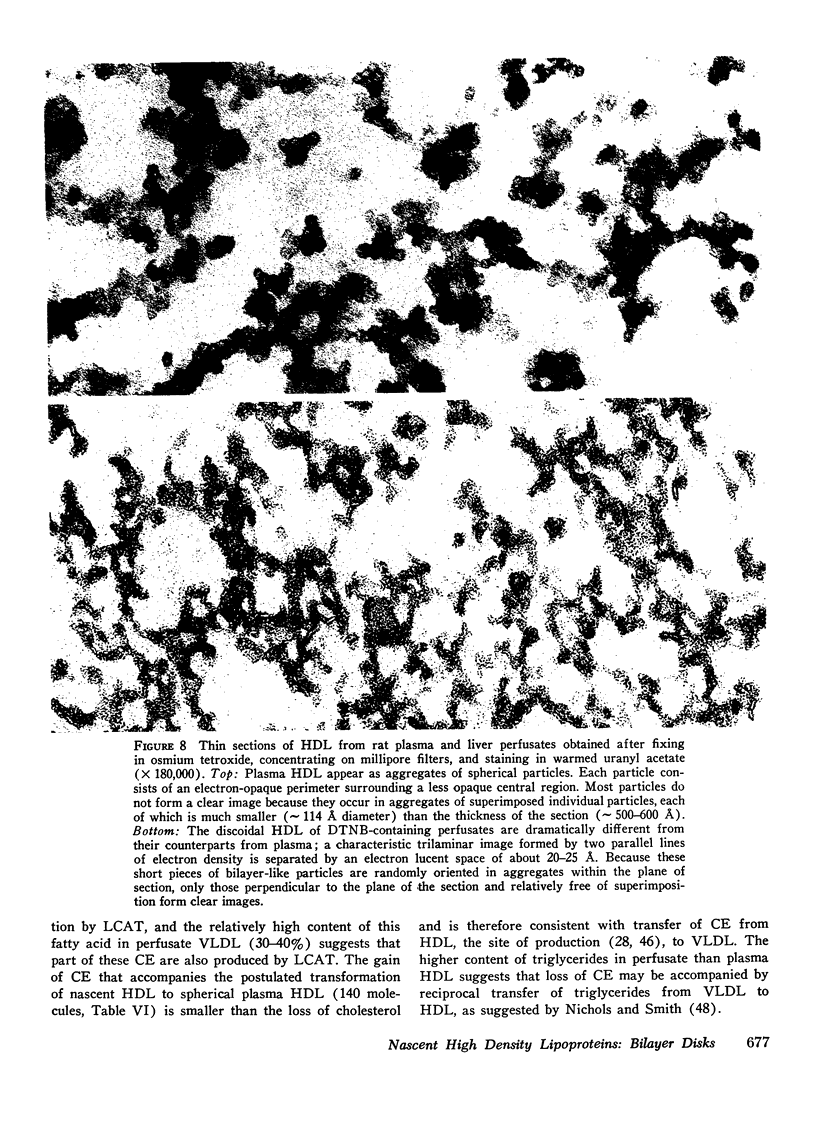
Rat livers were perfused for 6 h without added plasma proteins using washed erythrocytes and buffer in a recirculating system. An inhibitor to the enzyme lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (5,5'-dithionitrobenzoic acid) was added in some experiments to prevent modification of substrate-lipids contained in secreted lipoproteins. The inhibitor did not detectably alter hepatic ultrastructure or gas exchange, but it inhibited the secreted lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase by more than 85%. Very low density lipoproteins in perfusate were unaltered but the high density lipoproteins obtained from livers perfused with the inhibitor appeared disk-shaped in negative stain by electron microscopy with a mean edge thickness of 46 +/- 5 A and a mean diameter of 190 +/- 25 A. The high density lipoproteins were composed predominantly of polar lipids and protein with only small amounts of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides. The major apoprotein of these discoidal fractions had the same electrophoretic mobility as the arginine-rich apoprotein, whereas plasma high density lipoproteins contained mainly the A-I approtein. In all these respects the discoidal perfusate high density lipoproteins closely resemble those found in human plasma which is deficient in lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase. Perfusate high density lipoproteins obtained in the absence of the enzyme inhibitor more closely resembled plasma high density lipoproteins in chemical composition (content of cholesteryl esters and apoproteins) and in electron microscopic appearance. Purified lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase synthesized cholesteryl esters at a substantially faster rate from substrate lipids of perfusate high density lipoproteins than those from plasma. The discoidal high density lipoproteins were the best substrate for this reaction. Thin sections of plasma high density lipoproteins indicated a spherical particle whereas discoidal high density lipoproteins stained with the characteristic trilaminar image of membranes. These observations suggest that the liver secretes disk-shaped lipid bilayer particles which represent both the nascent form of high density lipoproteins and preferred substrate for lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akanuma Y., Glomset J. In vitro incorporation of cholesterol-14C into very low density lipoprotein cholesteryl esters. J Lipid Res. 1968 Sep;9(5):620–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomhoff J. P. High density lipoproteins in cholestasis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1974;9(6):591–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson B., Ekman R., Petersson B. G. An abnormal high density lipoprotein in cholestatic plasma isolated by zonal ultracentrifugation. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 1;50(2):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80484-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz A. A., Rubinstein H. M. Laboratory note--standardization of the Ellman reaction. Clin Biochem. 1972 Jun;5(2):136–138. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9120(72)80022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Park C. R. Control of gluconeogenesis in liver. I. General features of gluconeogenesis in the perfused livers of rats. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 10;242(11):2622–2636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faergeman O., Havel R. J. Metabolism of cholesteryl esters of rat very low density lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1210–1218. doi: 10.1172/JCI108039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Purification and substrate specificity of lecithin-cholesterol acyl transferase from human plasma. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jul 8;15(5):355–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J. Phospholipid substrate specificity of purified human plasma lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1974;137:15–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E. A protein cofactor of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1493–1498. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90776-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E. Lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase: effects of substrate composition upon enzyme activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 11;270(4):513–518. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90116-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T., Norum K. R., Glomset J. A., Nichols A. V. Plasma lipoproteins in familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency: structure of low and high density lipoproteins as revealed by elctron microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1141–1148. doi: 10.1172/JCI106586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIDEZ L. I., ROHEIM P. S., EDER H. A. EFFECT OF DIET ON THE CHOLESTEROL ESTER COMPOSITION OF LIVER AND OF PLASMA LIPOPROTEINS IN THE RAT. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:377–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Norum K. R. The metabolic role of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase: perspectives form pathology. Adv Lipid Res. 1973;11:1–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Berry M. N., Williams M. C., Severinghaus E. M. A simple and inexpensive membrane "lung" for small organ perfusion. J Lipid Res. 1974 Mar;15(2):182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Blaurock A. E., Sata T. Cholestasis: lamellar structure of the abnormal human serum lipoprotein. Science. 1971 Apr 30;172(3982):475–478. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3982.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L. Synthesis and secretion of plasma lipoproteins. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1972;26(0):7–24. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7547-0_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kashyap M. L. Interchange of apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):32–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI107171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P. A rapid electrophoretic technique for identification of subunit species of apoproteins in serum lipoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):350–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer K. H., Utermann G., Menzel H. J. On the polypeptide composition of an abnormal high density lipoprotein (LP-E) occurring in LCAT-deficient plasma. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 1;45(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80803-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTIMORE G. E. Effect of insulin on potassium transfer in isolated rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jun;200:1315–1319. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.6.1315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Bennett B. D., Morré D. J., Gray M. E., Thistlethwaite W., LeQuire V. S. Lipoproteins associated with the Golgi apparatus isolated from epithelial cells of rat small intestine. Lab Invest. 1971 Nov;25(5):435–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. B. Apoproteins of the lipoproteins in a nonrecirculating perfusate of rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1976 Jan;17(1):85–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. B. Lipoproteins in a nonrecirculating perfusate of rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1974 Nov;15(6):544–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjos O. D., Faergeman O., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Characterization of remnants produced during the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins of blood plasma and intestinal lymph in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):603–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI108130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller K., Laggner P., Kratky O., Kostner G., Holasek A., Glatter O. X-ray small angle scattering of human plasma high density lipoprotein LpA from HDL2: application of a new evaluation method. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80931-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLS A. V., SMITH L. EFFECT OF VERY LOW-DENSITY LIPOPROTEINS ON LIPID TRANSFER IN INCUBATED SERUM. J Lipid Res. 1965 Apr;6:206–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. P. Electrophoretic separation of plasma lipoproteins in agarose gel. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):693–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel S. P., Rubinstein D. Secretion of apolipoproteins in very low density and high density lipoproteins by perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1974 Jul;15(4):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norum K. R., Glomset J. A., Nichols A. V., Forte T., Albers J. J., King W. C., Mitchell C. D., Applegate K. R., Gong E. L., Cabana V. Plasma lipoproteins in familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency: effects of incubation with lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase in vitro. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1975;142:31–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osuga T., Portman O. W. Origin and disappearance of plasma lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase. Am J Physiol. 1971 Mar;220(3):735–741. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.3.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Hansma H., Ostwald R. Characterization of guinea pig plasma lipoproteins: the appearance of new lipoproteins in response to dietary cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1972 Sep;13(5):624–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sata T., Havel R. J., Jones A. L. Characterization of subfractions of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins separated by gel chromatography from blood plasma of normolipemic and hyperlipemic humans. J Lipid Res. 1972 Nov;13(6):757–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigurdsson G., Nicoll A., Lewis B. Conversion of very low density lipoprotein to low density lipoprotein. A metabolic study of apolipoprotein B kinetics in human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1481–1490. doi: 10.1172/JCI108229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. B., Boyer J. L. Production of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase by the isolated perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 15;218(3):549–551. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Engelman D. M. Current models for the structure of biological membranes. J Cell Biol. 1969 Sep;42(3):613–646. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.3.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokke K. T., Norum K. R. Determination of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransfer in human blood plasma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Feb;27(1):21–27. doi: 10.3109/00365517109080184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swell L., Law M. D. Release of lipoprotein cholesterol esters by the isolated perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 16;231(2):302–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Menzel H. J., Langer K. H., Dieker P. Lipoproteins in lecithin-cholesterol-acyltransferase(LCAT)-deficiency. II. Further studies on the abnormal high-density-lipoproteins. Humangenetik. 1975;27(3):185–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00278345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins M. H., Blaurock A. E., Engelman D. M. Bilayer structure in membranes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 17;230(11):72–76. doi: 10.1038/newbio230072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Herbert P. N., Levy R. I. Biosynthesis of lymph and plasma lipoprotein apoproteins by isolated perfused rat liver and intestine. J Lipid Res. 1973 Mar;14(2):215–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Levy R. I. Total inhibition of hepatic beta-lipoprotein production in the rat by orotic acid. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 10;242(9):2246–2254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]