Abstract
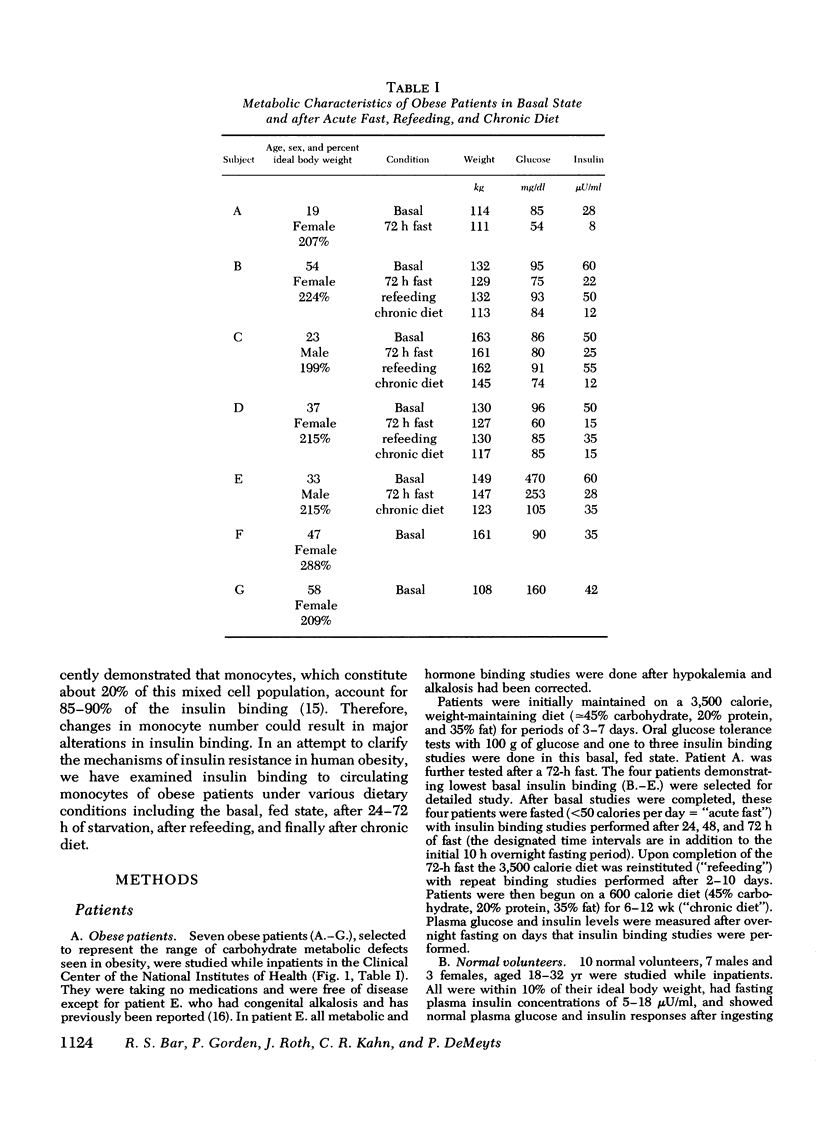
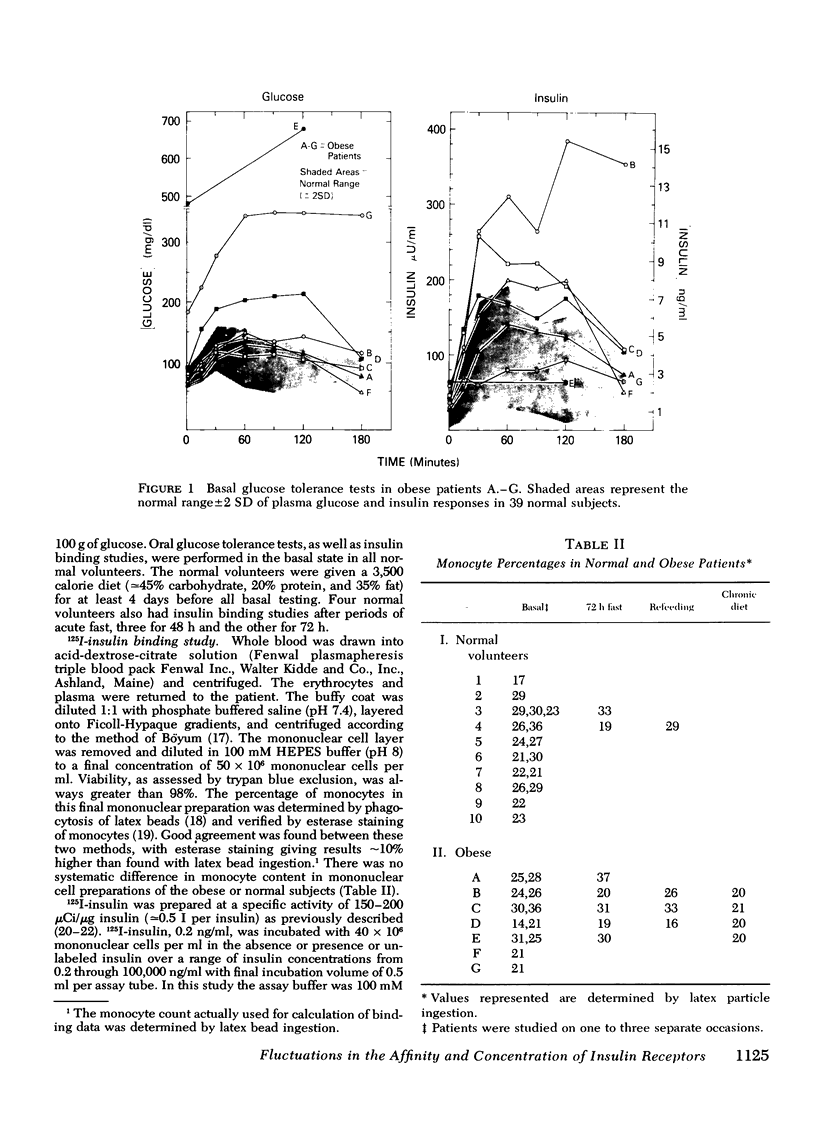
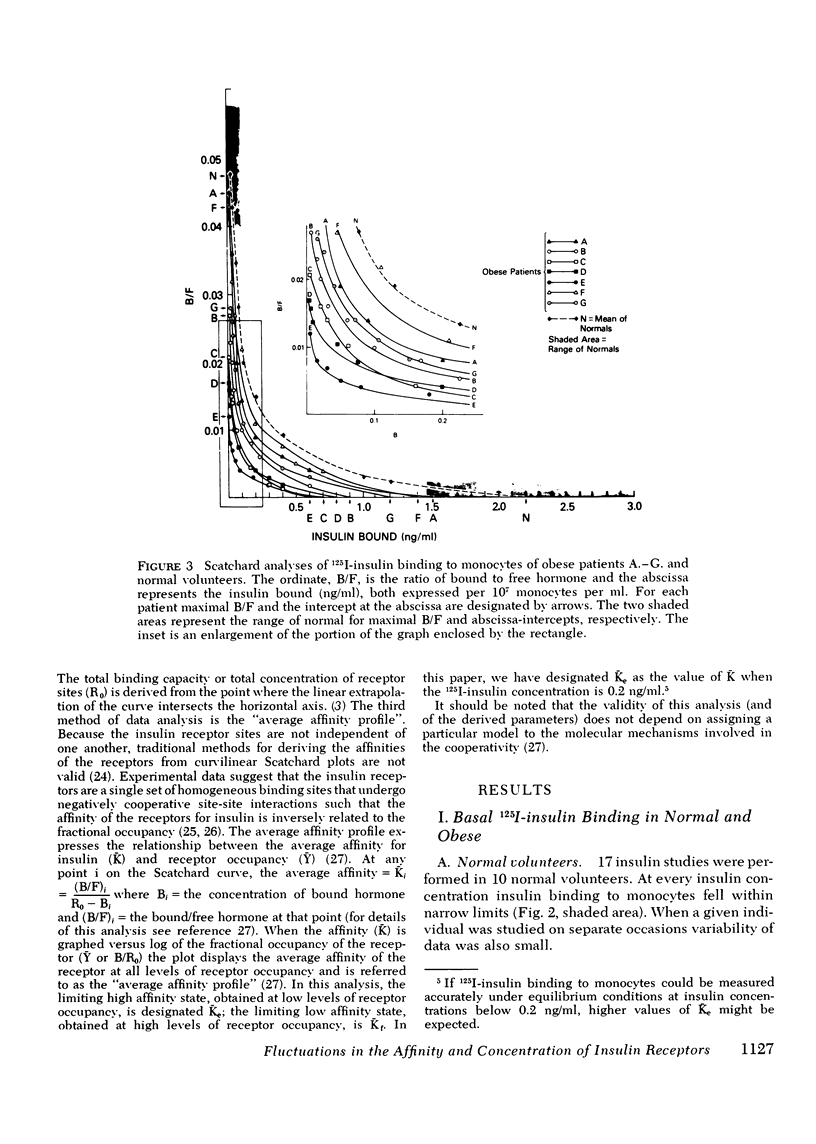
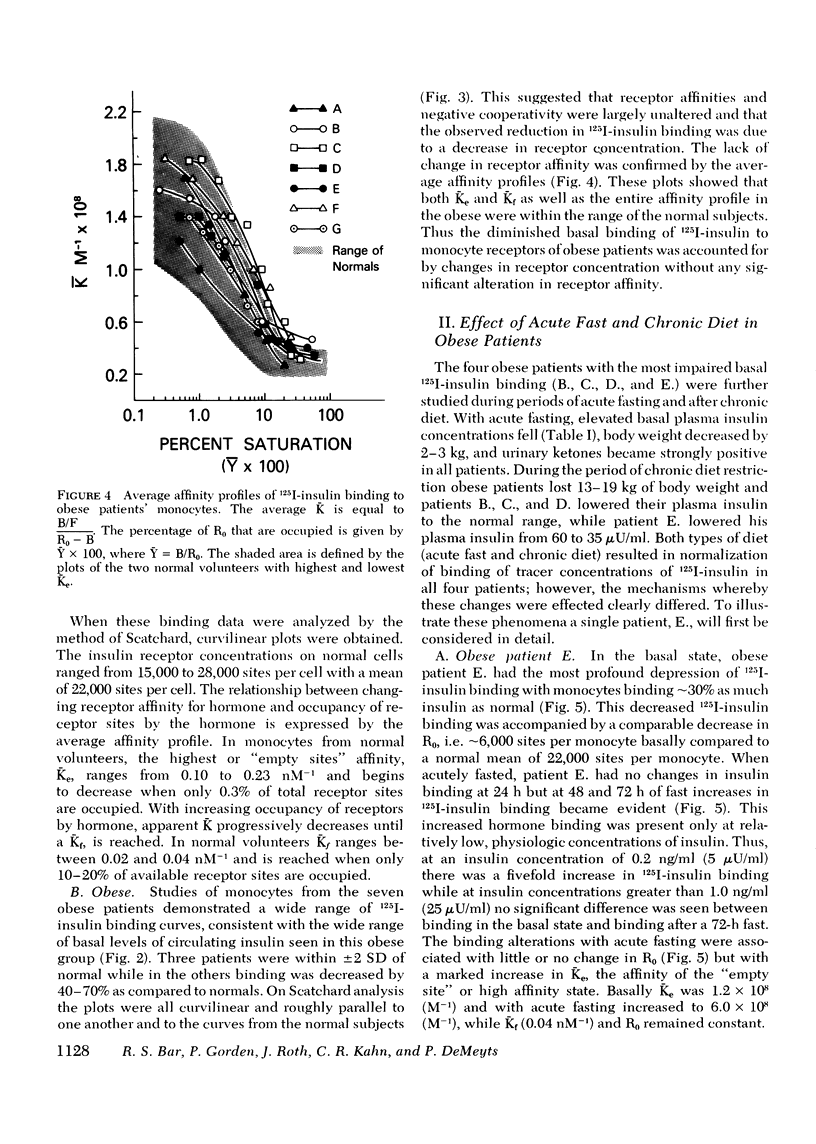
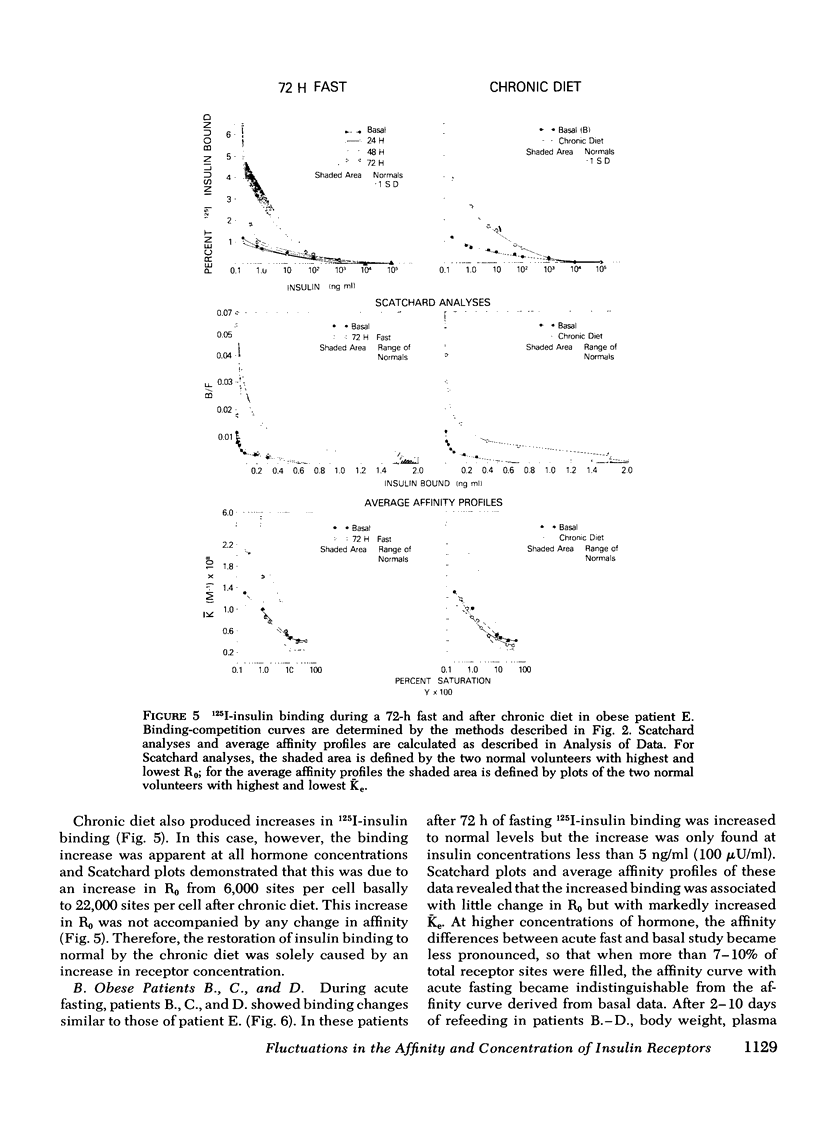
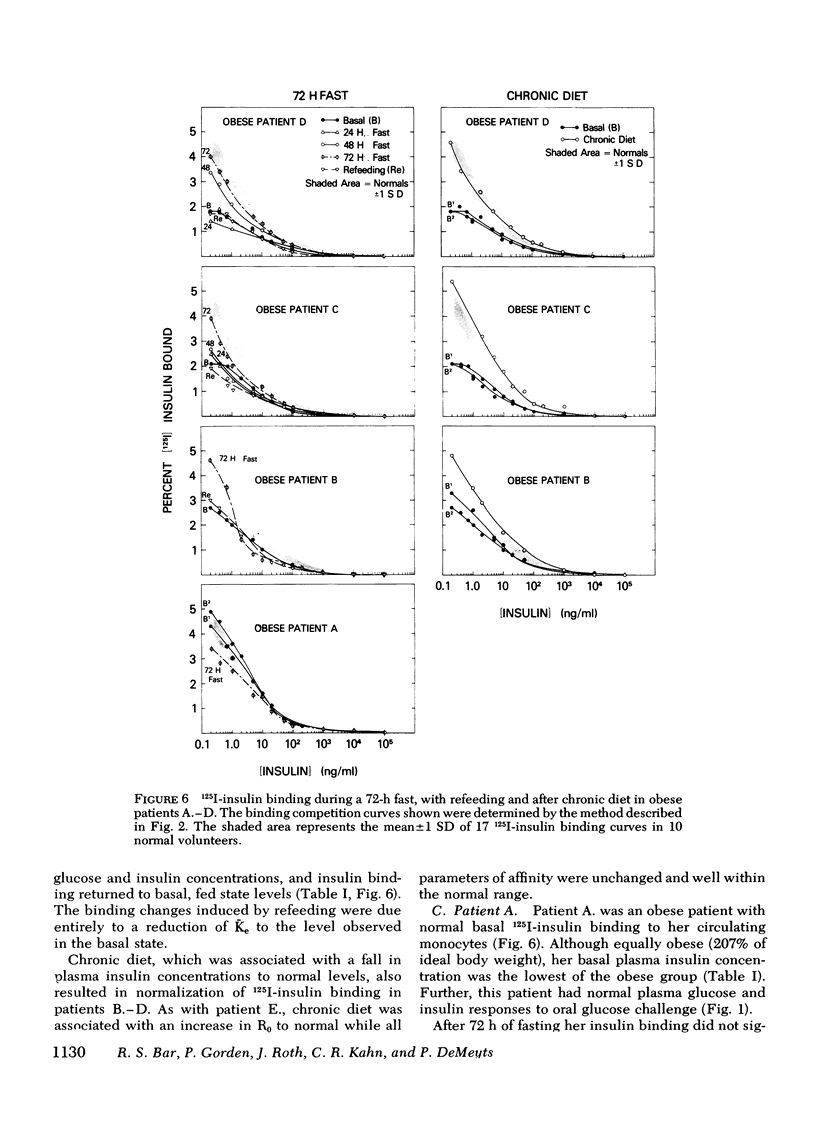
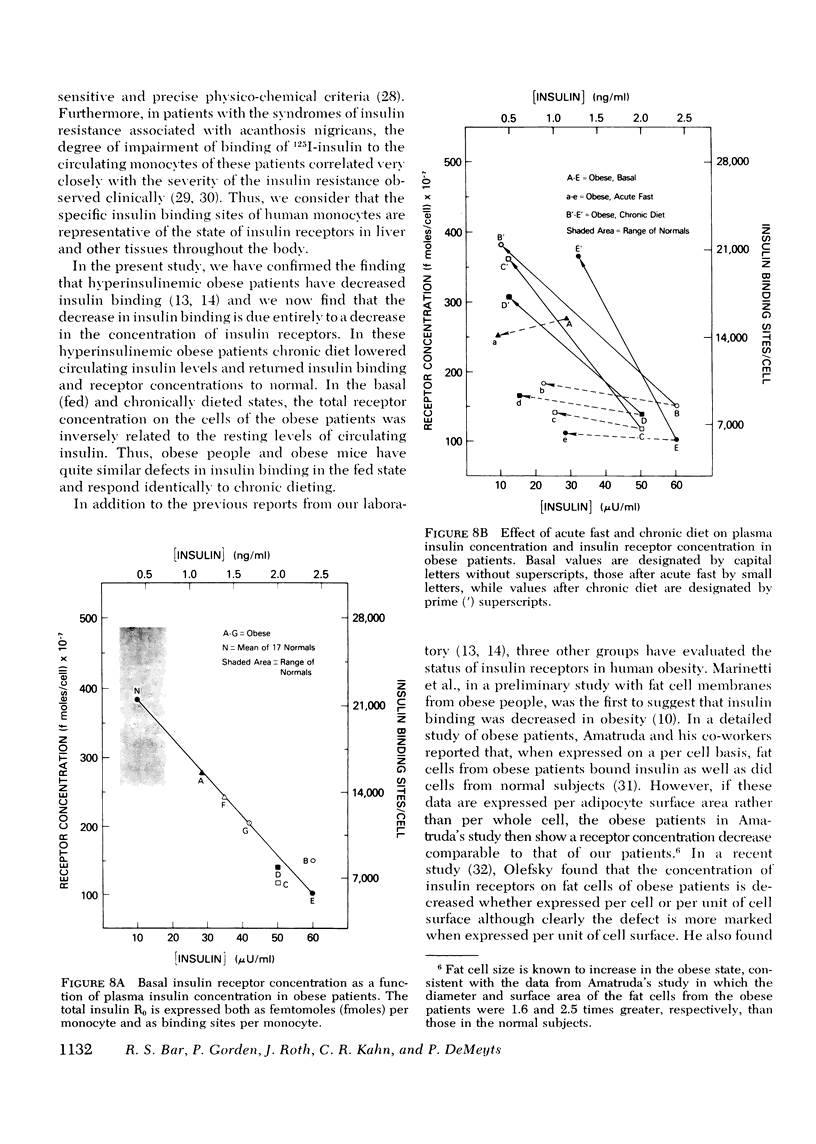
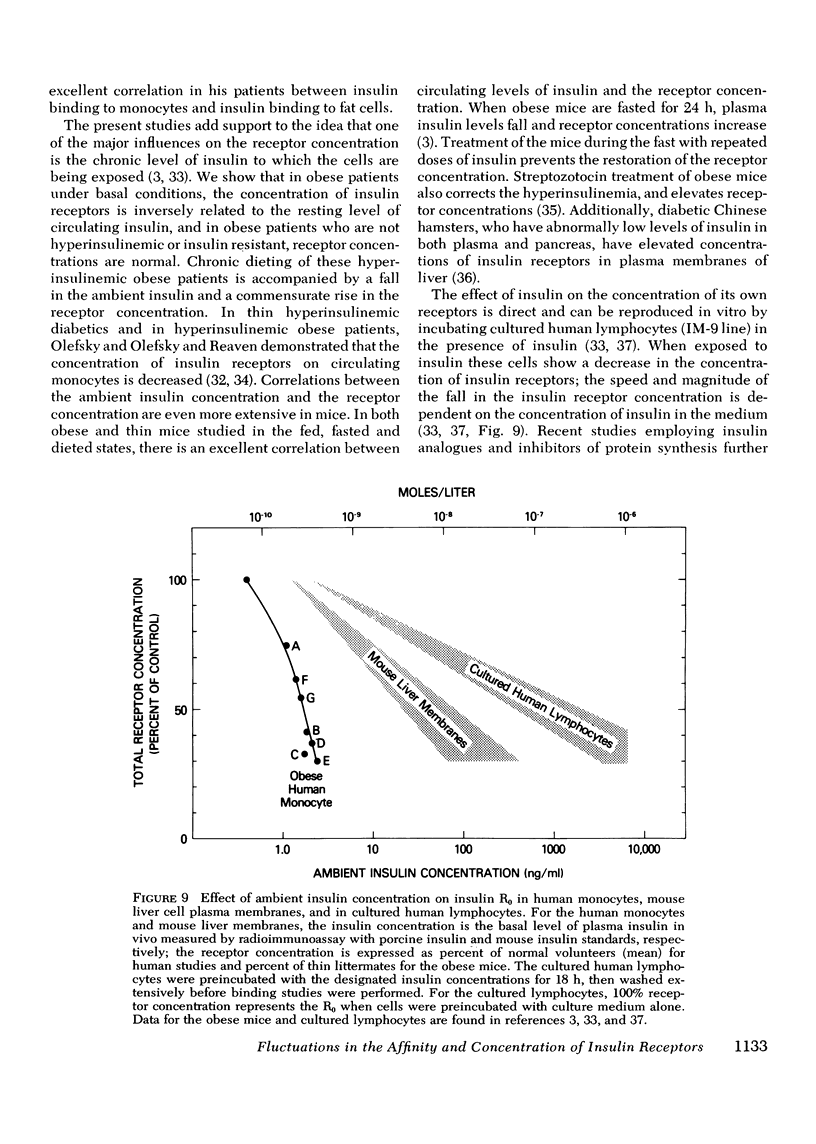
The binding of 125I-insulin to insulin receptors on circulating monocytes of obese patients and normal volunteers has been determined under various dietary states. In the basal, fed state the monocytes of obese patients with clinical insulin resistance (n= 6) bound less insulin than normals (n =10) because of a decrease in insulin receptor concentration (obese = 6,000-13,000 sites per monocyte versus normals 15,000-28,000 sites per monocyte). The single obese patient without evidence of clinical insulin resistance demonstrated normal binding of insulin with 16,000 sites per monocyte. In all patients, the total receptor concentration was inversely related to the circulating levels of insulin measured at rest after an overnight fast. For the obese patients with basally depressed insulin binding, a 48-72-h fast lowered circulating insulin and increased binding to normal levels but only at low hormone concentrations; this limited normalization of 125I-insulin binding was associated with increased receptor affinity for insulin without change in receptor concentration. Refeeding after the acute fasting periods resulted in return to the elevated plasma insulin levels, the basal receptor affinity, and the depressed insulin binding observed in the basal, fed state. Chronic diet restored plasma insulin levels, insulin binding, and receptor concentration to normal without change in affinity. When the data from this study are coupled with previous in vivo and in vitro findings they suggest that the insulin receptor of human monocytes is more sensitive to regulation by ambient insulin than the receptors of obese mice and cultured human lymphocytes. The results further indicate than an insulin receptor undergoes in vivo modulation of its interaction with insulin by changing receptor concentration and by altering the affinity of existing receptors.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amatruda J. M., Livingston J. N., Lockwood D. H. Insulin receptor: role in the resistance of human obesity to insulin. Science. 1975 Apr 18;188(4185):264–266. doi: 10.1126/science.164059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer J. A., Gorden P., Gavin J. R., 3rd, Lesniak M. A., Roth J. Insulin receptors in human circulating lymphocytes: application to the study of insulin resistance in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Apr;36(4):627–633. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-4-627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer J. A., Gorden P., Roth J. Defect in insulin binding to receptors in obese man. Amelioration with calorie restriction. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):166–174. doi: 10.1172/JCI107907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter D., Lazarus N. R. The control of insulin receptors in the New Zealand obese mouse. Diabetologia. 1975 Aug;11(4):261–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00422389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Lehrer R. I. Phagocytosis by human monocytes. Blood. 1968 Sep;32(3):423–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meyts P., Roth J. Cooperativity in ligand binding: a new graphic analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1118–1126. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90473-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeyts P., Bainco A. R., Roth J. Site-site interactions among insulin receptors. Characterization of the negative cooperativity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1877–1888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Kahn C. R., Roth J., Bar R. S. Antibodies that impair insulin receptor binding in an unusual diabetic syndrome with severe insulin resistance. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.170678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgue M. E., Freychet P. Insulin receptors in the heart muscle. Demonstration of specific binding sites and impairment of insulin binding in the plasma membrane of the obese hyperglycemic mouse. Diabetes. 1975 Aug;24(8):715–723. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.8.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P. Interactions polypeptide hormones with cell membrane specific receptors: studies with insulin and glucagon. Diabetologia. 1976 May;12(2):83–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00428972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Gardner J. D., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin action in isolated rat thymocytes. I. Binding of 125 I-insulin and stimulation of -aminoisobutyric acid transport. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6919–6926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Levitin H. Congenital alkalosis with diarrhea. A sequel to Darrow's original description. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Jun;78(6):876–882. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-78-6-876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepp K. D., Langley J., Funcke HJ Von, Renner R., Kemmler W. Increased insulin binding capacity of liver membranes from diabetic Chinese hamsters. Nature. 1975 Nov 13;258(5531):154–154. doi: 10.1038/258154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Flier J. S., Bar R. S., Archer J. A., Gorden P., Martin M. M., Roth J. The syndromes of insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. Insulin-receptor disorders in man. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):739–745. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin-receptor interaction in the obese-hyperglycemic mouse. A model of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz I. M., Hunston D. L. Protein interactions with small molecules. Relationships between stoichiometric binding constants, site binding constants, and empirical binding parameters. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):3001–3009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. Y., Lam K. W., Yam L. T. Esterases in human leukocytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Jan;21(1):1–12. doi: 10.1177/21.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Decreased insulin binding to lymphocytes from diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1323–1328. doi: 10.1172/JCI107878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, Bagdade J. D. Human insulin secretion: as integrated approach. Annu Rev Med. 1970;21:219–240. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.21.020170.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz D. Some endocrine and metabolic aspects of obesity. Annu Rev Med. 1970;21:241–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.21.020170.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., Bianco A. R., Handwerger B. S., Kahn C. R. Demonstration that monocytes rather than lymphocytes are the insulin-binding cells in preparations of humah peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes: implications for studies of insulin-resistant states in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):474–478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soli A. H., Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin receptor deficiency in genetic and acquired obesity. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):769–780. doi: 10.1172/JCI108155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll A. H., Goldfine I. D., Roth J., Kahn C. R. Thymic lymphocytes in obese (ob-ob) mice. A mirror of the insulin receptor defect in liver and fat. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4127–4131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll A. H., Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin binding to liver plasm membranes in the obese hyperglycemic (ob/ob) mouse. Demonstration of a decreased number of functionally normal receptors. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4702–4707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meyts P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, Gavin J. R., 3rd, Lesniak M. A. Insulin interactions with its receptors: experimental evidence for negative cooperativity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 1;55(1):154–161. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]