Abstract
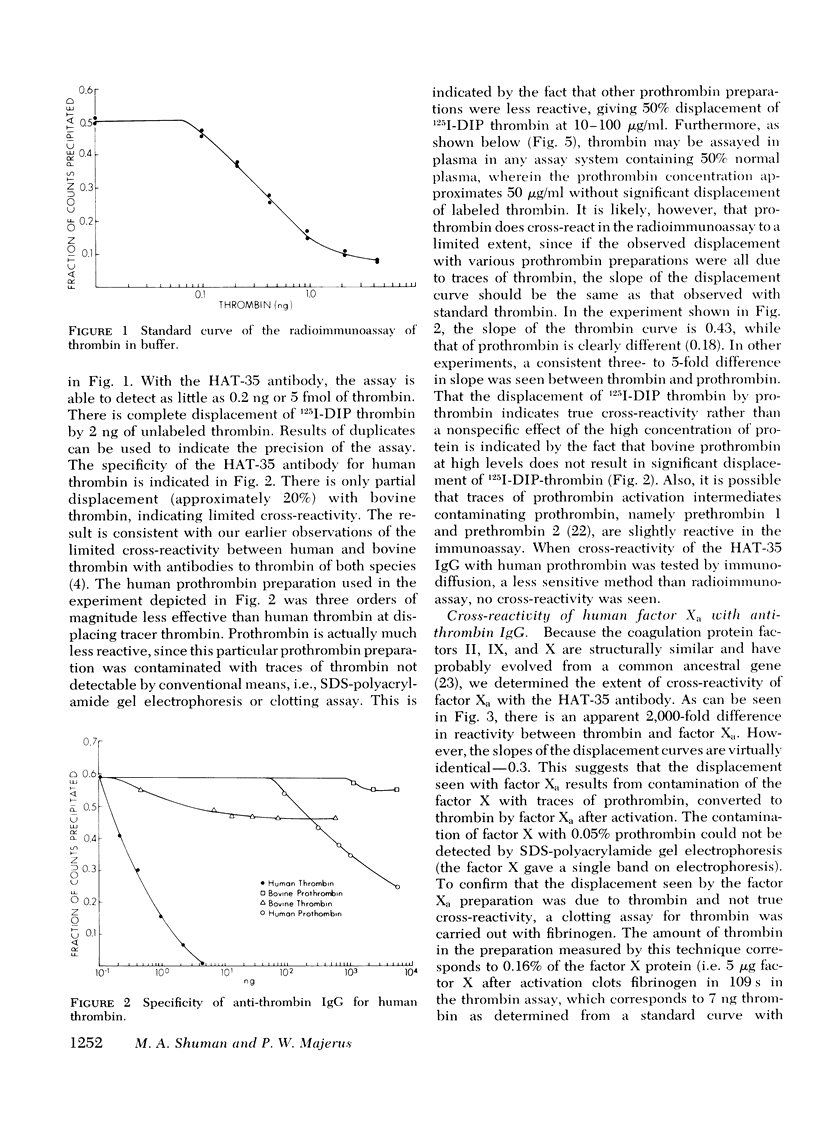
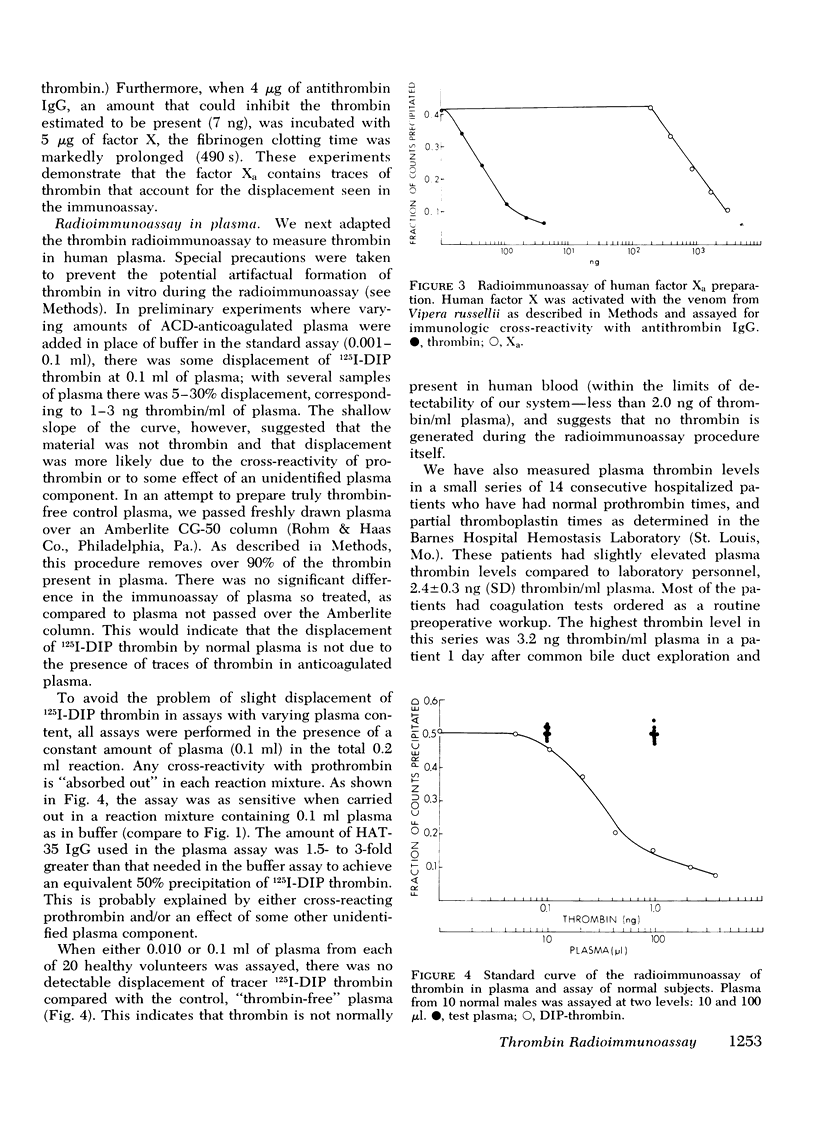
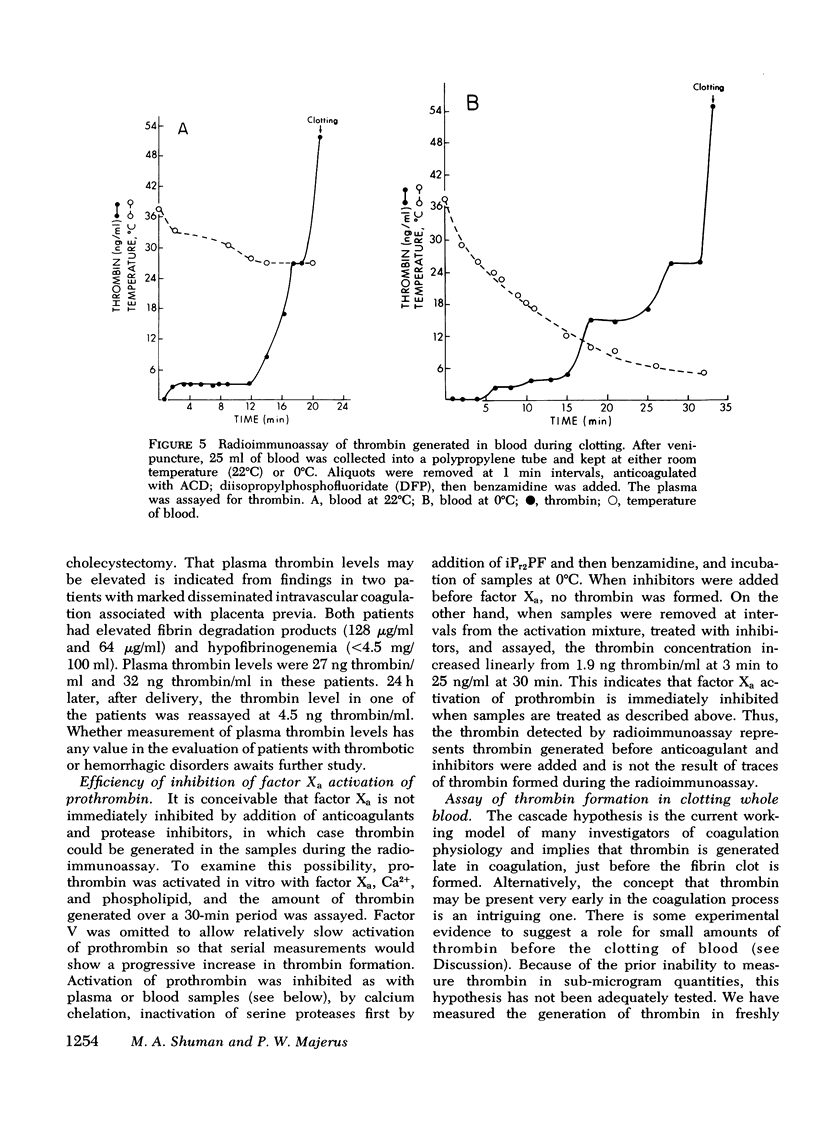
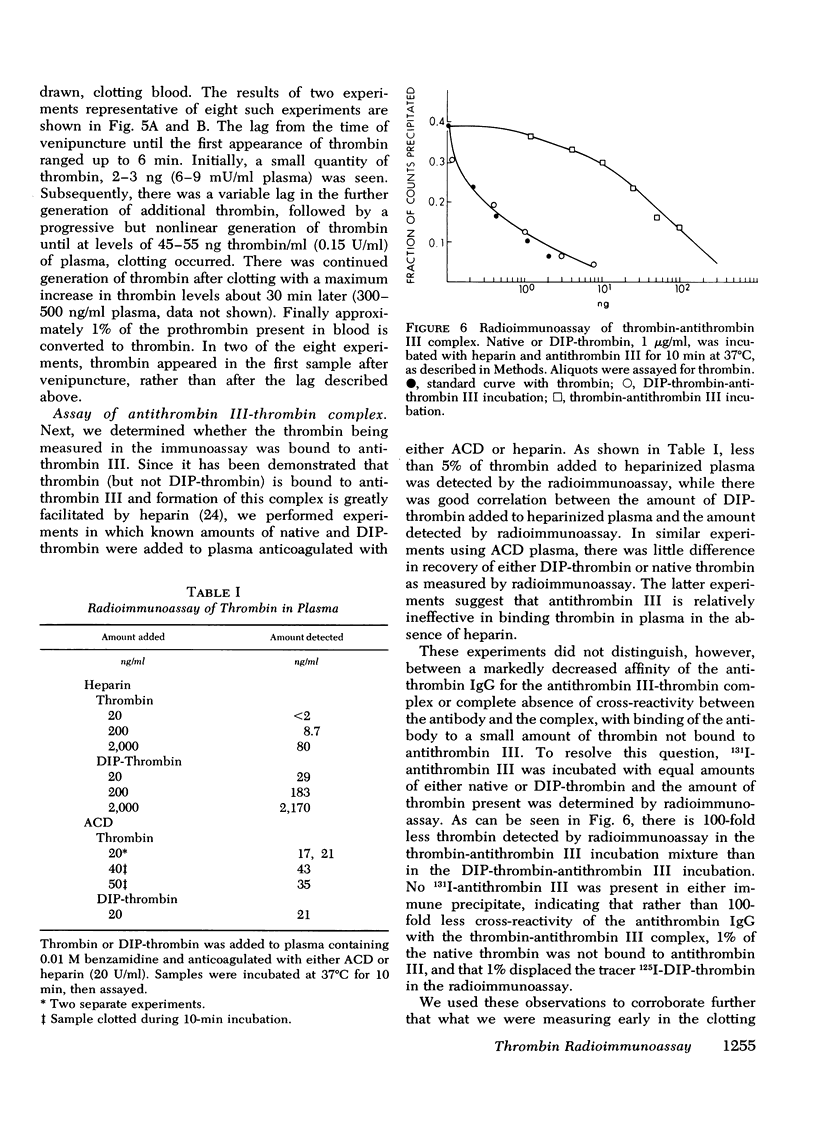
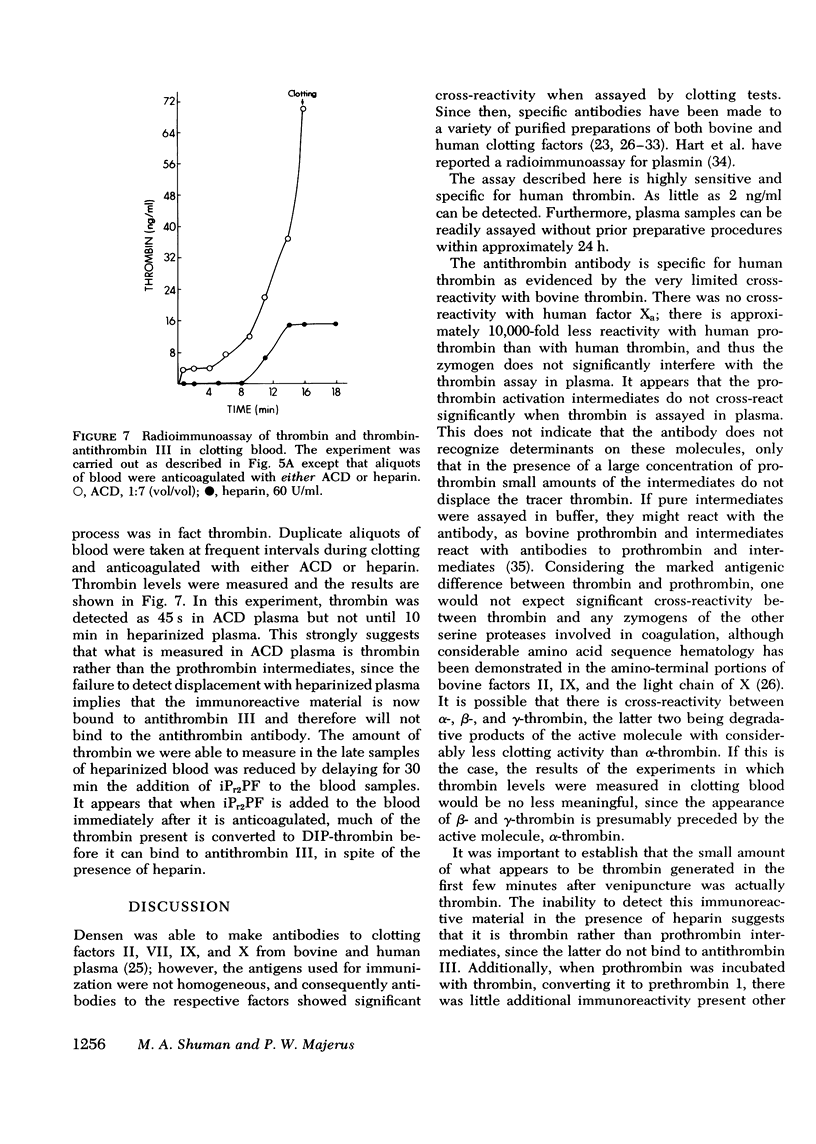
We have developed a radioimmunoassay for human thrombin using rabbit anti-human thrombin IgG. The assay can measure 2 ng thrombin/ml plasma, 500-fold more sensitive than clotting assays. Human prothrombin is less reactive in the assay than thrombin by at least four orders of magnitude, and there is no demonstrable cross-reactivity with human factor Xa, the clotting factor structurally most similar to thrombin. The assay does not detect thrombin bound to anthithrombin III. Using the assay, we have demonstrated that plasma from 20 normal subjects does not contain detectable thrombin. We measured thrombin generation in clotting blood in polypropylene tubes and observed that thrombin appears (approximately equal to 3 ng/ml) within 45 S-5 min after venipuncture. This material is thrombin, not intermediates of prothrombin activation, since it disappears after addition of heparin, which promotes thrombin antithrombin III complex formation. After a plateau of 2-10 min, there is further thrombin generation, which results in clotting after 15-27 min at a level of 40-50 ng thrombin/ml. The thrombin generated 9-25 min before clotting may activate factors V and VIII and stimulate platelet aggregation and release. In contrast, the cascade hypothesis assigns a role for thrombin only late in blood clotting. Radioimmunoassay of thrombin and other clotting factors will be useful for clinical and physiological studies of blood clotting especially since the assay seems specific for thrombin and is independent of other activities that affect bioassays.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BACHMANN F., DUCKERT F., KOLLER F. The Stuart-Prower factor assay and its clinical significance. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1958 May 1;2(1-2):24–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilezikian S. B., Nossel H. L., Butler V. P., Jr, Canfield R. E. Radioimmunoassay of human fibrinopeptide B and kinetics of fibrinopeptide cleavage by different enzymes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):438–445. doi: 10.1172/JCI108110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohn H. Comparative studies on the fibrin-stabilizing factors from human plasma, platelets and placentas. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Dec 8;202:256–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb16339.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W. The effect of proteolytic enzymes on bovine factor V. I. Kinetics of activation and inactivation by bovine thrombin. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1438–1445. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing M. R., Butkowski R. J., Clark M. M., Mann K. G. Human prothrombin activation. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):8897–8906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G., Jackson C. M. The conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. II. Differentiation between thrombin- and factor Xa-catalyzed proteolyses. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):606–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Coan M. H., Enfield D. L., Titani K., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. A comparison of bovine prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), and factor X (Stuart factor). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):427–430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldebrant C. M., Butkowski R. J., Bajaj S. P., Mann K. G. The activation of prothrombin. II. Partial reactions, physical and chemical characterization of the intermediates of activation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7149–7163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). IV. Radioimmunoassay of AHF antigen. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Dec;80(6):822–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Schmer G., Hermodson M. A., Teller D. C., Davie E. W. Characterization of human, bovine, and horse antithrombin III. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):368–373. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legaz M. E., Schmer G., Counts R. B., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of human Factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3946–3955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Heldebrant C. M., Fass D. N. Multiple active forms of thrombin. II. Mechanism of production from prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):6106–6114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Esmon C. T., Jackson C. M. The conversion of prothrombin to thrombin. I. Characterization of the reaction products formed during the activation of bovine prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):594–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRYDZ H. STUDIES ON PROCONVERTIN (FACTOR VII). VI. THE PRODUCTION IN RABBITS OF AN ANTISERUM AGAINST FACTOR VII. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1965;17:66–72. doi: 10.3109/00365516509077285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prydz H., Gladhaug A. Factor X. Immunological studies. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971;25(1):157–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPAPORT S. I., SCHIFFMAN S., PATCH M. J., AMES S. B. The importance of activation of antihemophilic globulin and proaccelerin by traces of thrombin in the generation of intrinsic prothrombinase activity. Blood. 1963 Feb;21:221–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J. S., Beeler D. L., Rosenberg R. D. Activation of human prothrombin by highly purified human factors V and X-a in presence of human antithrombin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1607–1617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Damus P. S. The purification and mechanism of action of human antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6490–6505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmer G., Kirby E. P., Teller D. C., Davie E. W. The isolation nd characterization of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2512–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. S. Human prothrombin activation. Science. 1968 Oct 4;162(3849):127–129. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3849.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman M. A., Tollefsen D. M., Majerus P. W. The binding of human and bovine thrombin to human platelets. Blood. 1976 Jan;47(1):43–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg S. A., Nemerson Y. The control of prothrombin conversion. Kinetic control by mechanisms inherent in two activation pathways. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 17;14(12):2636–2644. doi: 10.1021/bi00683a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenn K. S., Blout E. R. Mechanism of bovine prothrombin activation by an insoluble preparation of bovine factor X a (thrombokinase). Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4502–4515. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straughn W., 3rd, Wagner R. H. A simple method for preparing fibrinogen. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 Jul 31;16(1):198–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taswell C., McDuffie F. C., Mann K. G. Immunochemical relationships of the intermediates of prothrombin activation. Immunochemistry. 1975 Apr;12(4):339–343. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin E. T., Eisenkramer L., Butler J. V. Heparin interaction with activiated factor X and its inhibitor. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1975;52:239–242. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-0946-8_19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



