Abstract
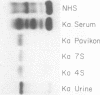
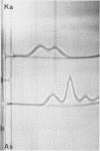
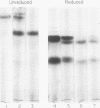
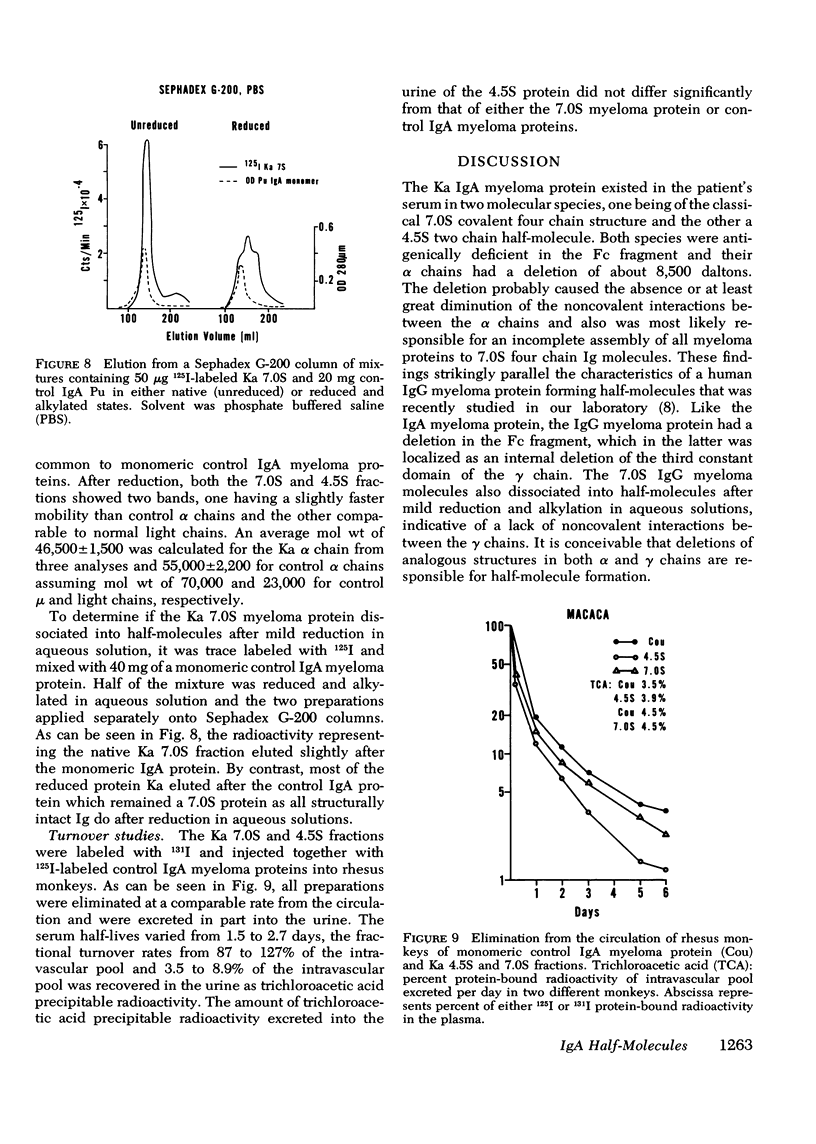
A lambda, IgAl myeloma protein that formed two chain half-molecules was obtained from a patient who had typical multiple myeloma. His serum contained 1.3 g/100 ml of an IgA paraprotein of gamma-1 electrophoretic mobility, his urine predominantly lambda Bence Jones protein, and only small amounts of IgA paraprotein. Analytical ultracentrifugation of the isolated serum IgA protein showed 7.0S and 4.5S protein peaks but no IgA polymers. When the 7.0S and 4.5S protein peaks were tested with an antiserum specific for alpha chain, both fractions were antigenically deficient compared to control IgA myeloma proteins but showed a line of identity to their F(ab')2 fragments. The serum and 7.0S protein fraction showed double precipitin lines in IgA radial immunodiffusion plates and in immunoelectrophoretic analysis, one line being formed by the myeloma protein and the other by residual normal IgA. The myeloma protein did not form a precipitin line with antisera specific for the IgA Fc fragment. Sodium dodecylsulfate-urea-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis demonstrated that both the 7.0S and 4.5S fractions of the myeloma protein consisted of covalently linked heavy and light chains, 4.5S fraction being apparently the half-molecule of the 7.0S protein. The heavy chain had a mol wt of 46,500 daltons compared to 55,000 daltons for normal alpha chains. Reduction and alkylation in aqueous solutions resulted in dissociation of the 7.0S myeloma protein fractions into smaller units, probably half-molecules, suggesting that the noncovalent interactions between the alpha chains were substantially weakened or absent, presumably as a result of a deletion in the Fc portion of the alpha chain. The catabolic rates of the radio-labeled 7.0S and 4.5S protein in rhesus monkeys were similar to those of control IgA myeloma proteins; the excretion of protein-bound radioactivity of the IgA half-molecules into the urine was no greater than that of the 7.0S or of control IgA myeloma proteins. It is suggested that the myeloma IgA half-molecule is probably derived from an IgAl mutant that is carried in the human genome and that it is unlikely a representative of a rare IgA subclass or an IgA l allotypic variant.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevan M. J. Interchain disulfide bond formation studied in two mouse myelomas which secrete immunoglobulin A. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Apr;1(2):133–138. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birshtein B. K., Preud'homme J. L., Scharff M. D. Variants of mouse myeloma cells that produce short immunoglobulin heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3478–3482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Despont J. P., Abel C. A., Grey H. M., Penn G. M. Structural studies on a human IgA1 myeloma protein with a carboxy-terminal deletion. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1517–1525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANEK F., RIHA I. PURIFICATION AND STRUCTURAL CHARACTERIZATION OF 5S GAMMA-GLOBULIN IN NEW-BORN PIGS. Immunochemistry. 1964 Apr;1:49–63. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(64)90056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs J. R. Immunocytoma o' mice an' men. Br Med J. 1971 Apr 10;2(5753):67–72. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5753.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs J. R., Jacobs A. A half-molecule GK plasmacytoma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jul;5(1):199–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman R., Mushinski J. F., Potter M. 2-chain immunoglobulin A molecules: abnormal or normal intermediates in synthesis. Science. 1968 Mar 22;159(3821):1355–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3821.1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushinski J. F. Gamma-A half molecules: defective heavy chain mutants in mouse myeloma proteins. J Immunol. 1971 Jan;106(1):41–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., WISSLER F. C., LIPMAN L. N., WOERNLEY D. L. Separation of univalent fragments from the bivalent rabbit antibody molecule by reduction of disulfide bonds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Aug;89:230–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Kunkel H. G. Human immunoglobulins: classes, subclasses, genetic variants, and idiotypes. Adv Immunol. 1973;16:1–59. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokesová L., Rejnek J. Molecular heterogeneity of newborn piglet IgG. Immunochemistry. 1973 Sep;10(9):607–609. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. A., Smith D. F., Appella E. Chemical characterization of a mouse immunoglobulin A heavy chain with a 100-residue deletion. Amino acid and carbohydrate compositions and NH2-and COOH-terminal sequences. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6605–6610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND G. B., CAMPBELL D. H. The use of antigen-coated glass as a specific adsorbent for antibody. J Immunol. 1958 Apr;80(4):294–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki T., Appella E., Itano H. A. Chain models of 6.6S and 3.9S mouse myeloma gamma A immunoglobulin molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):1071–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Fishkin B. G. The catabolism of human G immunoglobulins of different heavy chain subclasses. 3. The catabolism of heavy chain disease proteins and of Fc fragments of myeloma proteins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Apr;10(4):599–607. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Heath V. C., Lang J. E. Human myeloma IgG half-molecules. Structural and antigenic analyses,. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2157–2163. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Heath V. C., Lang J. E. IgG half-molecules: clinical and immunologic features in a patient with plasma cell leukemia. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):305–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Human myeloma IgG half-molecules. Catabolism and biological properties. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):588–594. doi: 10.1172/JCI108128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Strober W. Metabolism of immunoglobulins. Prog Allergy. 1969;13:1–110. doi: 10.1159/000385919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]