Abstract
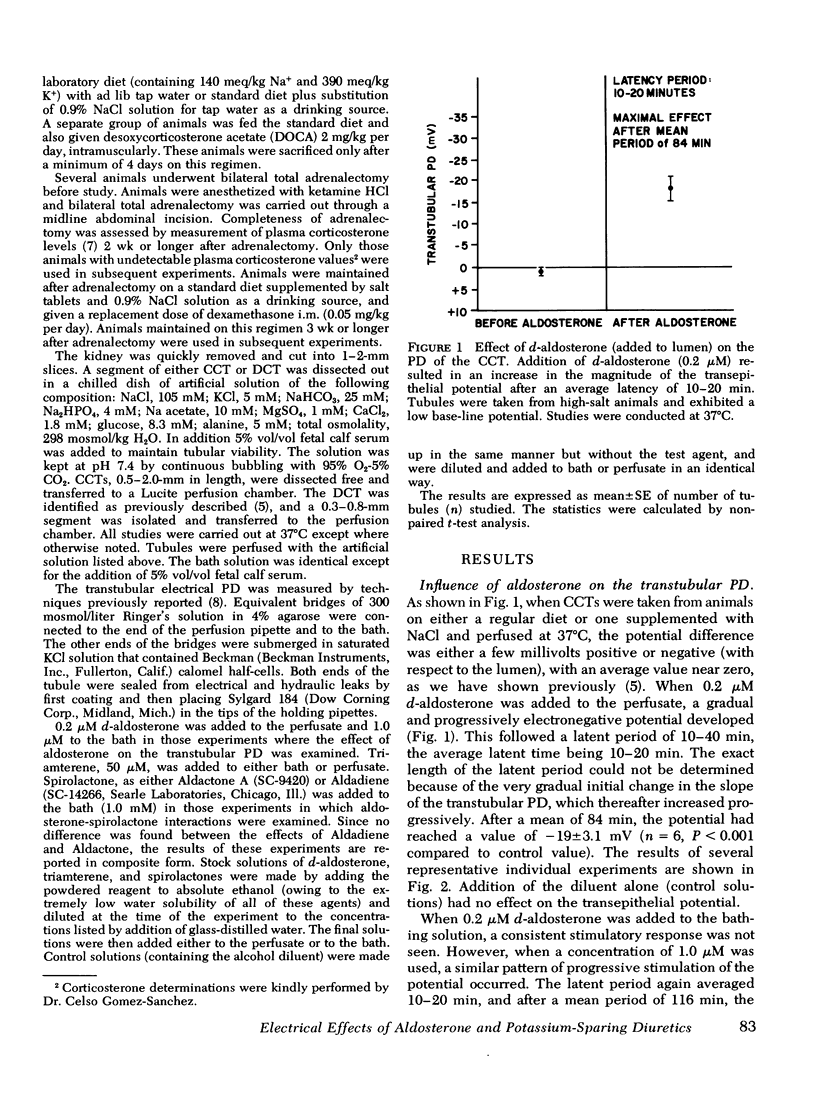
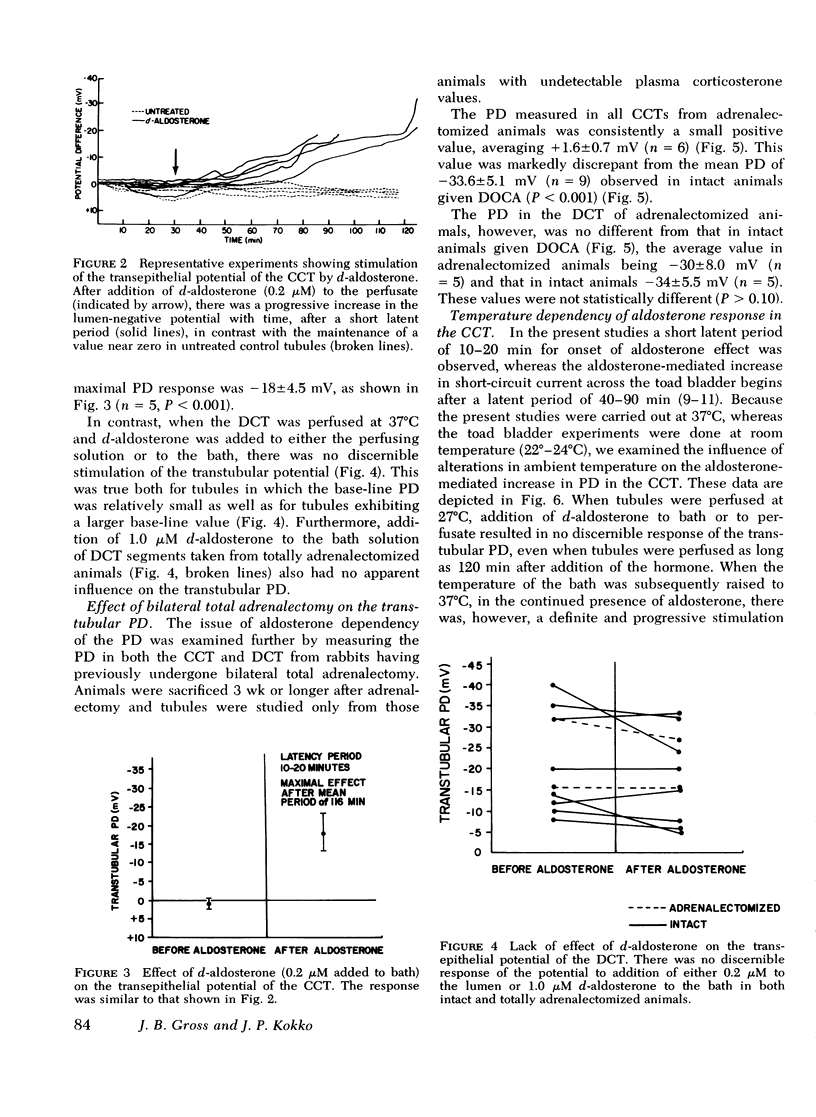
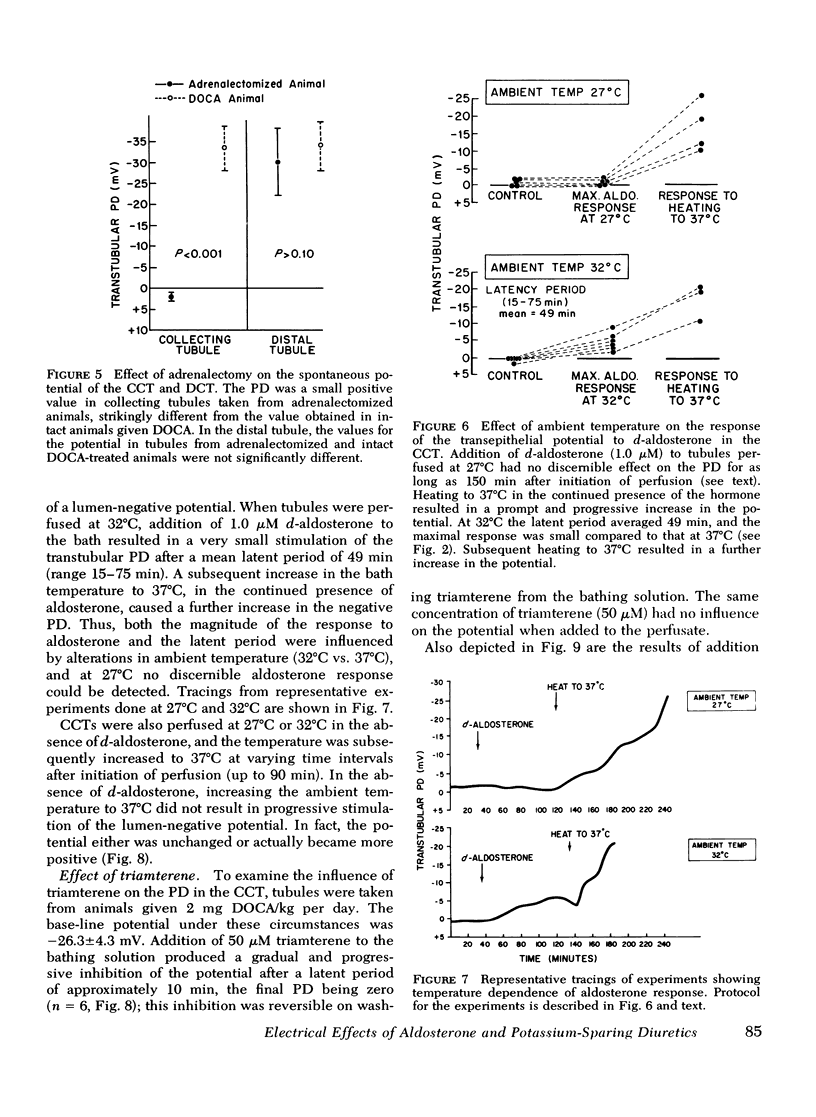
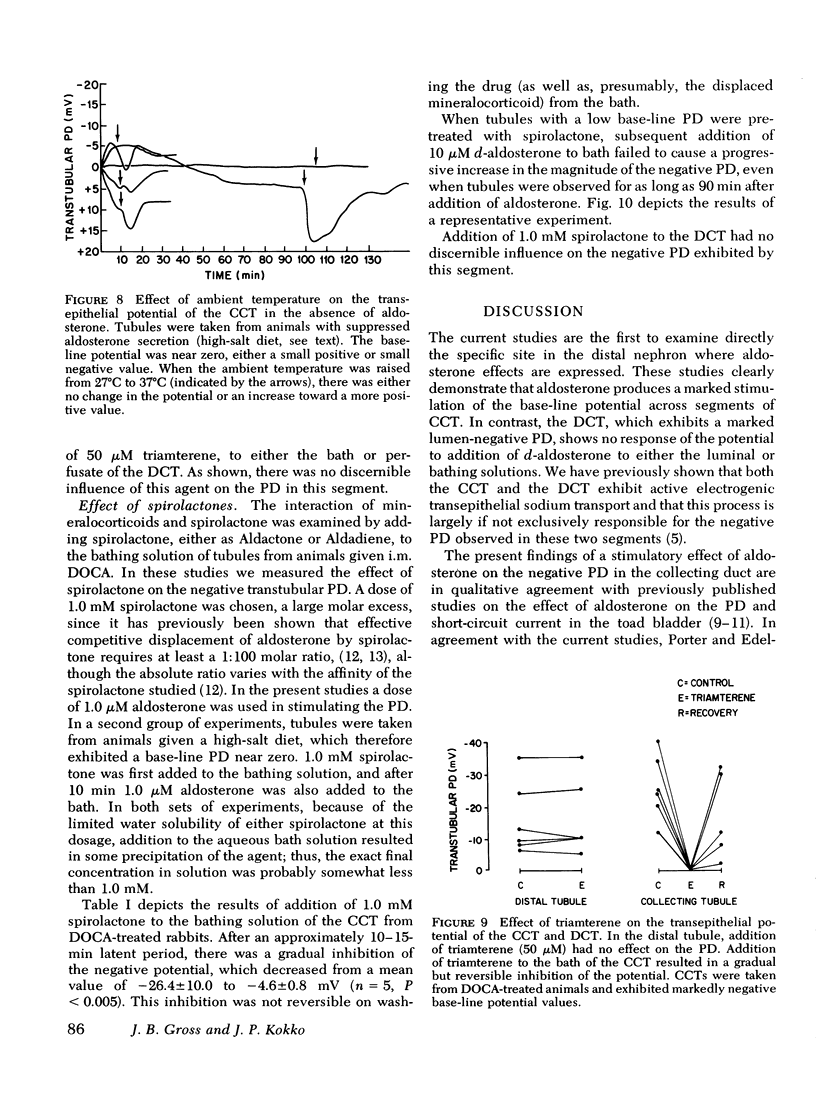
We have previously shown that the transtubular potential of the rabbit cortical collecting tubule varies in concert with changes in plasma mineralocorticoid levels, while the potential of the distal convoluted tubule is invariant with such changes. In the present studies we have examined the effects of in vitro addition of d-aldosterone to isolated tubules, as well as the effects of triamterene and spirolactone. d-Aldosterone (0.2 mum added to the perfusate or 1 muM added to the bathing medium) resulted in a marked stimulation of the transtubular potential difference (lumen-negative) after a short latent period. d-Aldosterone had no effect on the potential difference of distal convoluted tubules of intact or adrenalectomized rabbits. Both the magnitude of the response and the length of the latent period in the cortical collecting tubule after aldosterone were markedly temperature-dependent. Triamterene caused a gradual but reversible inhibition of the potential difference in the cortical collecting tubule but had no effect in the distal tubule. Spirolactone, when added before aldosterone, blocked the electrical response to the hormone in the cortical collecting tubule, and produced a gradual inhibition of the potential difference in mineralocorticoid-stimulated tubules. Spirolactone had no effect on the potential difference of the distal tubule. We conclude that (a) the influence of aldosterone on the potential across the distal nephron is restricted to the distal convoluted tubule, (b) the electrical response to aldosterone and the latent period are temperature-dependent, (c) the response to aldosterone is blocked by spirolactone, and (d) triamterene inhibits the potential difference only in the cortical collecting tubule.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BABA W. I., TUDHOPE G. R., WILSON G. M. Triamterene, a new diuretic drug. II. Clinical trial in oedematous patients. Br Med J. 1962 Sep 22;2(5307):760–764. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5307.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRABBE J. Stimulation of active sodium transport by the isolated toad bladder with aldosterone in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40:2103–2110. doi: 10.1172/JCI104436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton T., Snart R. S. Effect of hormones on the permeability of toad bladder (Bufo marinus). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;135(5):1059–1062. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funder J. W., Feldman D., Highland E., Edelman I. S. Molecular modifications of anti-aldosterone compounds: effects on affinity of spirolactones for renal aldosterone receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 May 15;23(10):1493–1501. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90386-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatzy J. T. The effect of K+-sparing diuretics on ion transport across the excised toad bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Mar;176(3):580–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Sanchez C., Murry B. A., Kem D. C., Kaplan N. M. A direct radioimmunoassay of corticosterone in rat serum. Endocrinology. 1975 Mar;96(3):796–798. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-3-796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. B., Imai M., Kokko J. P. A functional comparison of the cortical collecting tubule and the distal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1284–1294. doi: 10.1172/JCI108048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer K., Wiederholt M., Stolte H. Hemmung der Natriumresorption im proximalen und distalen Konvolut adrenalektomierter Ratten. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;291(1):43–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P. Proximal tubule potential difference. Dependence on glucose on glucose, HCO 3 , and amino acids. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1362–1367. doi: 10.1172/JCI107308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P. Sodium chloride and water transport in the descending limb of Henle. J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1838–1846. doi: 10.1172/JCI106401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER G. A., EDELMAN I. S. THE ACTION OF ALDOSTERONE AND RELATED CORTICOSTEROIDS ON SODIUM TRANSPORT ACROSS THE TOAD BLADDER. J Clin Invest. 1964 Apr;43:611–620. doi: 10.1172/JCI104946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter G. A. Action of aldosterone on transepithelial sodium transport. Basic Life Sci. 1975;6:105–141. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8954-9_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter G. A. In vitro inhibition of aldosterone-stimulated sodium transport by steroidal spirolactones. Mol Pharmacol. 1968 May;4(3):224–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter G. A., Kimsey J. The effect of a new anti-aldosterone agent SC19886 on aldosterone-stimulated transepithelial sodium transport. J Steroid Biochem. 1972 Feb;3(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(72)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARP G. W., LEAF A. BIOLOGICAL ACTION OF ALDOSTERONE IN VITRO. Nature. 1964 Jun 20;202:1185–1188. doi: 10.1038/2021185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlich E., Baldamus C. A., Ullrich K. J. Einfluss von Aldosteron auf den Natriumtransport in den Sammelrohren der Säugetierniere. Pflugers Arch. 1969;308(2):111–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00587019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlich E., Halbach R., Ullrich K. J. Einfluss von Aldosteron auf den Ausstrom markierten Natriums aus den Sammelrohren der Ratte. Pflugers Arch. 1970;320(3):261–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00587457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhall P. B., Tisher C. C. Response of the distal tubule and cortical collecting duct to vasopressin in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):3095–3108. doi: 10.1172/JCI107509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



