Abstract
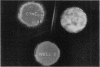
In the course of studying antinuclear antibodies in the rheumatic diseases, a new precipitin reaction (provisionally referred to as PM-1) was observed between calf thymus nuclear extract and polymyositis sera. Objectives of this study were to further define the immunologic nature of this reaction and to determine its specificity for polymyositis. Immunodiffusion studies using calf thymus nuclear extract revealed the PM-1 precipitin line in 17 of 28 patients with polymyositis. This reaction was not produced by sera of 460 patients with other diseases. Enzyme and heat treatments of the nuclear extract showed that PM-1 was distinct from native DNA, ribonucleoprotein, and Sm antigens. Fractionation of PM-1-positive serum by 30% ammonium sulphate and Sephadex G-200 chromatography revealed that the factor producing the PM-1 precipitin reaction was in a serum fraction which showed only IgG by immunoelectrphoresis against anti-whole human serum. Because of the apparent strong specificity, the PM-1 system may represent a marker antibody for polymyositis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Reichlin M., Mattioli M. Description of a serological reaction characteristic of polymyositis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Jan;5(1):12–20. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. C., Irvin W. S., LaRoque R. L., Velez C., Daly V., Kaiser A. D., Holman H. R. Association of autoantibodies to different nuclear antigens with clinical patterns of rheumatic disease and responsiveness to therapy. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):350–359. doi: 10.1172/JCI106502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. C., Irvin W. S., Tan E. M., Gould R. G., Holman H. R. Mixed connective tissue disease--an apparently distinct rheumatic disease syndrome associated with a specific antibody to an extractable nuclear antigen (ENA). Am J Med. 1972 Feb;52(2):148–159. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90064-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern G. M., Rose A. L., Jacobs K. Circulating antibodies in polymyositis. J Neurol Sci. 1967 Jul-Aug;5(1):181–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(67)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Pearson C. M. Rheumatic disease sera reactive with capillaries in the mouse kidney. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jan-Feb;15(1):23–28. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIR D. M., HOLBOROW E. J., JOHNSON G. D. A clinical study of serum antinuclear factor. Br Med J. 1961 Apr 1;1(5230):933–937. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5230.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]