Abstract
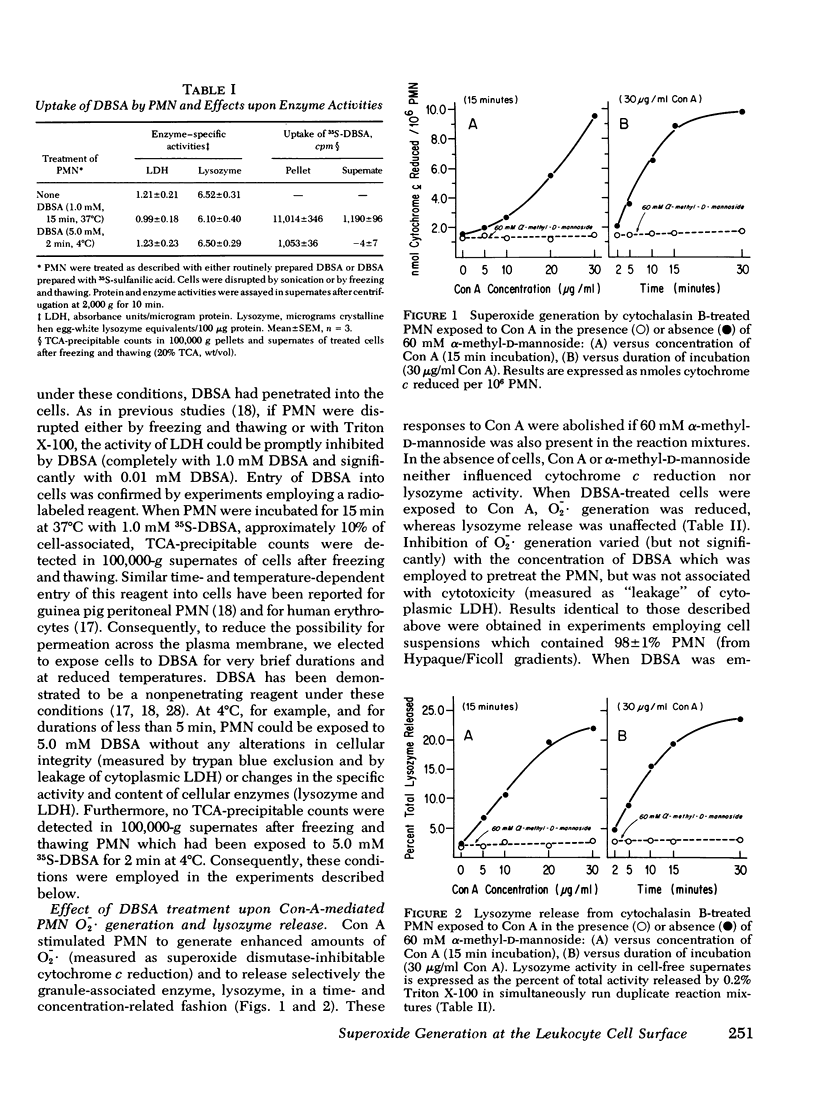
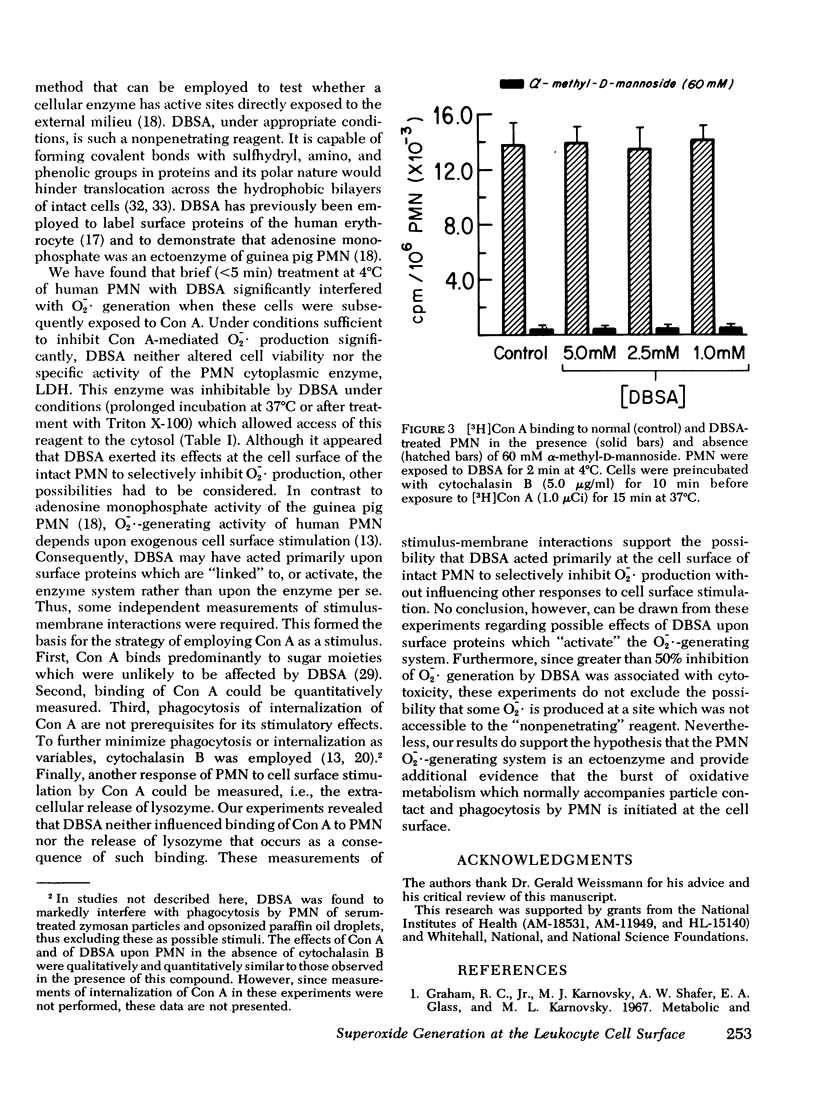
Superoxide anion (O-2-) generation by human peripheral blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes is enhanced when these cells encounter appropriate soluble or particulate stimuli. O-2- generation requires intact, viable cells and proceeds independently of phagocytosis. To investigate the possibility that the O-2--generating system is associated with the outer surface of the polymorphonuclear leukocyte plasma membrane, we have examined the effects upon O-2- production of p-diazobenzenesulfonic acid, a reagent which can react predominantly with proteins of the external cell membrane. When normal human polymorphonuclear leukocytes were preincubated with cytochalasin B (to minimize endocytosis) and then exposed to the surface-active lectin, concanavalin A, the cells were stimulated to generate O-2- in a concentration- and time-dependent fashion and selectively to discharge the granule-associated enzyme, lysozyme, into the surrounding medium. These responses, as well as cellular binding of [H] concanavalin A, could be blocked by alpha-methyl-D-mannoside. Brief treatment (less than 5 min at 4 degrees C) of the cells with p-diazobenzenesulfonic acid (1.0-5.0 mM) significantly interfered with concanavalin A-mediated O-2- generation but had no influence upon lysozyme release or upon binding of [3H] concanavalin A. The diazonium salt did not alter cell viability or the specific activity of the cytoplasmic enzyme, lactate dehydrogenase (inhibitable under conditions which allowed entry of this reagent into the cytosol). p-Diazobenzenesulfonic acid, therefore, very likely exerted its effects at the cell surface of the intact polymorphonuclear leukocyte, selectively inhibiting O-2- production (either directly or indirectly) without influencing another response to lectin-cell contact: release of lysozyme. These results support the possibility that a polymorphonuclear leukocyte ectoenzyme is responsible for O-2- production.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C. Sulfanilic acid diazonium salt: a label for the outside of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 3;183(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs R. T., Drath D. B., Karnovsky M. L., Karnovsky M. J. Localization of NADH oxidase on the surface of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by a new cytochemical method. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):566–586. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Babior B. M. Biological defense mechanisms. The effect of bacteria and serum on superoxide production by granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1662–1672. doi: 10.1172/JCI107717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePierre J. W., Karnovsky M. L. Ecto-enzymes of the guinea pig polymorphonuclear leukocyte. I. Evidence for an ecto-adenosine monophosphatase, adenosine triphosphatase, and -p-nitrophenyl phosphates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7111–7120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Feit F., Weissmann G. Enhancement of nitroblue tetrazolium dye reduction by leukocytes exposed to a component of complement in the absence of phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):516–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Kaplan H. B., Radin A., Frosch M. Independent effects of IgG and complement upon human polymorphonuclear leukocyte function. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1282–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Roos D., Kaplan H. B., Weissmann G. Complement and immunoglobulins stimulate superoxide production by human leukocytes independently of phagocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1155–1163. doi: 10.1172/JCI108191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Weissmann G. Generation of C5-derived lysosomal enzyme-releasing activity (C5a) by lysates of leukocyte lysosomes. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1583–1588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J., Shafer A. W., Glass E. A., Karnovsky M. L. Metabolic and morphological observations on the effect of surface-active agents of leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1967 Mar;32(3):629–647. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGGINS H. G., HARRINGTON K. J. Reaction of amino acids and proteins with diazonium compounds. II. Spectra of protein derivatives. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Dec;85:409–425. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90506-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD A. N., WILD F. The reactions of diazonium compounds with amino acids and proteins. Biochem J. 1957 Apr;65(4):651–659. doi: 10.1042/bj0650651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M., Oades Z. G. Stimulation of human neutrophils by soluble and insoluble immunoglobulin aggregates. Secretion of granule constituents and increased oxidation of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):1053–1061. doi: 10.1172/JCI108152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstein S., Soberman R., Goldstein I., Weissmann G. Concanavalin A induces microtubule assembly and specific granule discharge in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):781–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Lehmeyer J. E. Elaboration of toxic oxygen by-products by neutrophils in a model of immune complex disease. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):836–841. doi: 10.1172/JCI108359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. S., Finch S. C., Basford R. E. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte activation: effects of phospholipase C. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jun;140(2):540–543. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repine J. E., White J. G., Clawson C. C., Holmes B. M. The influence of phorbol myristate acetate on oxygen consumption by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jun;83(6):911–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo D., Zabucchi G., Rossi F. Reversible metabolic stimulation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and macrophages by concanavalin A. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 23;243(125):111–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Zatti M., Patriarca P., Cramer R. Effect of specific antibodies on the metabolism of guinea pig polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1971 Jan;9(1):67–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salin M. L., McCord J. M. Free radicals and inflammation. Protection of phagocytosine leukocytes by superoxide dismutase. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1319–1323. doi: 10.1172/JCI108208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salin M. L., McCord J. M. Superoxide dismutases in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):1005–1009. doi: 10.1172/JCI107816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins: cell-agglutinating and sugar-specific proteins. Science. 1972 Sep 15;177(4053):949–959. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4053.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedesco F., Trani S., Soranzo M. R., Patriarca P. Stimulation of glucose oxidation in human polymorphonuclear leucocytes by C3-Sepharose and soluble C567. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 1;51(1):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80894-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinberg H. M., Melnick R. L., Maguire J., Packer L. Studies on mitochondrial proteins. II. Localization of components in the inner membrane: labeling with diazobenzenesulfonate, a non-penetrating probe. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 12;345(1):118–128. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90251-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULMER D. D., VALLEE B. L., WACKER W. E. Metalloenzymes and myocardial infarction. II. Malic and lactic dehydrogenase activities and zinc concentrations in serum. N Engl J Med. 1956 Sep 6;255(10):450–456. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195609062551001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weening R. S., Wever R., Roos D. Quantitative aspects of the production of superoxide radicals by phagocytizing human granulocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):245–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Zurier R. B., Spieler P. J., Goldstein I. M. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from leukocytes exposed to immune complexes and other particles. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):149s–165s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



