Abstract
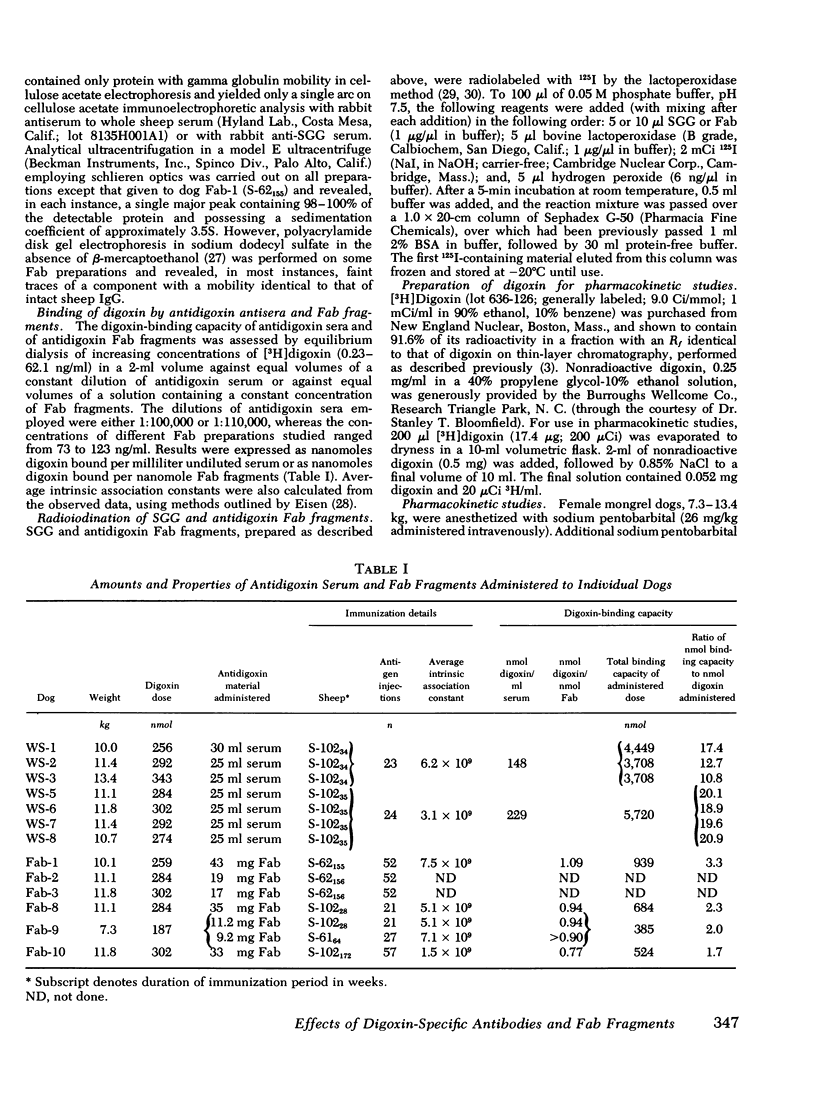
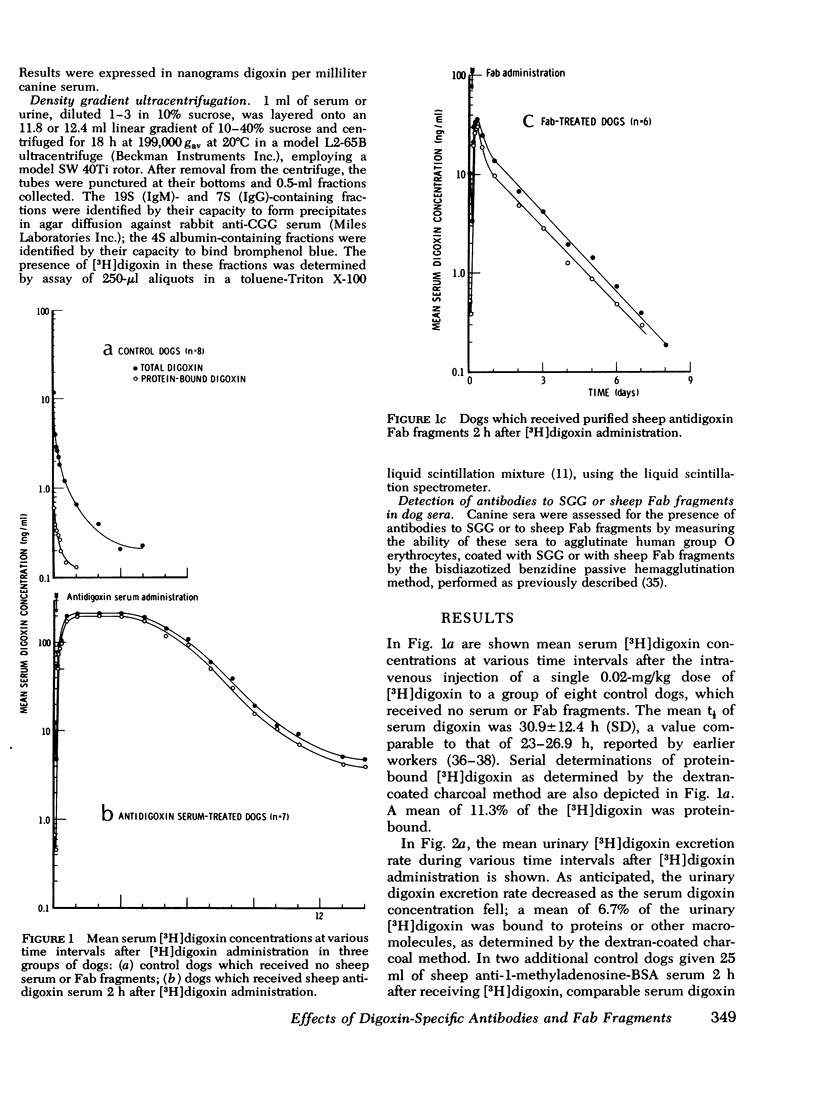
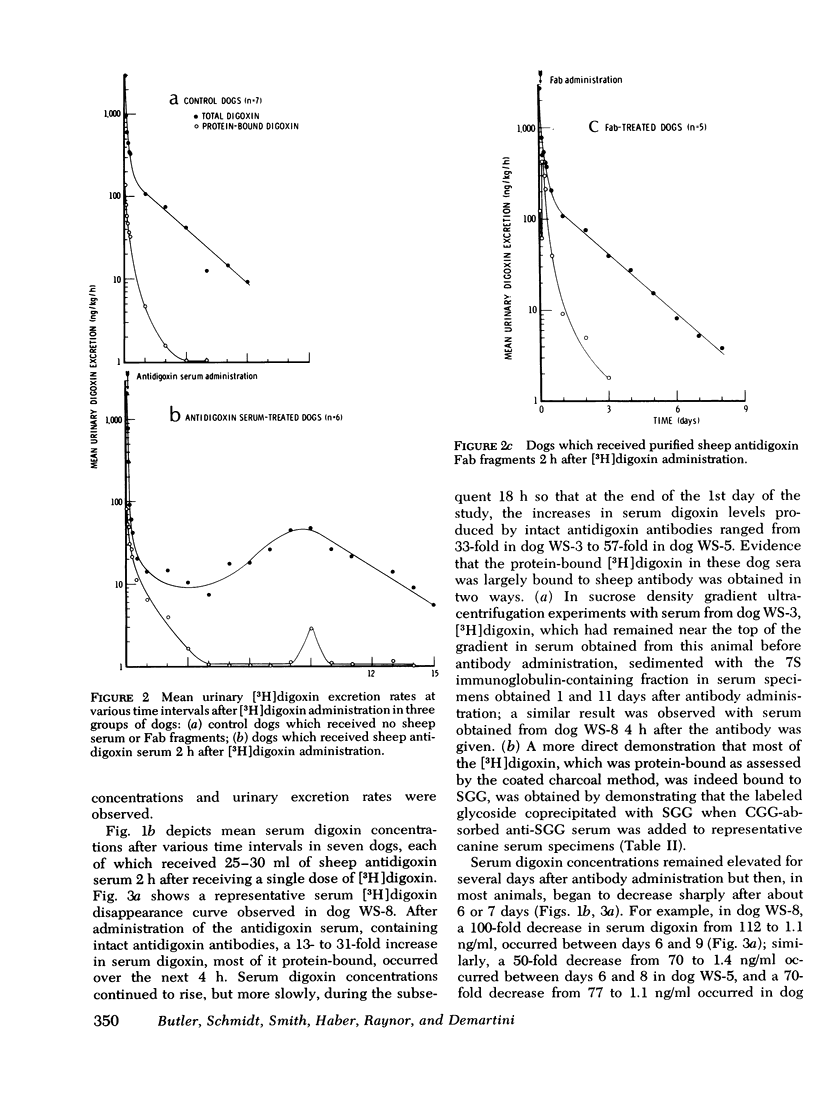
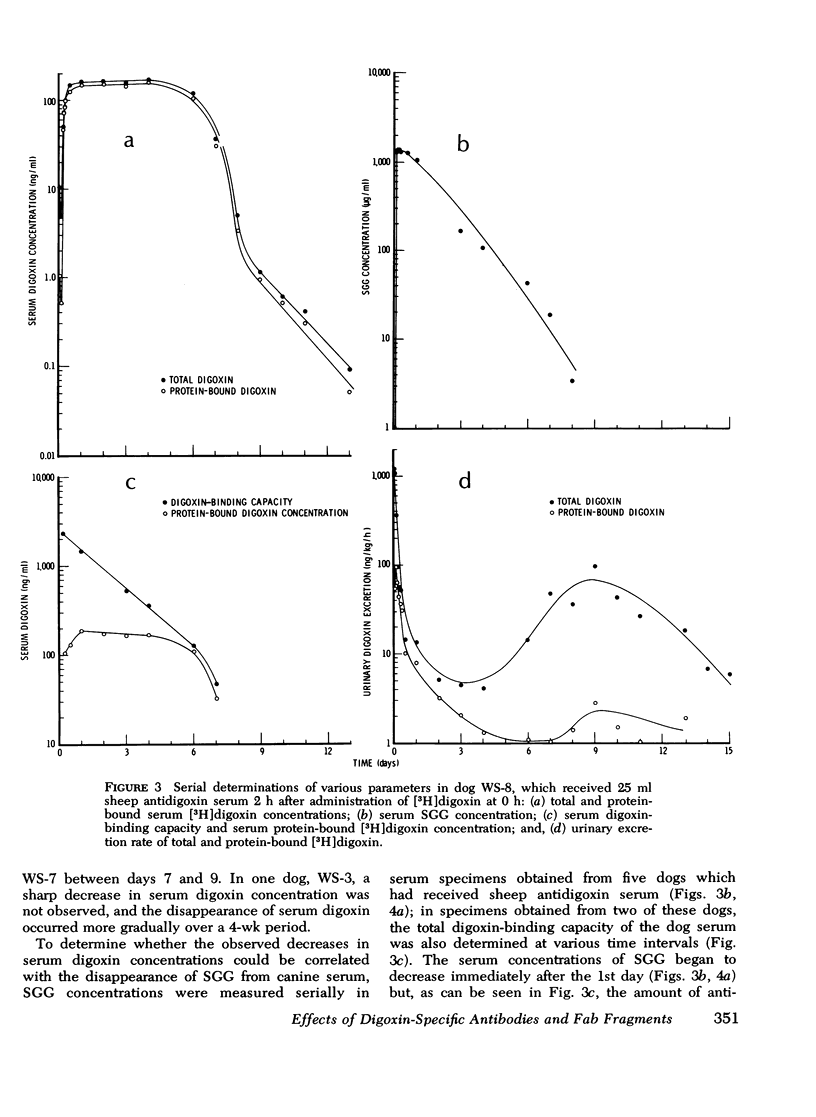
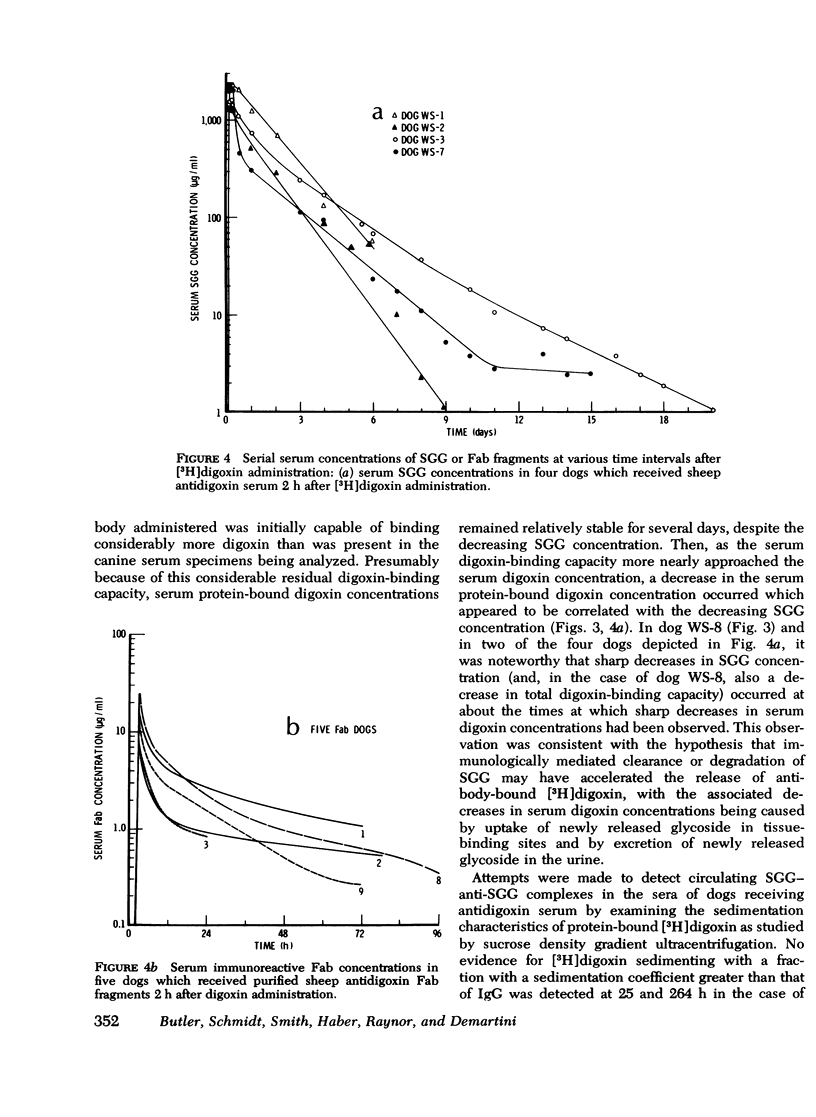
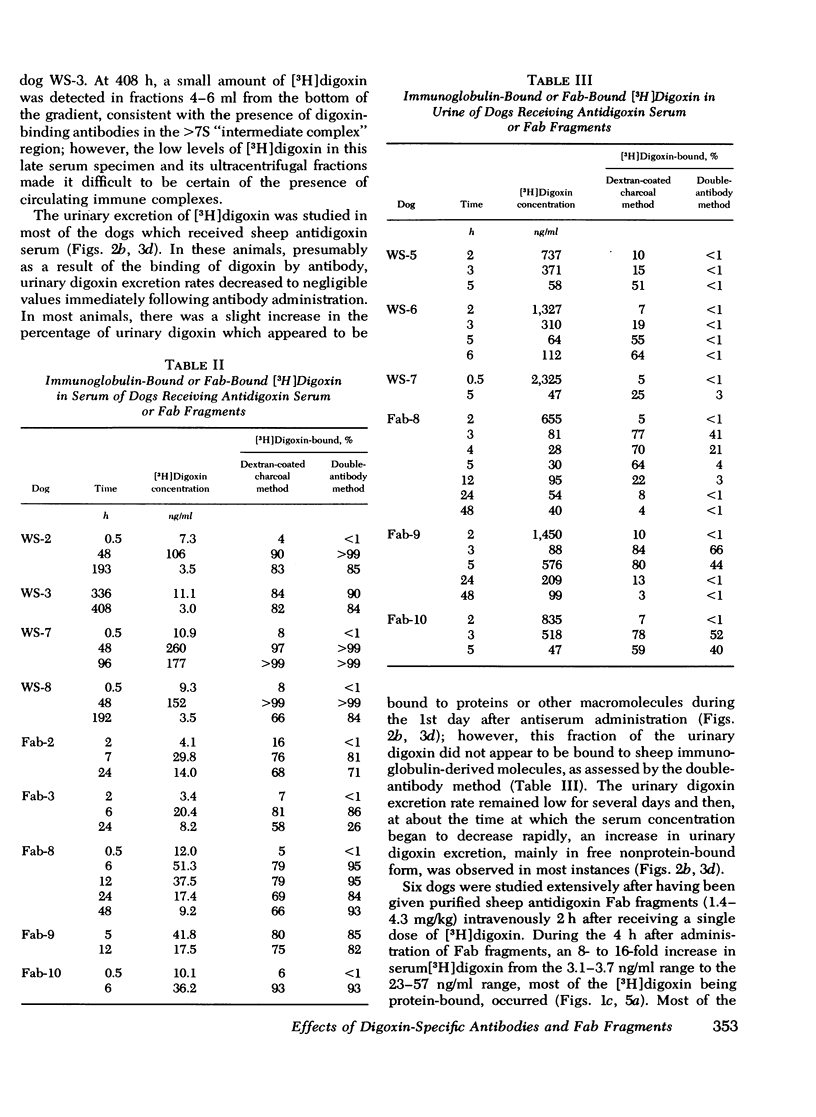
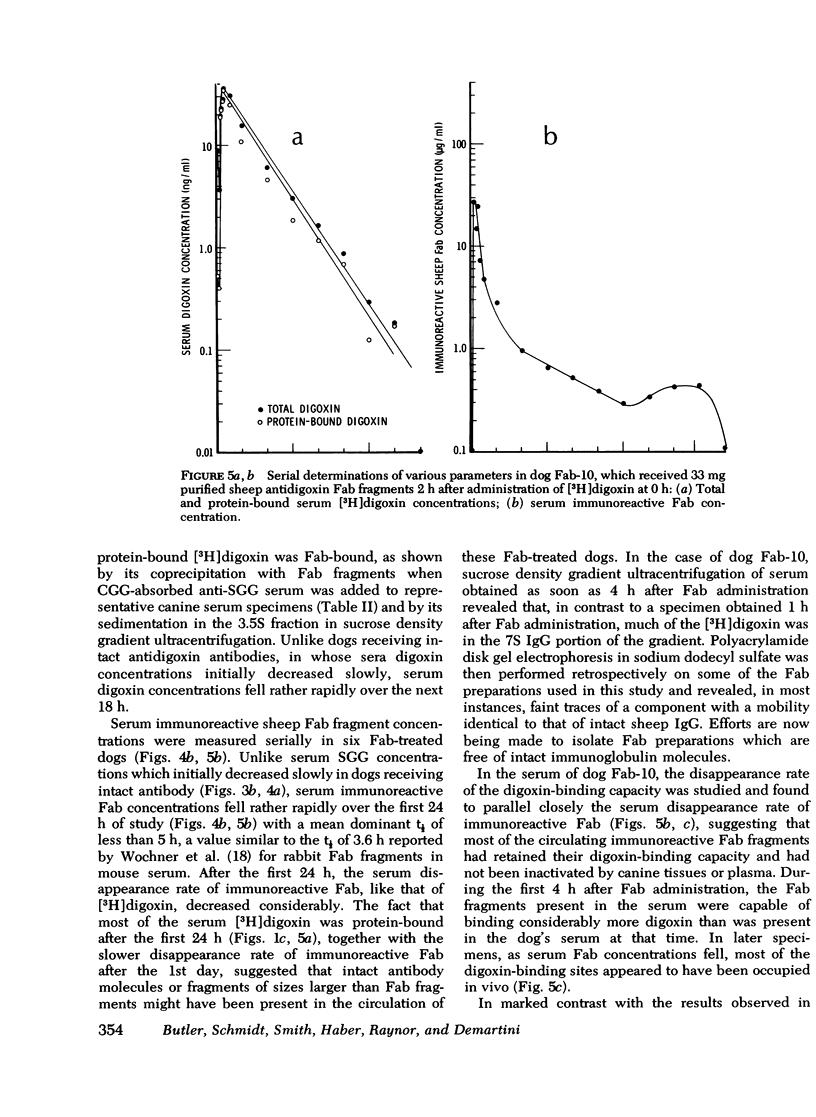
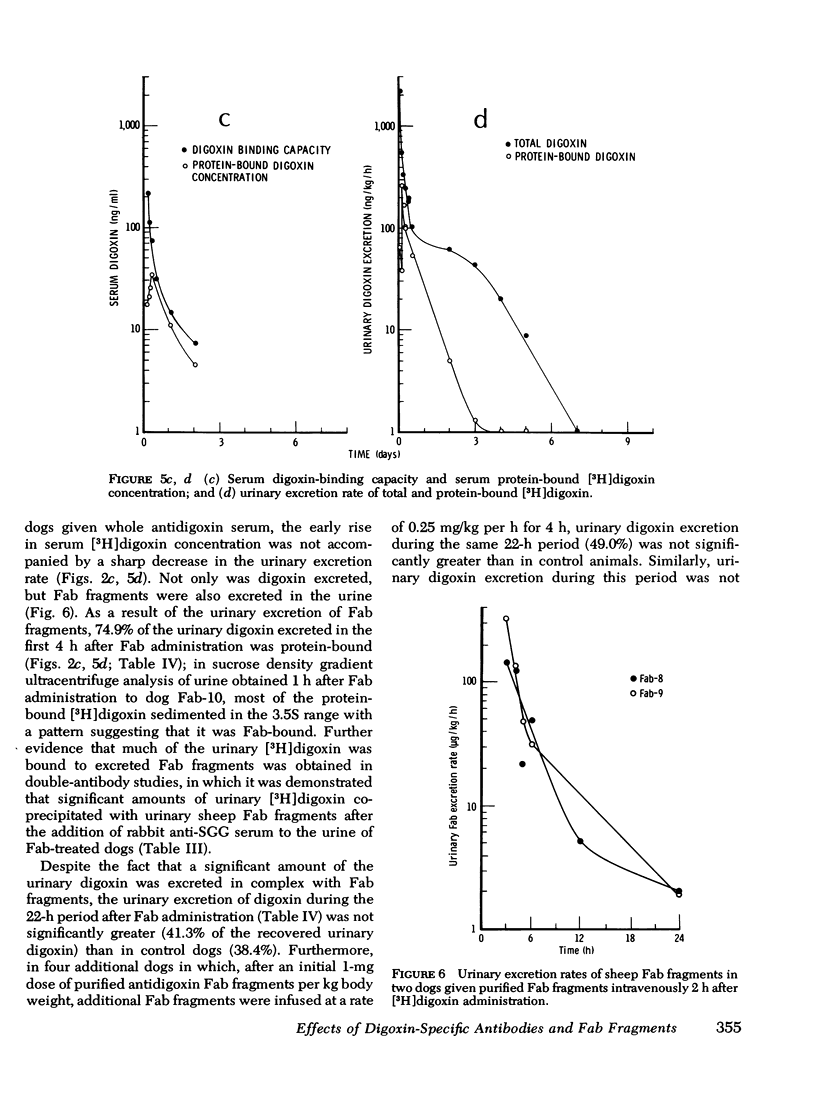
Intact sheep antidigoxin antibodies and their Fab fragments have both been found to exert profound effects on digoxin pharmacokinetics in [3H] digoxin-treated dogs. Both classes of molecule remove digoxin from the extravascular space and sequester it in the circulation in protein-bound form, a form in which the digoxin is presumably inactive. These two classes of molecule differ, however, in that the intact antibody molecules interfere with digoxin excretion, thereby promoting the retention of the glycoside; this retained digoxin is eventually released in free, active form when the administered antibody is metabolically degraded. In contrast, urinary excretion of digoxin continues in Fab-treated dogs, with significant quantities of digoxin being excreted promptly in the urine in complex with Fab fragments. These differences in urinary excretion, together with the probable decreased immunogenicity of sheep antidigoxin Fab fragments, suggest that such fragments possess potential advantages over intact antibody molecules for use in the therapy of life-threatening digoxin intoxication in man.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTLER V. P., Jr, VAUGHAN J. H. HEMAGGLUTINATION BY RHEUMATOID FACTOR OF CELLS COATED WITH ANIMAL GAMMA GLOBULINS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jul;116:585–593. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr I., Smith T. W., Klein M. D., Hagemeijer F., Lown B. Correlation of the electrophysiologic action of digoxin with serum digoxin concentration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Mar;180(3):710–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bismuth C., Gaultier M., Conso F., Efthymiou M. L. Hyperkalemia in acute digitalis poisoning: prognostic significance and therapeutic implications. Clin Toxicol. 1973;6(2):153–162. doi: 10.3109/15563657308990513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulter V. P., Jr, Schmidt D. H., Watson J. F., Gardner J. D. Production and properties of digoxin-specific antibodies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;242(0):717–730. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb19133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler V. P., Jr, Chen J. P. Digoxin-specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jan;57(1):71–78. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler V. P., Jr Digoxin: immunologic appraoches to measurement and reversal of toxicity. N Engl J Med. 1970 Nov 19;283(21):1150–1156. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197011192832109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler V. P., Jr, Watson J. F., Schmidt D. H., Gardner J. D., Mandel W. J., Skelton C. L. Reversal of the pharmacological and toxic effects of cardiac glycosides by specific antibodies. Pharmacol Rev. 1973 Jun;25(2):239–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curd J., Smith T. W., Jaton J. C., Haber E. The isolation of digoxin-specific antibody and its use in reversing the effects of digoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2401–2406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty J. E., Perkins W. H. Tissue concentration and turnover of tritiated digoxin in dogs. Am J Cardiol. 1966 Jan;17(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(66)90259-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISEN H. N. EQUILIBRIUM DIALYSIS FOR MEASUREMENT OF ANTIBODY-HAPTEN AFFINITIES. Methods Med Res. 1964;10:106–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANGER B. F., BEISER S. M. ANTIBODIES SPECIFIC FOR RIBONUCLEOSIDES AND RIBONUCLEOTIDES AND THEIR REACTION WITH DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:68–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., KUMATE J., URRUSTI J., MORALES C. THE SELECTIVITY OF THE HUMAN PLACENTA IN THE TRANSFER OF PLASMA PROTEINS FROM MOTHER TO FETUS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:1938–1951. doi: 10.1172/JCI105068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Kilno D. R., Swartz T. J., Butler V. P., Jr Effects of digoxin-specific antibodies on accumulation and binding of digoxin by human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1973 Aug;52(8):1820–1833. doi: 10.1172/JCI107364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold H. K., Smith T. W. Reversal of ouabain and acetyl strophanthidin effects in normal and failing cardiac muscle by specific antibody. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1655–1661. doi: 10.1172/JCI107716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison C. E., Jr, Brandenburg R. O., Ongley P. A., Orvis A. L., Owen C. A., Jr The distribution and excretion of tritiated substances in experimental animals following the administration of digoxin-3H. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 May;67(5):764–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusser C., Boesman M., Nordin J. H., Isliker H. Effect of chemical and enzymatic radioiodination on in vitro human Clq activities. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):820–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARLINER J. S., BELAVAL G. S. INCIDENCE OF REACTIONS FOLLOWING ADMINISTRATION OF ANTIRABIES SERUM; STUDY OF 526 CASES. JAMA. 1965 Aug 2;193:359–362. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03090050035009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekwick R. A. The serum proteins in multiple myelomatosis. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1248–1257. doi: 10.1042/bj0341248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuschinsky K., Lahrtz H., Lüllmann H., van Zwieten P. A. Accumulation and release of 3H-digoxin by guinea-pig heart muscle. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Jun;30(2):317–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb02138.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel W. J., Bigger J. T., Jr, Butler V. P., Jr The electrophysiologic effects of low and high digoxin concentrations on isolated mammalian cardiac tissue: reversal by digoxin-specific antibody. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1378–1387. doi: 10.1172/JCI106933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A. ENZYMATIC DIGESTION OF RABBIT GAMMA GLOBULIN AND ANTIBODY AND CHROMATOGRAPHY OF DIGESTION PRODUCTS. Methods Med Res. 1964;10:134–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Axen R., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1491–1492. doi: 10.1038/2151491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reza M. J., Kovick R. B., Shine K. I., Pearce M. L. Massive intravenous digoxin overdosage. N Engl J Med. 1974 Oct 10;291(15):777–778. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197410102911508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Haimovich J., Sela M. Purification of antibodies with immunoadsorbents prepared using bromoacetyl cellulose. Immunochemistry. 1967 Jan;4(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(67)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIEGELBERG H. L., WEIGLE W. O. THE CATABOLISM OF HOMOLOGOUS AND HETEROLOGOUS 7S GAMMA GLOBULIN FRAGMENTS. J Exp Med. 1965 Mar 1;121:323–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.3.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt D. H., Butler V. P., Jr Immunological protecion against dixin toxicity. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):866–871. doi: 10.1172/JCI106558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt D. H., Butler V. P., Jr Reversal of digoxin toxicity with specific antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1738–1744. doi: 10.1172/JCI106663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt D. H., Kaufman B. M., Butler V. P., Jr Persistence of hapten-antibody complexes in the circulation of immunized animals after a single intravenous injection of hapten. J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):278–294. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Butler V. P., Jr, Haber E. Characterization of antibodies of high affinity and specificity for the digitalis glycoside digoxin. Biochemistry. 1970 Jan 20;9(2):331–337. doi: 10.1021/bi00804a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Haber E. Digitalis (fourth of four parts). N Engl J Med. 1973 Nov 22;289(21):1125–1129. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197311222892106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Haber E., Yeatman L., Butler V. P., Jr Reversal of advanced digoxin intoxication with Fab fragments of digoxin-specific antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 8;294(15):797–800. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604082941501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W. Use of antibodies in the study of the mechanism of action of digitalis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;242(0):731–765. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb19134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W., Willerson J. T. Suicidal and accidental digoxin ingestion. Report of five cases with serum digoxin level correlations. Circulation. 1971 Jul;44(1):29–36. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.44.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. F., Butler V. P., Jr Biologic activity of digoxin-specific antisera. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):638–648. doi: 10.1172/JCI106853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wochner R. D., Strober W., Waldmann T. A. The role of the kidney in the catabolism of Bence Jones proteins and immunoglobulin fragments. J Exp Med. 1967 Aug 1;126(2):207–221. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



