Abstract
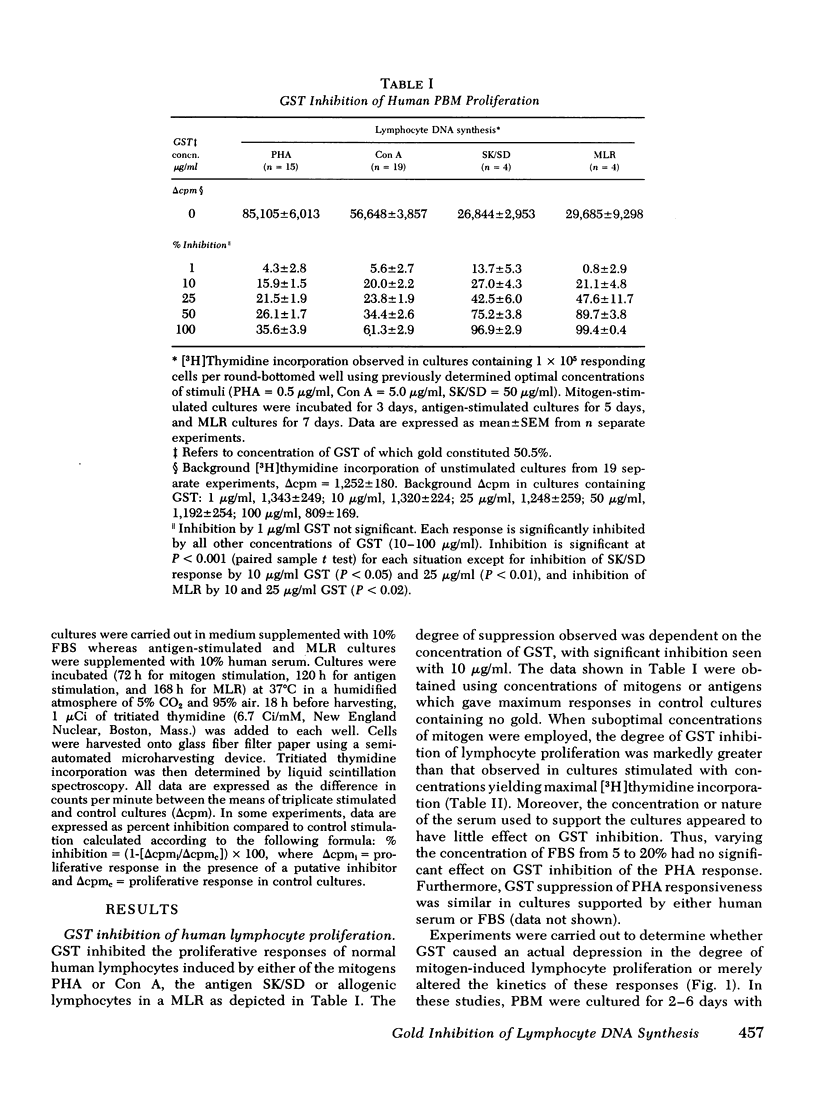
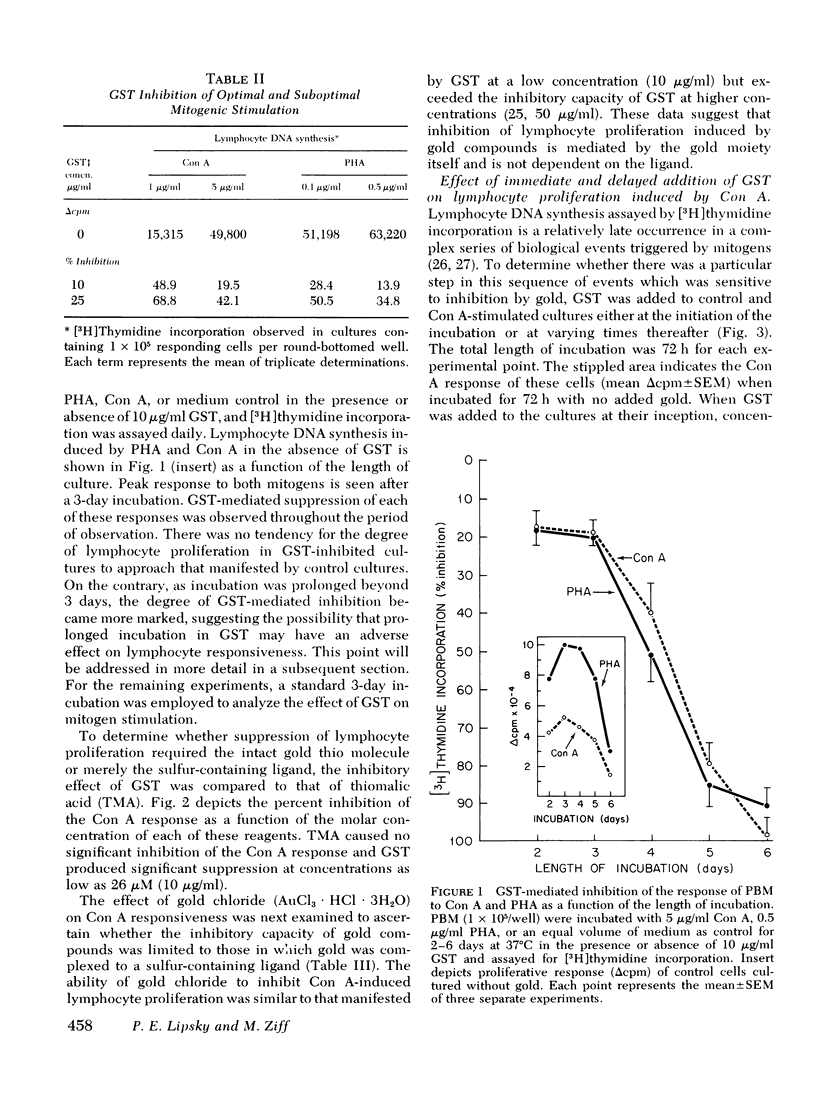
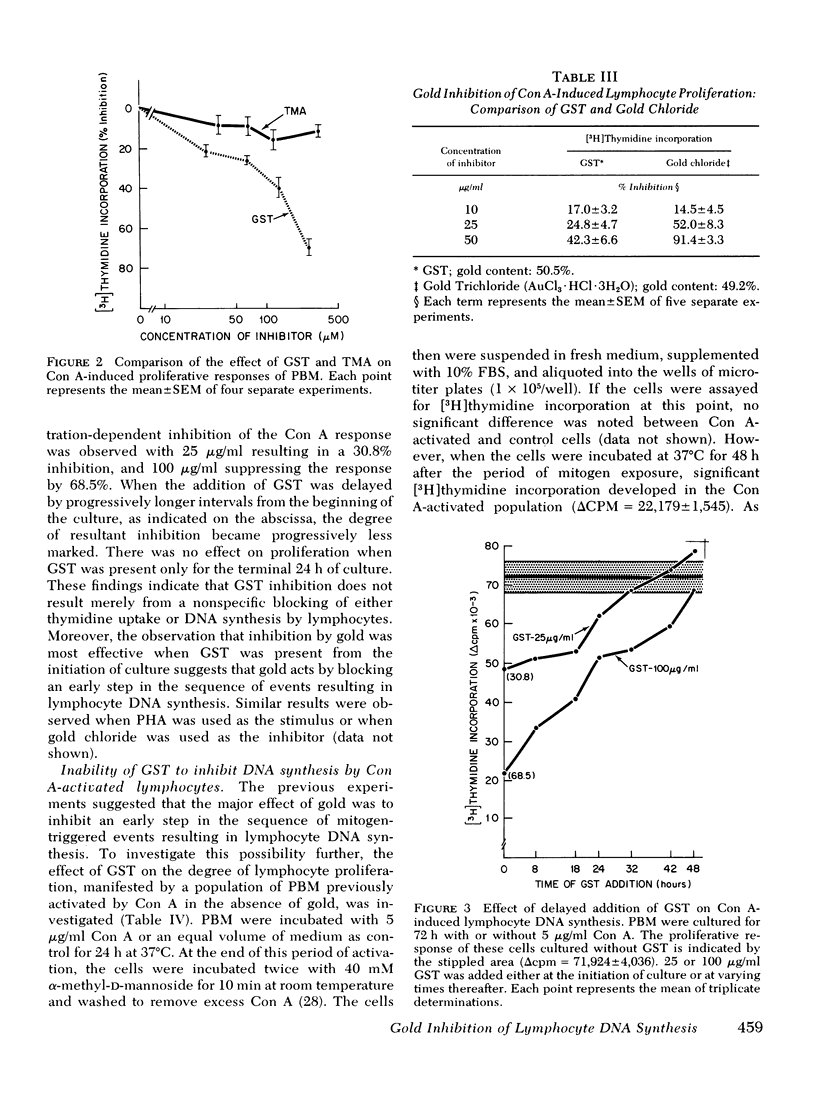
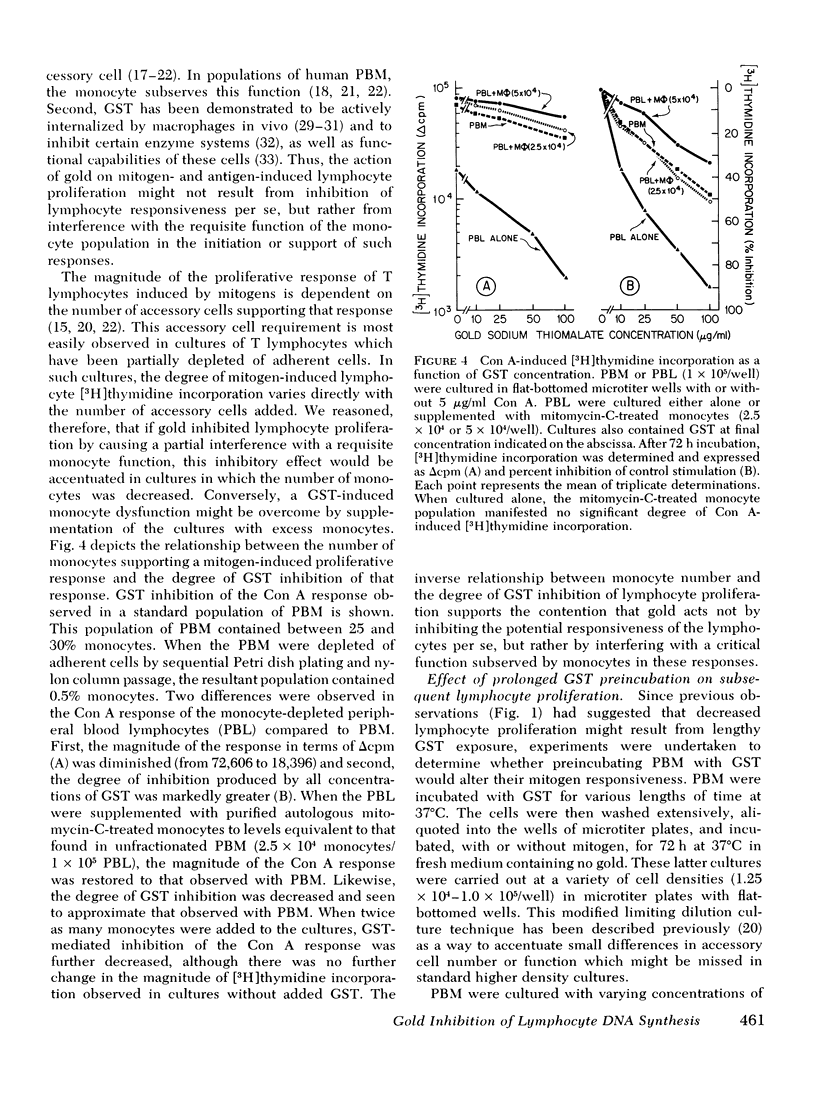
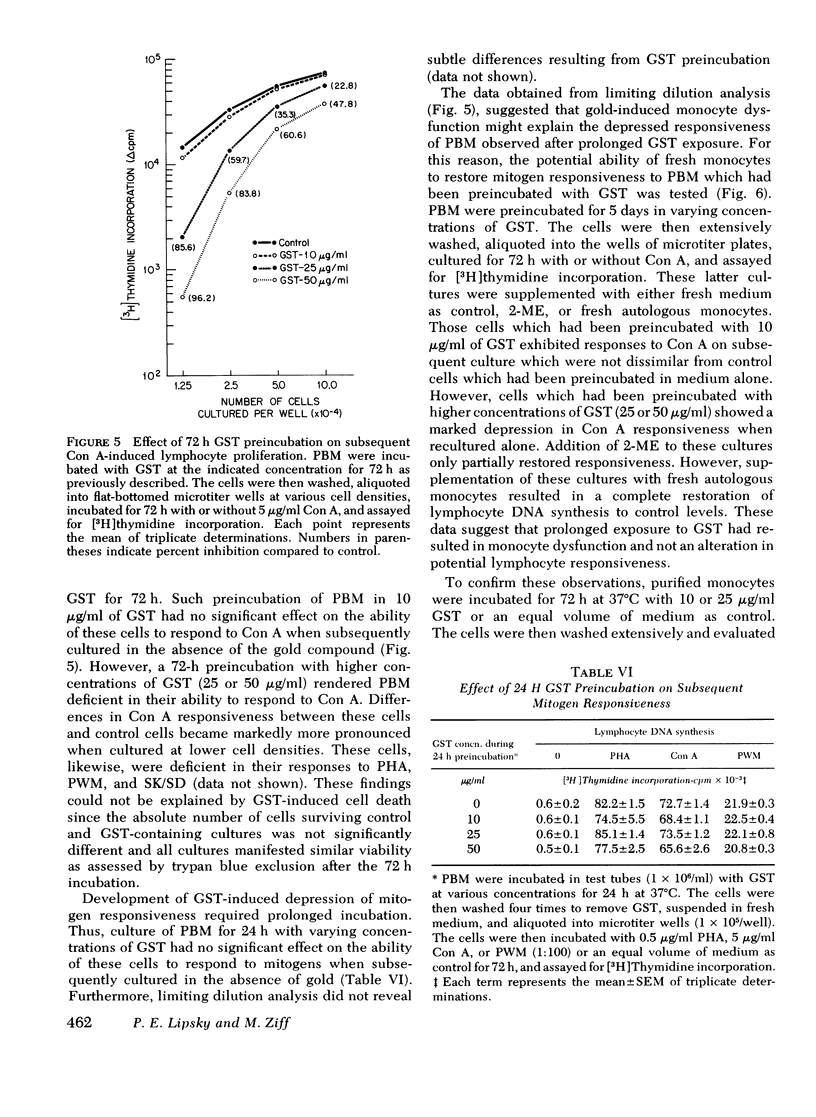
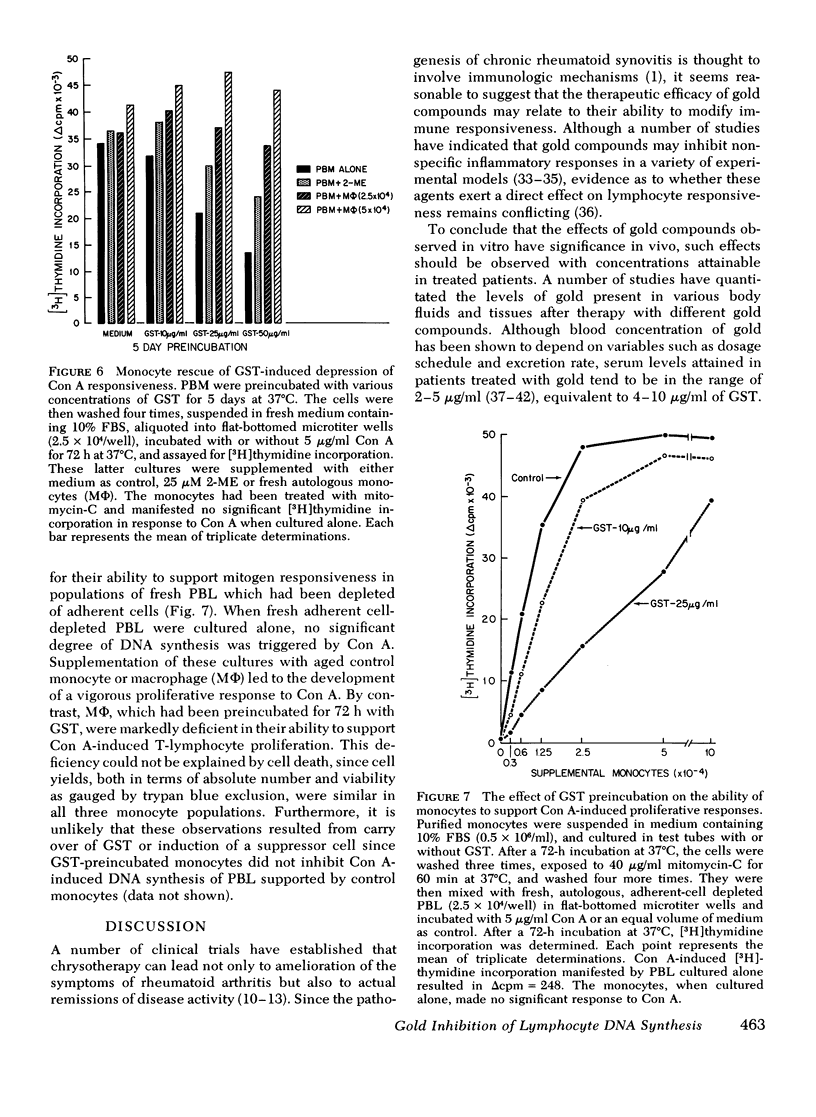
Gold sodium thiomalate (GST) inhibited in vitro antigen- and mitogen-triggered human lymphocyte DNA synthesis. Inhibition of responsiveness was observed with concentrations of GST equivalent to gold levels found in serum or tissues of patients receiving chrysotherapy, Inhibition was dependent upon the gold ion itself since GST and gold chloride were both inhibitory whereas thiomalic acid was not. Inhibition could not be explained by nonspecific killing of cells or by an alteration in the kinetics of the responses. GST inhibited mitogen-induced proliferation most effectively when present from the initiation of culture and could not inhibit the responsiveness of cells which previously had been activated by concanvalin A. These findings indicated that GST blocked a critical early step in lymphocyte activation. The degree of GST-induced inhibition of proliferation was increased in cultures of cells partially depleted of monocytes. Moreover, inhibition was reversed by supplementation of these cultures with purified monocytes. These observations suggested that GST blocked thymus-derived (T)-lymphocyte activation by interfering with a requisite function of the monocyte population in initiating such responses. Prolonged incubation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells with GST resulted in diminished mitogen responsiveness upon subsequent culture in the absence of gold. The addition of fresh monocytes restored responsiveness to these populations. Furthermore, preincubation of purified monocytes with GST rendered them deficient in their ability to support mitogen-induced T-lymphocyte proliferation on subsequent culture. These observations indicate that the major effect of GST results from interference with the functional capability of the monocyte population.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON A. C., YOUNG M. R. UPTAKE OF DYES AND DRUGS BY LIVING CELLS IN CULTURE. Life Sci. 1964 Dec;3:1407–1414. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(64)90082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billings R., Grahame R., Marks V., Wood P. J., Taylor A. Blood and urine gold levels during chrysotherapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1975 Feb;14(1):13–18. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/14.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R. In vitro approaches to the mechanism of cell-mediated immune reactions. Adv Immunol. 1971;13:101–208. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill R. N. Effect of sodium aurothiomalate "mycrosin" on DNA synthesis in phytohaemagglutin-stimulated cultures of sheep lymphocytes. Experientia. 1971 Aug;27(8):913–914. doi: 10.1007/BF02135740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess L., MacDermott R. P., Schlossman S. F. Immunologic functions of isolated human lymphocyte subpopulations. II. Antigen triggering of T and B cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1122–1127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Wang J. L., Gunther G. R., Reeke G. N., Jr, Becker J. W. Molecular analysis of the initial events in mitogenesis. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1974;29:177–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erb P., Feldmann M. The role of macrophages in the generation of T-helper cells. I. The requirement for macrophages in helper cell induction and characteristics of the macrophage-T cell interaction. Cell Immunol. 1975 Oct;19(2):356–367. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90217-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froland S. S., Natvig J. B., Husby G. Immunological characterization of lymphocytes in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(1):67–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02017.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber R. C., Paulus H. E., Bluestone R., Pearson C. M. Clinical response and serum gold levels in chrysotherapy. Lack of correlation. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Jul;31(4):308–310. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.4.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb N. L., Smith P. M., Smith E. M. Tissue gold concentration in a rheumatoid arthritic receiving chrysotherapy. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jan-Feb;15(1):16–22. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame R., Billings R., Laurence M., Marks V., Wood P. J. Tissue gold levels after chrysotherapy. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Nov;33(6):536–539. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.6.536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M., Janossy G., Doenhoff M. Selective triggering of human T and B lymphocytes in vitro by polyclonal mitogens. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):1–18. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessop J. D., Johns R. G. Serum gold determinations in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving sodium aurothiomalate. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 May;32(3):228–232. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.3.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessop J. D., Vernon-Roberts B., Harris J. Effects of gold salts and prednisolone on inflammatory cells. I. Phagocytic activity of macrophages and polymorphs in inflammatory exudates studied by a "skin-window" technique in rheumatoid and control patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Jul;32(4):294–300. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.4.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Unanue E. R. Critical role of determinant presentation in the induction of specific responses in immunocompetent lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):967–990. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWRENCE J. S. Studies with radioactive gold. Ann Rheum Dis. 1961 Dec;20:341–352. doi: 10.1136/ard.20.4.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. C., Ziff M. Intra-articular administration of gold salts. Arthritis Rheum. 1966 Oct;9(5):682–692. doi: 10.1002/art.1780090505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky P. E., Ellner J. J., Rosenthal A. L. Phytohemagglutinin-induced proliferation of guinea pig thymus-derived lymphocytes. I. Accessory cell dependence. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):868–875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewi G., Dorling J., Howard A. Mononuclear cells from inflammatory joint effusions: electron-microscopic appearances and immunoglobulin synthesis. J Rheumatol. 1974 Mar;1(1):34–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewi G., Lance E. M., Reynolds J. Study of lymphoid cells from inflamed synovial membranes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Dec;34(6):524–528. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.6.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohrmann H. P., Novikovs L., Graw R. G., Jr Cellular interactions in the proliferative response of human T and B lymphocytes to phytomitogens and allogeneic lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 Jun 1;139(6):1553–1567. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.6.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorber A., Cohen R. L., Chang C. C., Anderson H. E. Gold determination in biological fluids by atomic absorption spectrophotometry: application to chrysotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Apr;11(2):170–177. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascarenhas B. R., Granda J. L., Freyberg R. H. Gold metabolism in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with gold compounds--reinvestigated. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Jul-Aug;15(4):391–402. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. D., Leu R. W. Macrophage requirement for production of guinea pig migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in vitro. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):606–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. L., Lewis D. C., Ziff M. Electron-dense deposits following injection of gold sodium thiomalate and thiomalic acid. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Jun;11(3):436–443. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page R. C., Davies P., Allison A. C. Participation of mononuclear phagocytes in chronic inflammatory diseases. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1974 May;15(5):413–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persellin R. H., Ziff M. The effect of gold salt on lysosomal enzymes of the peritoneal macrophage. Arthritis Rheum. 1966 Feb;9(1):57–65. doi: 10.1002/art.1780090107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein H. M., Dietz A. A. Serum gold. II. Levels in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Mar;32(2):128–132. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter G. P. McFarland W,+MACFARLAND W: Interaction of lymphocytes and a radioresistant cell in PPD-stimulated human leukocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1970 Sep;105(3):661–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtke J. R., Hatfield S. Activation of purified human thymus-derived (T) cells by mitogens. II. Monocyte- macrophage potentiation of mitogen-induced DNA synthesis. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):357–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon P. J., Papamichail M., Holborow E. J. Studies on synovial fluid lymphocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Nov;33(6):509–514. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.6.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigler J. W., Bluhm G. B., Duncan H., Sharp J. T., Ensign D. C., McCrum W. R. Gold salts in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. A double-blind study. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jan;80(1):21–26. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. D., Sachs C., Ziff M. In vitro synthesis of immunoglobulin by rheumatoid synovial membrane. J Clin Invest. 1968 Mar;47(3):624–632. doi: 10.1172/JCI105758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilágyi T., Muszbek L., Lévai G., Laczkó J. The effect of gold treatment on local Shwartzman phenomenon. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1968;15(4):331–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twomey J. J., Sharkey O., Jr, Brown J. A., Laughter A. H., Jordan P. H., Jr Cellular requirements for the mitotic response in allogeneic mixed leukocyte cultures. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):845–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Boxel J. A., Paget S. A. Predominantly T-cell infiltrate in rheumatoid synovial membranes. N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 11;293(11):517–520. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197509112931101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernon-Roberts B., Jessop J. D., Doré J. Effects of gold salts and prednisolone on inflammatory cells. II. Suppression of inflammation and phagocytosis in the rat. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 Jul;32(4):301–307. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.4.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron J. A., Jr, Horn R. G., Rosenthal A. S. Antigen-induced proliferation of guinea pig lymphocytes in vitro: functional aspects of antigen handling by macrophages. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):746–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahara I., Edelman G. M. Restriction of the mobility of lymphocyte immunoglobulin receptors by concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):608–612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. Immunoreactants in rheumatoid synovial effusions. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):276s–285s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. The immunopathology of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):265–336. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



