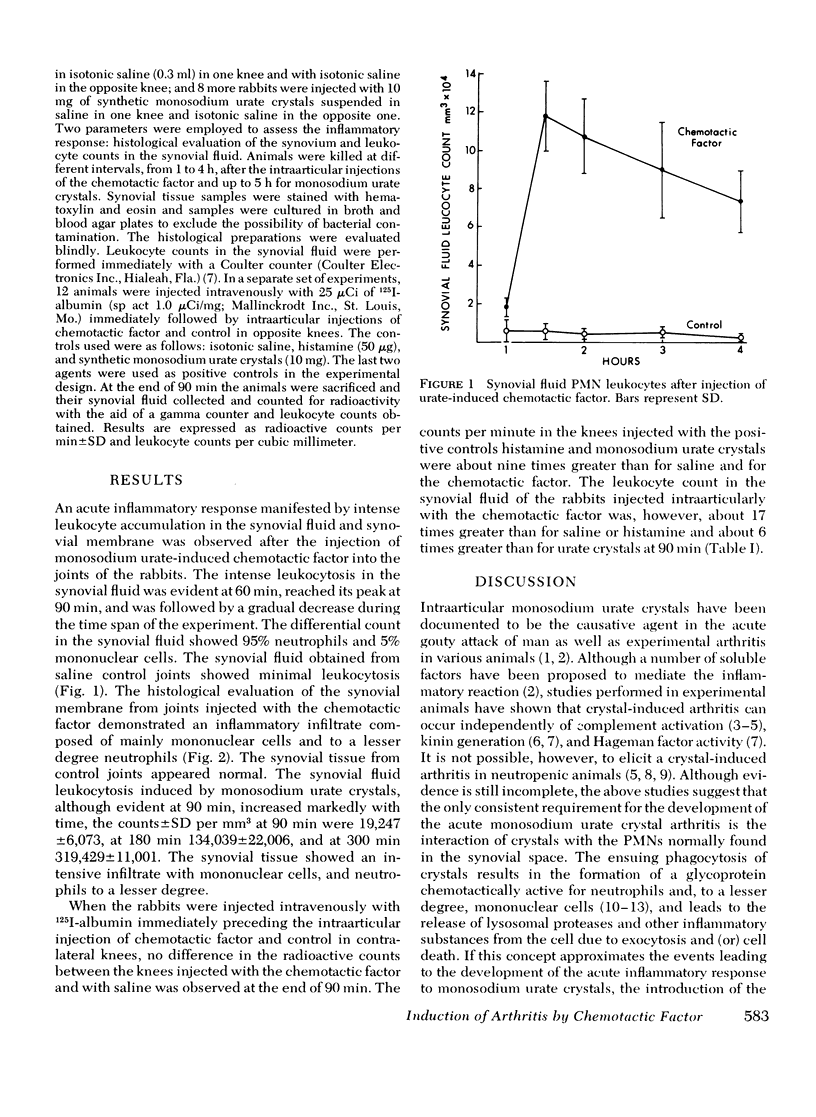
Abstract
The injection of monosidium urate-induced chemotactic factor into the joint cavities of rabbits induces an acute inflammatory response that resembles the one produced by monosodium urate crystals. The leukocyte accumulation induced by the factor was not accompanied by a measurable increase in vascular permeability as measured by appearance of 125I-albumin in the joint cavity. When histamine was injected into the joints, a marked increase in vascular permeability but no leukocytosis above control levels was observed. The above results suggest that the cell-derived factor is primarily responsible for the accumulation of cells seen in the acute inflammation induced by monosodium urate crystals.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHN Z. A., HIRSCH J. G. The isolation and properties of the specific cytoplasmic granules of rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:983–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. H., Garalla E. J. Suppression of urate crystal-induced canine joint inflammation by heterologous anti-polymorphonuclear leukocyte serum. Arthritis Rheum. 1968 Apr;11(2):145–150. doi: 10.1002/art.1780110204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenbaum L. M., Kim K. S. The kinin-forming and kininase activities of rabbit polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Feb;29(2):238–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Habal F. M., Macmorine D. R. Generation of a vasoactive peptide by a neutral protease of human neutrophil leukocytes. Agents Actions. 1976 Feb;6(1-3):183–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01972206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps P., McCarty D. J., Jr Crystal-induced arthritis. Postgrad Med. 1969 Jan;45(1):87–93. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1969.11696985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps P., McCarty D. J., Jr Crystal-induced inflammation in canine joints. II. Importance of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1966 Jul 1;124(1):115–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps P. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte motility in vitro. 3. Possible release of a chemotactic substance after phagocytosis of urate crystals by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 1969 Jun;12(3):197–204. doi: 10.1002/art.1780120306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps P., Prockop D. J., McCarty D. J. Crystal induced inflammation in canine joints. 3. Evidence against bradykinin as a mediator of inflammation. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Sep;68(3):433–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilberg I. Current concepts of the mechanism of acute inflammation in gouty arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Mar-Apr;18(2):129–134. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilberg I., Gallacher A., Mendell B. Studies on crystal-induced chemotactic factor. II. Role of phagocytosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Apr;85(4):631–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilberg I., Mandell B., Wochner R. D. Studies on crystal-induced chemotactic factor. I. Requirement for protein synthesis and neutral protease activity. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jan;83(1):56–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilberg I., Osterland C. K. Anti-inflammatory effect of the trypsin-kallikrein inhibitor in acute arthritis induced by urate crystals in rabbits. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Sep;76(3):472–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilberg I. Studies on the mechanism of inflammation induced by calcium pyrophosphate crystals. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Jul;82(1):86–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilberg I. Urate crystal arthritis in animals lacking Hageman factor. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Mar-Apr;17(2):143–148. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilbert I., Gallacher A., Mehta J. M., Mandell B. Urate crystal-induced chemotactic factor: isolation and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):815–819. doi: 10.1172/JCI108533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharius R. M., Zell T. E., Morrison J. H., Woodlock J. J. Glycoprotein staining following electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jul;30(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




