Abstract
Hemoglobin is the major biosynthetic product of developing erythroid cells. Assembly of hemoglobin requires the balanced production of globin protein and the oxygen-carrying heme moiety. The heme-regulated inhibitor kinase (HRI) participates in this process by phosphorylating eIF2α and inhibiting the translation of globin protein when levels of free heme are limiting. HRI is also activated in erythroid cells subjected to oxidative stress. Phospho-eIF2α-mediated translational repression induces the assembly of stress granules (SG), cytoplasmic foci that harbor untranslated mRNAs and promote the survival of cells subjected to adverse environmental conditions. We have found that differentiating erythroid, but not myelomonocytic or megakaryocytic, murine and human progenitor cells assemble SGs, in vitro and in vivo. Targeted knockdown of HRI or G3BP, a protein required for SG assembly, inhibits spontaneous and arsenite-induced assembly of SGs in erythroid progenitor cells. This is accompanied by reduced globin production and increased apoptosis suggesting that G3BP+ SGs facilitate the survival of developing erythroid cells.
Keywords: erythroid cell, Stress Granule, HRI/ eIF2α, G3BP, α-globin
1. INTRODUCTION
Globin proteins are synthesized throughout erythroid cell maturation. The translation of globin proteins is coordinated with the synthesis of heme moieties to ensure the efficient assembly of haemoglobin. This process requires the heme-regulated inhibitor (HRI), a kinase that phosphorylates eIF2α to inhibit the translation of globin proteins when intracellular free heme is limiting [1]. Dysregulation of this process leads to apoptotic cell death and anemia [1; 2].
Sodium arsenite (SA), a pharmacological activator of HRI, induces the phosphorylation of eIF2α and the assembly of stress granules (SGs) [3]. SGs are discrete cytoplasmic foci at which untranslated mRNAs accumulate in a dynamic process that modulates the degradation, storage and translational re-initiation of mRNA to help re-program protein expression in cells exposed to adverse environmental conditions [4]. The assembly of SGs enhances the survival of stressed cells by poorly characterized mechanisms [4].
In addition to untranslated mRNAs, SGs harbor small, but not large, ribosomal subunits as well as an eclectic collection of translation factors, RNA binding proteins, and signalling molecules. The Ras GAP SH3 domain-Binding Protein (G3BP) is an essential component of stress granules whose overexpression nucleates SG assembly and whose knockdown inhibits SG assembly [5]. G3BP is a multifunctional RNA-binding protein [6], that has been implicated in various aspects of cell survival and proliferation [7; 8].
Based on the known importance of translational control mechanisms in erythroid cell physiology, we investigated the role of cytoplasmic SGs in the regulation of α-globin mRNA stability and protein synthesis. We found that a subset of CD34+ murine and human bone marrow cells in the erythroid (but not myeloid or megakaryocytic) lineage assemble SGs. Lentivirus-delivered shRNAs targeting HRI or G3BP inhibit both spontaneous and arsenite-induced SG assembly, suggesting that formation of spontaneous SGs is HRI dependent. Inhibition of SGs through G3BP knockdown also reduces α-globin mRNA and protein levels as well as CD34+ cell viability. Our data provide evidence that G3BP and SGs promote α-globin transcript stability and survival of cells in the erythroid lineage.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Cell culture and drug treatment
Primary normal human bone marrow CD34+ cells were cultured in a two-phase liquid culture system [9]. To screen for lineage specificity of SG formation, cells were cultured in media containing cytokines supporting erythroid, myeloid and megakaryocytic differentiation [10]. To support erythroid differentiation, 100 ng ml−1 stem cell factor, 10 ng ml−1 interleukin-3, 10 ng ml−1 interleukin-6 and 0.5 U ml−1 erythropoietin were added to Serum-Free Expansion Medium (Stem Cell Technologies). The concentration of erythropoietin was increased to 3 U ml−1 on day 7. To support megakaryocytic and granulocytic differentiation, 50 ng ml−1 thrombopoietin, 15 ng ml−1 granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (Neupogen) and 40 ng ml−1 FLT-3 ligand were added. In all other experiments, cells were cultured with cytokines supporting erythroid and myeloid differentiation (cytokine combination listed above, without thrombopoietin).
CD34+ cell samples for Western blot analysis of p-eIF2α/ eIF2α or α-globin were cultured in media supporting erythroid differentiation. To induce SGs, CD34+ cells were treated with SA (0.5 mM final concentration) for 45 minutes. To inhibit polysome disassembly, CD34+ cells were treated with 20 μM emetine alone for 60 minutes prior to culture in the absence or presence of SA for 45 minutes.
2.2. Antibodies
All antibodies used in this study are listed in Supplementary material, Table S1.
2.3. Lentiviral vectors and infection and knockdown effects
Primary CD34+ cells were infected with shRNA lentiviruses targeting non-overlapping regions in the 3'-UTR of HRI or G3BP mRNAs [9]. Four days after infection, cells were collected for further assays. Lentiviral shRNA target sequences for HRI or G3BP silencing are listed in Table S1.
Knockdown efficiencies were verified by real-time quantitative PCR following reverse transcription (RT-qPCR). Effects of HRI or G3BP silencing on p-eIF2α/eIF2α or α-globin expression were evaluated by Western blot on cells collected four days after lentivirus infection. Knockdown effects on SGs were assessed by quantifying the percentage of cells with SGs (>100 cells from different fields).
2.4. Cytospin
Bone marrow-derived CD34+ cells (>0.5 × 105) were collected, washed twice in cold PBS, resuspended in 200 μl of 4% paraformaldehyde, rocked at room temperature for 10 minutes, resuspended in 100 μl PBS and then cytospun onto round (12 mm) coverslips at 700 rpm for 4 minutes. Air-dried coverslips were placed in a 24-well plate and processed for immunofluorescence microscopy. For hematopoietic lineage detection, CD34+ were incubated for 60 minutes tumbling at 4C° with the specific florochrome-labeled antibodies (listed in Table S1) in blocking solution, followed by 3 washings in PBS of 5 minutes each, and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde before cytospin.
2.5. Whole Murine and Human bone marrow experiments
Total bone marrow cells from 6 month old wild type Balb/c male mice were harvested, washed twice in cold PBS and then processed for imunofluroescence with anti-mouse lineage specific florochrome-labeled antibodies (listed in Table S1) as described above.
Unprocessed human bone marrow from healthy donor patient (Lonza Walkersville, Inc.), containing 22.8 × 106 cells/mL, V≥ 10mL, was delivered fresh at 4 C and aliquoted in vials containing 2 × 106 cells/mL. Hematopoietic lineage marker staining and SGs detection was performed as described above.
2.6. Immunofluorescent microscopy
General immunofluorescence procedures were performed on cytospun CD34+ cells, mouse or human bone marrow cells, as described previously [11]. Images were captured by a Nikon Eclipse 800 microscope with CCD-SPOT RT digital camera (Diagnostic Instruments), using 100× magnification objective. The images were compiled with Adobe Photoshop CS3 (v.10.0.1) (Adobe Systems).
2.7. Western blot
Western blot assays on human hematopoietic CD34+ cell samples were performed under standard conditions as previously described [12], using antibodies listed in Table S1. Protein concentrations were determined using the Micro BCA Protein Assay (Fisher Scientific). Protein band densities were quantified using Image J software.
2.8. Flow cytometry
Primary human bone marrow CD34+ cells were infected with lentiviruses expressing shRNAs [9], selected with puromycin the following day and analyzed for hematopoietic differentiation by flow cytometry on day 7 of culture. Flow cytometry was performed using antibodies against antigens expressed on erythroid cells, glycophorin A (GlyA-FITC-conjugated antibody) and CD71- PECy5-conjugated antibody (both BD Biosciences). Live/dead cell absolute numbers and apoptosis were assesed by flow cytometry on day 7 in culture using phycoerythrin labeled annexin V antibody (BD Pharmingen). Flow cytometry was performed on a FACS Calibur cytometer (BD Biosciences) and data was analyzed using FlowJo software (Tree star).
2.9. Statistics
Statistical significance was determined by two tailed Student's t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.001.
3. RESULTS
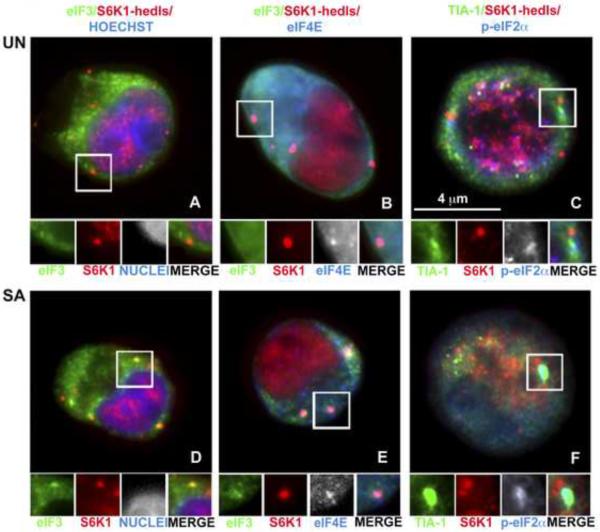
Normal erythrocyte differentiation requires the balanced production of the hemoglobin precursors globin and heme. The translation of globin transcripts is controlled by HRI, an eIF2α kinase that is activated when heme concentrations are low. We hypothesized that HRI kinase would be activated during erythroid differentiation, and that phosphorylation of eIF2α would trigger SG assembly. First we investigated whether hematopoietic cells are capable of forming SGs under stress conditions. We used immunofluorescence microscopy to visualize SGs in normal bone marrow-derived CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells cultured in media containing cytokines supporting erythroid, myeloid and megakaryocytic differentiation [10]. After 4 days of normal differentiation, cells were cultured in the presence or absence of SA (SA, 500 μM) for 45 minutes, and stained using antibodies reactive with SGs (eIF3b, TIA-1, phospho-eIF2α and eIF4E) or processing bodies (PBs) (S6K1/Hedls and eIF4E) (Figure 1). PBs are cytoplasmic mRNP aggregates that are distinct from, but dynamically linked to, SGs [4]. PBs are constitutive components of cycling cells, and are thought to play a role in mRNA degradation. Dynamic interactions between SGs and PBs suggest that mRNA may be transferred from SGs to PBs for decay [13]. We found that hedls+ PBs are prominent components of unstressed CD34+ progenitor cells (Figure 1, upper panels: red). Unexpectedly, small TIA-1+ SGs were also observed in the cytoplasm of these cells (Figure 1C: green). When these cells are subjected to SA-induced oxidative stress (Figure 1D – F), large TIA-1+ SGs and Hedls+ PBs were sometimes found in close physical apposition (Figure 1F). In addition, granules containing both SG and PB markers were commonly observed (Figure 1D and 1E: insets) suggesting that SGs and PBs can fuse together in these cells. These findings indicate that SGs assemble in differentiating primary human hematopoietic progenitor cells in the absence of exogenous stress.
Figure 1. Human bone marrow-derived CD34+ hematopoietic cells assemble cytoplasmic SGs and PBs.
CD34+ cells, collected at day 4 of in vitro differentiation, were cultured in the absence (UN; A, B, C) or presence (SA; D, E, F) of SA for 45 minutes. Samples were stained for SG markers (eIF3b, green; TIA-1, green; p-eIF2α, blue), a PB specific marker (S6K1-hedls, red) or SG/PB marker (eIF4E, blue). Cells were counterstained with Hoechst (A, D) to reveal nuclei. Enlarged views (1.8 fold) of boxed areas show separate channels and merged views.
To confirm that these cytoplasmic granules are indeed SGs, we treated differentiating hematopoietic cells with emetine (Figure S1), a drug that freezes ribosomes onto polysomes and promotes SG disassembly [13]. In CD34+ cells treated with emetine (20μM) for 120 minutes, both spontaneous (upper panel) and SA-induced (lower panel) SGs were disassembled. This result indicates that untranslated mRNAs found in these granules are in equilibrium with polysomes, an invariant property of normal SGs.
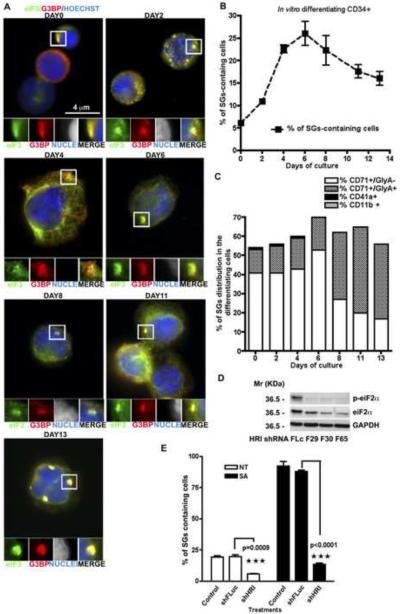
During the in vitro differentiation of human bone marrow CD34+ cells over the course of two weeks, spontaneous cytoplasmic SGs were observed in a fraction of CD34+ cells (Figure 2A and 2B). The percentage of eIF3b/G3BP+ SGs peaked at day 6 (27%), then slowly decreased over time (Figure 2B). No abnormal morphological changes were seen in these cells at various stages of differentiation, as assessed by May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining (Figure S2A). Fluorescence microscopy using antibodies specific for erythroid (CD71 ± GlyA), megakaryocytic (CD41a), or myeloid (CD11b) cells revealed the expected maturation of each lineage (Figure S2B) which ruled out a preferential overgrowth of the erythroid lineage under these culture conditions. Normal erythroid cell differentiation was also confirmed by hemoglobinization data, assessed at different time points, using 2,7-diaminofluorene (DAF) staining (Figure S2C).
Figure 2. CD34+ erythroid precursor cells assemble HRI/p-eIF2α-induced SGs during in vitro maturation.
(A) CD34+ cells, collected at different days of in vitro differentiation were stained for SG markers eIF3b (eIF3, green) and G3BP (G3BP, red), in combination with Hoechst (blue) to reveal nuclei. Enlarged views (3.2 fold) of boxed areas depict separate channels and merged views of SGs. (B) The mean percentage (n=3) of differentiating CD34+ cells with SGs (quantified by counting >100 cells per sample per experiment). (C) Lineage and maturation specific assembly of SGs. CD34+ cells were stained for the indicated differentiation markers as well as markers specific for immature erythroid precursors (CD71), in combination with SG markers. At the indicated times, cells were processed for immunofluorescence microscopy and the percentage of SGs in cells from each lineage was quantified. n=3 ± SEM. (D) HRI knockdown reduces eIF2α phosphorylation. Representative western blots are shown, withGAPDH as loading control. (E) Percentage of spontaneous and arsenite-induced SGs in CD34+ hematopoietic cells. CD34+ cells were infected with the indicated lentiviruses four days prior to culture with or without SA. Cells treated with each shRNA were pooled together before cytospin and SG quantification. n=3 ± SEM
SGs are almost exclusively found in immature and mature erythroid cells. At early time points the majority of SGs are found in immature (CD71+GlyA−) erythroid cells, while at later times, SGs are mainly found in mature (CD71+ GlyA+) erythroid cells (Figure 2C). On day 6 of the in vitro differentiation, when the highest % of SGs is detected, an average of 28% erythroid precursor cells (CD71+GlyA−) and approximately 4% of mature erythroid cells (CD71+ GlyA+) contained cytoplasmic SGs (Figure S2D). These data suggest that cyclic assembly/disassembly of SGs in different sub-populations of erythroid cells may be a part of normal erythroid development.
To determine whether HRI contributes to SG assembly in developing erythroid cells, we infected CD34+ human bone marrow progenitor cells with lentiviral vectors expressing shRNAs targeting HRI transcripts. Three independent shRNAs significantly reduced the expression of HRI transcripts in these cultures (Figure S2E). Knockdown of HRI inhibited eIF2α phoshorylation (Figure 2D) and significantly reduced the spontaneous and SA-induced (Figure 2E) assembly of SGs in these cultures. These results confirm that HRI is the eIF2α kinase that regulates SG assembly in developing erythroid cells.
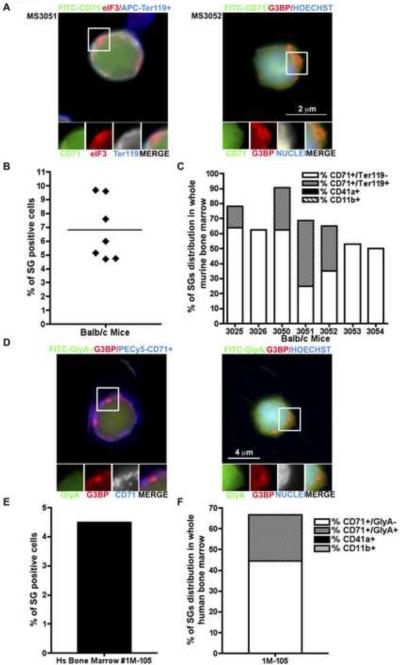
To determine whether SGs are found in differentiating hematopoietic cells in vivo under normal physiological conditions, we harvested bone marrow from seven 6-month old healthy wild type Balb/c mice (Figure S3A) and stained cells for erythroid (CD71 and Ter119), granulocytic (CD11b+) and megakaryocytic (CD41+) surface markers as well as intracellular SG markers (Figure 3A–C). Approximately 5–10% of the bone marrow cells contained SGs as assessed by G3BP and eIF3 staining (Figure 3B). As also seen in our in vitro experiments, SGs were almost exclusively observed in erythroid cells (CD71 ± Ter119) (Figure 3C). Approximately 8–15% of CD71+Ter119− and 4% CD71+Ter119+ cells show positive SGs staining (Figure S3B).
Figure 3. Mouse and human bone marrow erythroid precursor cells assemble SGs during in vivo maturation.
Total bone marrow cells Balb/c male mice were stained for markers of lineage differentiation (CD71-FITC, TER119-APC, CD41-FITC and CD11b-PECy5) and SGs (eIF3b and G3BP). (A) Left panel: A CD71+/Ter119+ erythroid cell (green/blue) containing eIF3b+ SGs (red) in bone marrow from sample MS3051. Right panel: A CD71+ erythroid cell (green) containing, G3BP+ SG (red) from sample MS3052. Enlarged views (1.7 fold) of boxed areas show separate channels and merged views of RNA granules. (B) The mean percentage of SGs containing cells was quantified by counting >100 cells from 3 independent fields per animal (seven mice). (C) Murine bone marrow cells were stained for the indicated differentiation markers, in combination with the SG markers eIF3 and G3BP. The percentage of SG positive cells from each lineage was quantified. Values are the means of 3 independent fields in which >100 cells were counted. (D–F) Total human fresh bone marrow collected from a healthy donor was stained for markers of lineage differentiation (CD71-PECy5, GlyA-FITC, CD41-FITC and CD11b-PECy5) and SGs (eIF3b and G3BP). (D) Left panel: A CD71+/GlyA- erythroid cell (blue) containing G3BP+ SGs (red). Right panel: A GlyA+ erythroid cell (green) containing, G3BP+ SG (red). (E) The mean percentage of SGs was quantified by counting >100 cells from 3 independent fields. (F) Total human bone marrow cells, stained for the indicated differentiation markers and the SG marker G3BP, showed that the majority of SG containing cells are erythroid cells. Values are the means of three independent fields in which at least 100 cells were counted. Enlarged views (1.6 fold) of boxed areas show separate channels and merged views of RNA granules.
To obtain further evidence that SGs are spontaneously assembled in differentiating hematopoietic cells in vivo, we analyzed whole fresh bone marrow collected from a healthy human donor. Bone marrow cells were stained for erythroid (CD71 and GlyA), megakaryocytic (CD41+), and granulocytic (CD11b+) surface markers as well as intracellular SG markers (Figure 3D). Approximately 5% of freshly isolated human bone marrow cells contain G3BP+ SGs, the majority of which are erythroid cells (CD71 ± GlyA) (Figure 3E and 3F). An average of 8.5% erythroid precursor cells (CD71+GlyA−) and 4% mature erythroid cells (CD71+ GlyA+) contained cytoplasmic SGs (Figure S3C). These results reveal that 5–10% of bone marrow erythroid cells form SGs in vivo, demonstrating for the first time that SGs can form in bone marrow erythroid cells under normal physiological conditions in both mice and humans.
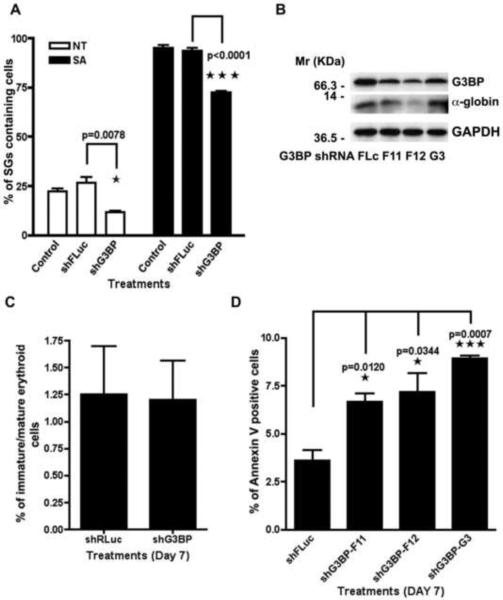
To investigate the role of stress granules in erythroid differentiation, we determined whether reduced expression of G3BP, a protein that is essential for SG assembly [5], alters the production of globin mRNA and protein as well as cell survival. CD34+ bone marrow cultures were infected with shRNA vectors targeting G3BP transcripts. Three independent shRNAs significantly reduced the expression of G3BP mRNA (Figure S4A) and protein (Figure 4B). Partial knockdown of G3BP reduced the spontaneous and SA induced assembly of SGs in these cultures (Figure 4A). Thus G3BP is required for the optimal assembly of spontaneous and arsenite-induced SGs in CD34+ erythroid progenitor cells.
Figure 4. Targeted knockdown of G3BP inhibits SGs formation and hampers expression of α-globin and erythroid cells survival.
(A) G3BP knockdown significantly reduces spontaneous and SA-induced SG assembly in bone-marrow-derived CD34+ hematopoietic cells. The experiment was performed as previously described in Figure 2E, relative to HRI silencing. n=3 ± SEM. (B) Western blot of α-globin and G3BP with GAPDH as loading control. Representative blots are shown. (C) Effect of G3BP knockdown on the expression of erythroid maturation markers. In vitro cultured CD34+ cells were infected with shRNA, cultured for 7 days, and processed for FACS for erythroid surface molecules CD71 and GlyA. No significant differences in the ratio of CD71+GlyA- immature to CD71+GlyA+ mature erythroid cells are found. n=3 ± SEM. (D) Human hematopoietic CD34+ cells treated with shG3BP lentivirus were harvested after 7 days for quantification of Annexin V positive cells n=3 ± SEM.
We also quantified α-globin RNA and protein expression in CD34+ cells treated with control or G3BP-specific shRNAs. Knock down of G3BP significantly reduced the expression of α-globin RNA in these cultures (Figure S4B). Although the knock down of G3BP protein was heterogeneous, α-globin protein levels were reduced in proportion to the reduction in G3BP protein expression (Figure 4B). Thus, SGs may serve to protect α-globin transcripts from degradation during erythroid differentiation.
We also determined whether abrogation of SGs through decreased expression of G3BP affects erythroid differentiation in vitro. CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells were treated with control (Luc) or G3BP-specific lentiviral shRNAs prior to quantifying the expression of GlyA and CD71 erythroid differentiation markers using flow cytometry. We monitored the ratio of CD71+GlyA− (immature)/CD71+GlyA+ (mature) cells to assess erythroid differentiation in culture. Despite its ability to decrease expression of α-globin, reduced expression of G3BP and SGs did not significantly affect the expression of erythroid differentiation markers (Figure 4C). However, when we investigated whether inhibition of SGs affects the survival of differentiating CD34+ progenitor cells, we found that after 7 days (Figure 4D) of in vitro culture, G3BP downregulation significantly increases the percentage of annexin V+ apoptotic cells. Absolute numbers of live and dead cells after G3BP knock down are reported in Figure S4C. These results suggest that spontaneous SGs may promote the survival of differentiating erythroid cells. SG assembly can promote the survival of cells exposed to adverse environmental conditions [3; 14].
4. DISCUSSION
In erythroid cells, post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms play a major role in determining the expression of α-globin protein. In terminally differentiated anucleated erythrocytes, highly stable globin transcripts continue to synthesize globin protein to support the production of hemoglobin. The stability of α-globin transcripts is determined by the binding of α-complex to C-rich motifs located in the 3'-UTR [15; 16]. The α-complex masks the binding site for an erythroid-enriched endoribonuclease, ErEN [17], to ensure that α-globin transcripts are available for translation. The translation of these transcripts is regulated by HRI [1]. When the concentration of intracellular heme is limiting, HRI phosphorylates eIF2α to inhibit the translation of α-globin [1; 3; 4; 13]. In this study, we show that HRI-induced phosphorylation of eIF2α triggers the assembly of SGs in differentiating erythrocytes. Our results also implicate SGs in the regulation of α-globin mRNA stability and translation.
In cultures of differentiating CD34+ progenitor cells, spontaneous SGs are observed in the CD71+ erythroid lineage, but not in the CD11b+ myeloid or CD41+ megakaryocytic lineages. SGs are assembled in both CD71+/GlyA− immature erythroid cells and in more mature CD71+/GlyA+ erythroid cells (Figure 2). Thus, SG assembly appears to occur throughout the erythroid differentiation process and may modulate gene expression in both early and late erythroid precursor cells.
In developing erythroid cells, HRI acts as a heme sensor and translational repressor. Our in vitro results suggest that HRI is activated to maintain hemoglobin homeostasis throughout erythroid development. This conclusion is supported by the appearance of SGs in murine (Figure 3A–C and Figure S2B) and human (Figure 3DF and Figure S2C) bone marrow-derived erythroid cells. The further finding that targeted knock down of HRI inhibits phosphorylation of eIF2α, as well as spontaneous and oxidative stress-induced SG assembly (Figure 2), identifies HRI as the eIF2α kinase in erythroid progenitor cells.
Finally, we demonstrate that knockdown of the essential SG component G3BP inhibits the spontaneous and arsenite-induced assembly of SGs in cultured CD34+ progenitor cells. G3BP knockdown is accompanied by decreased expression of α-globin transcripts (Figure 4). SG inhibition may cause α-globin transcripts that normally reside in the cytoplasm to become more susceptible to degradation. Alternatively, this effect could be dependent on interactions between G3BP and Egr-1, an erythroid stimulator [18].
SG abrogation upon G3BP knockdown does not prevent erythroid differentiation despite α-globin downregulation, as assessed by expression of GlyA (Figure 4E). It does, however, promote increasing apoptotic cell death (Figure 4F and 4G) as assessed by expression of Annexin V. Since SGs are known to promote cell survival [3; 14], it is likely that their assembly contributes to the viability of erythrocytes throughout differentiation.
In conclusion, our data reveal that differentiating erythroid cells assemble SGs. This is the first example of the in vivo assembly of SGs in primary cells that have not been subjected to exogenous stress. It is conceivable that reduced levels of heme encountered under in vitro culture conditions, contribute to the assembly of SGs in this system, as fluctuations in iron concentration in vivo can confer physiological stress. We also show that G3BP, a protein essential for SG assembly, regulates the expression of α-globin transcripts as well as the survival of differentiating erythroid progenitor cells. SG-mediated reprogramming of globin metabolism may therefore play a key role in globin production during erythroid differentiation.
Supplementary Material
Highlights
A subset of differentiating erythroid cells assemble spontaneous stress granules
Stress granule assembly is a consequence of HRI-induce phosphorylation of eIF2α
Knockdown of G3BP inhibits stress granule assembly and erythroid cell survival
Acknowledgments
We thank members of the Anderson Lab for helpful discussions and advice. We thank Dr M. J. Weiss of The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia for kindly providing an aliquot of rabbit anti-human α-globin antibody and Johan Flygare for help with the DAF staining protocol. This work was supported by grants for the NIH and the American College of Rheumatology.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Conflict of interest disclosures: None.
REFERENCES
- [1].Chen JJ. Regulation of protein synthesis by the heme-regulated eIF2α kinase: relevance to anemias. Blood. 2007;109:2693–2699. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-08-041830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Brugnara C. Iron deficiency and erythropoiesis: new diagnostic approaches. Clin Chem. 2003;49:1573–8. doi: 10.1373/49.10.1573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].McEwen E, Kedersha N, Song B, et al. Heme-regulated inhibitor kinase-mediated phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 inhibits translation, induces stress granule formation, and mediates survival upon arsenite exposure. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:16925–33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M412882200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [4].Anderson P, Kedersha N. Stress granules: the Tao of RNA triage. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008;33:141–50. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2007.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Tourriere H, Chebli K, Zekri L, et al. The RasGAP-associated endoribonuclease G3BP assembles stress granules. J Cell Biol. 2003;160:823–31. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200212128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- [6].Irvine K, Stirling R, Hume D, et al. Rasputin, more promiscuous than ever: a review of G3BP. Int J Dev Biol. 2004;48:1065–77. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.041893ki. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Kociok N, Esser P, Unfried K, et al. Upregulation of the RAS-GTPase activating protein (GAP)-binding protein (G3BP) in proliferating RPE cells. J Cell Biochem. 1999;74:194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Zekri L, Chebli K, Tourriere H, et al. Control of fetal growth and neonatal survival by the RasGAP-associated endoribonuclease G3BP. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25:8703–16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.19.8703-8716.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Ebert BL, Pretz J, Bosco J, et al. Identification of RPS14 as a 5q- syndrome gene by RNA interference screen. Nature. 2008;451:335–9. doi: 10.1038/nature06494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].Ebert BL, Lee MM, Pretz JL, et al. An RNA interference model of RPS19 deficiency in Diamond-Blackfan anemia recapitulates defective hematopoiesis and rescue by dexamethasone: identification of dexamethasone-responsive genes by microarray. Blood. 2005;105:4620–6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-08-3313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [11].Ohn T, Kedersha N, Hickman T, et al. A functional RNAi screen links O-GlcNAc modification of ribosomal proteins to stress granule and processing body assembly. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:1224–31. doi: 10.1038/ncb1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Gilks N, Kedersha N, Ayodele M, et al. Stress granule assembly is mediated by prion-like aggregation of TIA-1. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15:5383–98. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E04-08-0715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Kedersha N, Stoecklin G, Ayodele M, et al. Stress granules and processing bodies are dynamically linked sites of mRNP remodeling. J Cell Biol. 2005;169:871–84. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200502088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Yamasaki S, Anderson P. Reprogramming mRNA translation during stress. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20:222–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.01.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Weiss IM, Liebhaber SA. Erythroid cell-specific determinants of alpha-globin mRNA stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14:8123–32. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Chkheidze AN, Lyakhov DL, Makeyev AV, et al. Assembly of the alpha-globin mRNA stability complex reflects binary interaction between the pyrimidine-rich 3' untranslated region determinant and poly(C) binding protein alphaCP. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:4572–81. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.7.4572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Liu H, Kiledjian M. An erythroid-enriched endoribonuclease (ErEN) involved in alpha-globin mRNA turnover. Protein Pept Lett. 2007;14:131–6. doi: 10.2174/092986607779816168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Schulze C, Buchse T, Mikkat S, et al. Erythropoietin receptor-mediated Egr-1 activation: structural requirements and functional implications. Cell Signal. 2008;20:1848–54. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.