Abstract
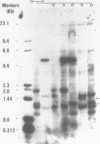
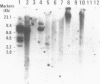
The probe 29C1 detects a hypervariable locus 18kb from the telomere of the human X and Y chromosomes, in the pseudoautosomal region. Here we report that hypervariability of fragments containing this sequence in the human population arises by loss or gain of a 31 base pair GC rich repeat. Labelled 29C1 does not detect a DNA fingerprint at low stringency, though the consensus repeat sequence does show some similarity to previously reported minisatellites. Sequence within the repeat block has G and C rich strands, a feature associated with sequences at the telomeres of many higher organisms. The repeat block shows sequence characteristics normally associated with a low methylation island, though the locus is methylated and does not appear to be transcribed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allshire R. C., Gosden J. R., Cross S. H., Cranston G., Rout D., Sugawara N., Szostak J. W., Fantes P. A., Hastie N. D. Telomeric repeat from T. thermophila cross hybridizes with human telomeres. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):656–659. doi: 10.1038/332656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke T., Bruford M. W. DNA fingerprinting in birds. Nature. 1987 May 14;327(6118):149–152. doi: 10.1038/327149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandley A. C., Mitchell A. R. Hypervariable minisatellite regions are sites for crossing-over at meiosis in man. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;48(3):152–155. doi: 10.1159/000132613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Brown W. R., Rappold G. A. Hypervariable telomeric sequences from the human sex chromosomes are pseudoautosomal. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):687–692. doi: 10.1038/317687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Smith B. A. Variability at the telomeres of the human X/Y pseudoautosomal region. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):213–219. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas J. F. Detection of DNA "fingerprints" of cultivated rice by hybridization with a human minisatellite DNA probe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6831–6835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges M., Cochaux P., Lequarre A. S., Young M. W., Vassart G. DNA fingerprinting in man using a mouse probe related to part of the Drosophila 'Per' gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7193–7193. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges M., Lequarré A. S., Castelli M., Hanset R., Vassart G. DNA fingerprinting in domestic animals using four different minisatellite probes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;47(3):127–131. doi: 10.1159/000132529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S. E., Higgs D. R., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J. Molecular basis of length polymorphism in the human zeta-globin gene complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5022–5026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. J., Darling S. M., Thomas N. S., Goodfellow P. N. A pseudoautosomal gene in man. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):740–743. doi: 10.1126/science.2877492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P. A., Hollis G. F., Korsmeyer S. J., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Clustered arrangement of immunoglobulin lambda constant region genes in man. Nature. 1981 Dec 10;294(5841):536–540. doi: 10.1038/294536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgs D. R., Goodbourn S. E., Wainscoat J. S., Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J. Highly variable regions of DNA flank the human alpha globin genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4213–4224. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman A. P., Nicholls R. D., Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B., Higgs D. R. Molecular characterisation of a hypervariable region downstream of the human alpha-globin gene cluster. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1857–1863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Morton D. B. DNA fingerprints of dogs and cats. Anim Genet. 1987;18(1):1–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.1987.tb00739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Kelly R., Taylor B. A., Bulfield G. Mouse DNA 'fingerprints': analysis of chromosome localization and germ-line stability of hypervariable loci in recombinant inbred strains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):2823–2836. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.2823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Individual-specific 'fingerprints' of human DNA. Nature. 1985 Jul 4;316(6023):76–79. doi: 10.1038/316076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott T. J., Wallis S. C., Pease R. J., Powell L. M., Scott J. A hypervariable region 3' to the human apolipoprotein B gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):9215–9216. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.9215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Bostock C., Robertson M., Christie S., Mitchen J. L., Dahlberg J. E. U1 small nuclear RNA genes are located on human chromosome 1 and are expressed in mouse-human hybrid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2211–2220. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C. A., Goodfellow P. J., Goodfellow P. N. Mapping the limits of the human pseudoautosomal region and a candidate sequence for the male-determining gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):273–275. doi: 10.1038/328273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Gil A., Maniatis T. The structure of the human zeta-globin gene and a closely linked, nearly identical pseudogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):553–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90311-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogstad S. H., Patton J. C., 2nd, Schaal B. A. M13 repeat probe detects DNA minisatellite-like sequences in gymnosperms and angiosperms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9176–9178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyer F., Simmler M. C., Johnsson C., Vergnaud G., Cooke H. J., Weissenbach J. A gradient of sex linkage in the pseudoautosomal region of the human sex chromosomes. Nature. 1986 Jan 23;319(6051):291–295. doi: 10.1038/319291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyer F., Simmler M. C., Vergnaud G., Johnsson C., Levilliers J., Petit C., Weissenbach J. The pseudoautosomal region of the human sex chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):221–228. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royle N. J., Clarkson R. E., Wong Z., Jeffreys A. J. Clustering of hypervariable minisatellites in the proterminal regions of human autosomes. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):352–360. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer R., Zischler H., Epplen J. T. (CAC)5, a very informative oligonucleotide probe for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):5196–5196. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.5196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmler M. C., Johnsson C., Petit C., Rouyer F., Vergnaud G., Weissenbach J. Two highly polymorphic minisatellites from the pseudoautosomal region of the human sex chromosomes. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):963–969. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04846.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Stephan D., Fischer Lindahl K. Gene organization and recombinational hotspots in the murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker N. G., Cheah K. S., Griffin J. R., Pope F. M., Solomon E. A highly polymorphic region 3' to the human type II collagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4613–4622. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. C., Ogilvie D. J., Wordsworth B. P. Lethal osteogenesis imperfecta and a collagen gene deletion. Length polymorphism provides an alternative explanation. Hum Genet. 1985;70(1):35–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00389455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassart G., Georges M., Monsieur R., Brocas H., Lequarre A. S., Christophe D. A sequence in M13 phage detects hypervariable minisatellites in human and animal DNA. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):683–684. doi: 10.1126/science.2880398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff R. K., Nakamura Y., White R. Molecular characterization of a spontaneously generated new allele at a VNTR locus: no exchange of flanking DNA sequence. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):347–351. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman A. R., White R. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6754–6758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]