Abstract
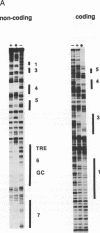
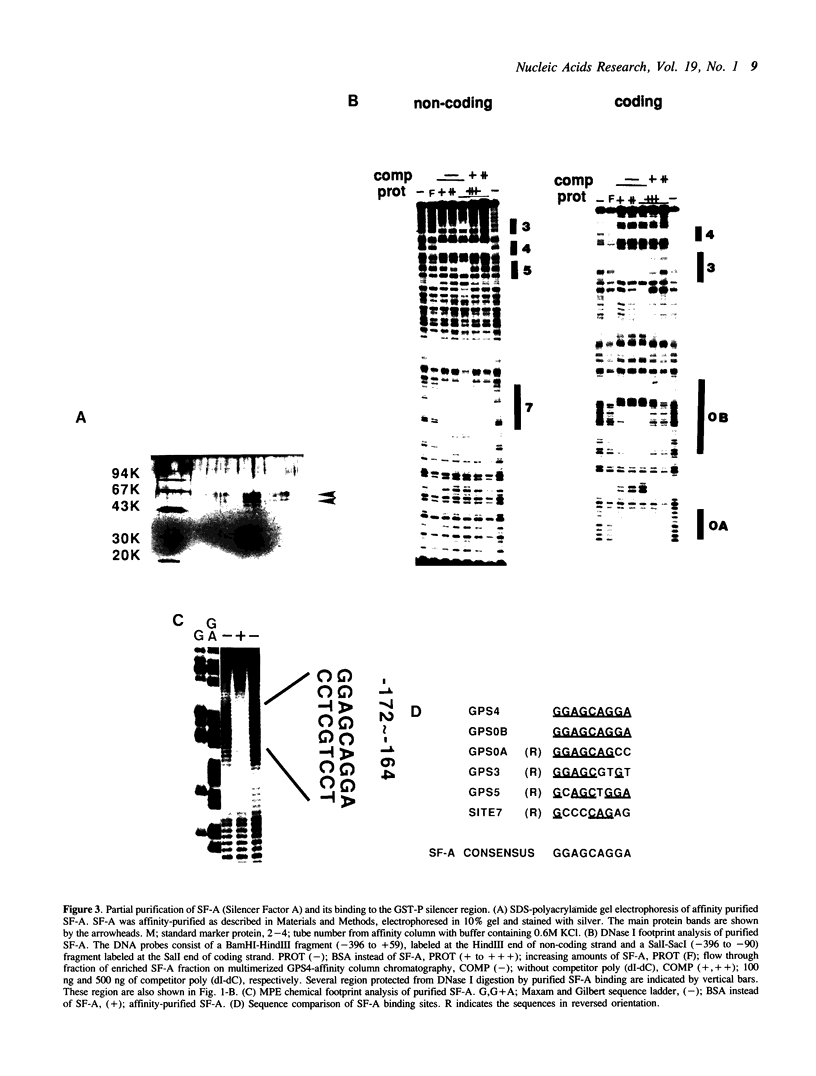
The glutathione transferase P (GST-P) gene is specifically expressed during chemical hepatocarcinogenesis of the rat, whereas mRNA of this gene is virtually undetectable in normal liver. We have previously identified a stretch of DNA, that acted negatively in transcription, at 400 bp upstream from the cap site of the rat GST-P gene. Further characterization has revealed that this negative fragment functions in an orientation and position independent manner, suggesting that it is acting as a silencer. This silencer consists of multiple negative elements to which nuclear factors bind. This silencer is active not only in rat non-hepatoma and hepatoma cells but also in human and mouse cell lines, suggesting that these elements function as general regulators of basal gene expression. At least two proteins bind to this silencer fragment, one of which, designated SF-A (Silencer Factor A), has been partially purified. SF-A binds to several regions in this silencer, and likely plays an important role on negative regulation of this gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Allegretto E. A., Karin M., Green M. R. A family of immunologically related transcription factors that includes multiple forms of ATF and AP-1. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1216–1226. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Yamamoto K. R., Tjian R. Two distinct transcription factors bind to the HSV thymidine kinase promoter in vitro. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):559–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Pastan I. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human DNA binding factor that represses transcription. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90605-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Heguy A., Dietlin T., Cooke T. Metal-responsive elements act as positive modulators of human metallothionein-IIA enhancer activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):606–613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Commitment and activation at pol II promoters: a tail of protein-protein interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90675-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani Y., Brenner M., Freese E. An RNA polymerase II promoter containing sequences upstream and downstream from the RNA startpoint that direct initiation of transcription from the same site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4289–4293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda A., Imagawa M., Maeda Y., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. Structural and functional analysis of an enhancer GPEI having a phorbol 12-O-tetradecanoate 13-acetate responsive element-like sequence found in the rat glutathione transferase P gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16919–16926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda A., Imagawa M., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. Functional cooperativity between two TPA responsive elements in undifferentiated F9 embryonic stem cells. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1131–1135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08219.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda A., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. The structure of the rat glutathione S-transferase P gene and related pseudogenes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3858–3863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai M., Okuda A., Muramatsu M. Multiple regulatory elements and phorbol 12-O-tetradecanoate 13-acetate responsiveness of the rat placental glutathione transferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9456–9460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K. Glutathione transferases as markers of preneoplasia and neoplasia. Adv Cancer Res. 1989;52:205–255. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60214-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savagner P., Miyashita T., Yamada Y. Two silencers regulate the tissue-specific expression of the collagen II gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6669–6674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid W., Strähle U., Schütz G., Schmitt J., Stunnenberg H. Glucocorticoid receptor binds cooperatively to adjacent recognition sites. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2257–2263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08350.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Frasch S., Nordheim A. Repression of c-fos transcription is mediated through p67SRF bound to the SRE. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2567–2574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugioka Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Kitagawa T., Muramatsu M. Changes in polypeptide pattern of rat liver cells during chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1985 Jan;45(1):365–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suguoka Y., Kano T., Okuda A., Sakai M., Kitagawa T., Muramatsu M. Cloning and the nucleotide sequence of rat glutathione S-transferase P cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6049–6057. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]